- Spring Boot
title: Spring Boot 整合 MyBatis shortTitle: 整合MyBatis category: - Java企业级开发 tag:
- Spring Boot
ORM 框架的本质是简化操作数据库的编码工作,常用的框架有两个,一个是可以灵活执行动态 SQL 的 MyBatis;一个是崇尚不用写 SQL 的 Hibernate。前者互联网行业用的多,后者传统行业用的多。
Hibernate 的特点是所有的 SQL 通过 Java 代码生成,发展到最顶端的就是 Spring Data JPA,基本上根据方法名就可以生成对应的 SQL 了。
MyBatis 早些时候用起来比较繁琐,需要各种配置文件,需要实体类和 DAO 的映射关联,经过不断地演化和改进,可以通过 generator 自动生成实体类、配置文件和 DAO 层代码,简化了不少开发工作。
随着 MyBatis-Plus 的出现,又进一步加速了 MyBatis 的发展。经过 MyBatis-Plus 的增强,开发者只需要简单的配置,就可以快速进行单表的 CRUD 操作;同时,MyBatis-Plus又提供了代码生成、自动分页、逻辑删除、自动填充等丰富功能,进一步简化了开发工作。
整合 MyBatis
第一步,在 pom.xml 文件中引入 starter。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
第二步,在 application.yml 文件中添加数据库连接配置。
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: Huicheng123**
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/codingmore-mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false
第三步,导入 SQL 文件。
第四步,新建 User.java 实体类。
@Data
@Builder
public class User {
private Integer id;
private Integer age;
private String name;
private String password;
@Tolerate
User() {}
}
这里使用了 lombok 的
- @Data 注解自动生成 getter/setter
- @Builder 生成链式调用
- 由于 @Data和@Builder 配合使用的时候会导致无参构造方法丢失,所以我们主动声明了无参构造方法,并使用
@Tolerate注解来告诉 lombok 请允许我们的无参构造方法存在(没有无参构造方法的时候会导致 ORM 映射出错)
第五步,新建 UserMapper.java 接口:
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM user")
List<User> getAll();
@Select("SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}")
User getOne(Integer id);
@Insert("INSERT INTO user(name,password,age) VALUES(#{name}, #{password}, #{age})")
void insert(User user);
@Update("UPDATE user SET name=#{name},password=#{password},age=#{age} WHERE id =#{id}")
void update(User user);
@Delete("DELETE FROM user WHERE id =#{id}")
void delete(Integer id);
}
第六步,在启动类 CodingmoreMybatisApplication 上添加 @MapperScan 注解来扫描 mapper。
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan
public class CodingmoreMybatisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CodingmoreMybatisApplication.class, args);
}
}
如果没有指定 @MapperScan 的扫描路径,将从声明该注解的类的包开始进行扫描。
第七步,在测试类中对 mapper 进行测试。
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
class CodingmoreMybatisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void testInsert() {
userMapper.insert(User.builder().age(18).name("沉默王二").password("123456").build());
userMapper.insert(User.builder().age(18).name("沉默王三").password("123456").build());
userMapper.insert(User.builder().age(18).name("沉默王四").password("123456").build());
log.info("查询所有:{}",userMapper.getAll().stream().toArray());
}
@Test
List<User> testQuery() {
List<User> all = userMapper.getAll();
log.info("查询所有:{}",all.stream().toArray());
return all;
}
@Test
void testUpdate() {
User one = userMapper.getOne(1);
log.info("更新前{}", one);
one.setPassword("654321");
userMapper.update(one);
log.info("更新后{}", userMapper.getOne(1));
}
@Test
void testDelete() {
log.info("删除前{}", userMapper.getAll().toArray());
userMapper.delete(1);
log.info("删除后{}", userMapper.getAll().toArray());
}
}
极简 xml 版本
极简 xml 版本比较适合更加复杂的 SQL,接口层只定义空的方法,然后在 xml 中编写对应的 SQL。编程喵🐱实战项目中使用的就是这种方式。
第一步,新建 PostMapper。
public interface PostMapper {
List<Posts> getAll();
Posts getOne(Long id);
void insert(Posts post);
void update(Posts post);
void delete(Long id);
}
第二步,在 resources 目录下新建 PostMapper.xml 文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="top.codingmore.mapper.PostMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="top.codingmore.entity.Posts">
<id column="posts_id" property="postsId"/>
<result column="post_author" property="postAuthor"/>
<result column="post_content" property="postContent"/>
<result column="post_title" property="postTitle"/>
</resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
posts_id, post_author, post_content, post_title
</sql>
<select id="getAll" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from posts;
</select>
<select id="getOne" parameterType="java.lang.Long" resultMap="BaseResultMap" >
SELECT
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
FROM users
WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="top.codingmore.entity.Posts">
insert into
posts
(post_author,post_content,post_title)
values
(#{postAuthor},#{postContent},#{postTitle});
</insert>
<update id="update" parameterType="top.codingmore.entity.Posts">
update
posts
set
<if test="postAuthor != null">post_author=#{postAuthor},</if>
<if test="postContent != null">post_content=#{postContent},</if>
post_title=#{postTitle}
where id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="delete">
delete from
posts
where
id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
接口中方法对应的 SQL 直接写在 xml 文件中,具体位置见下图:
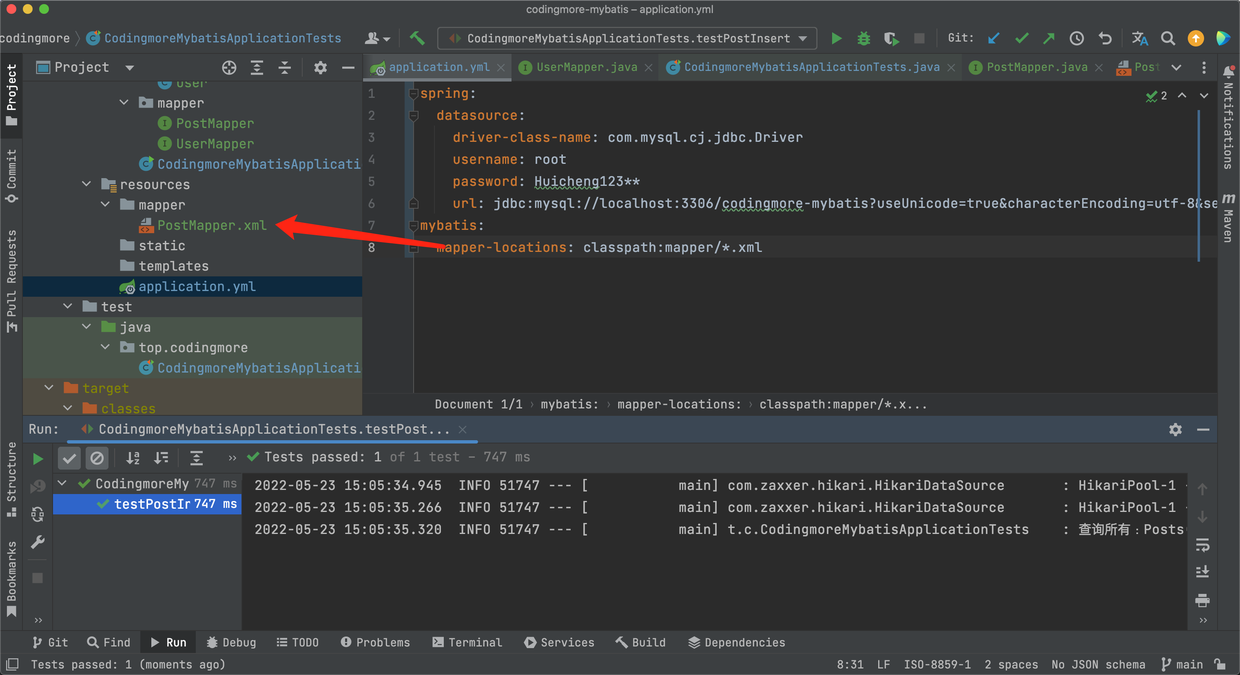
也可以看文件放在和 PostMapper.java 接口同级的目录下,但是这样会带来一个问题,就是 Maven 打包的时候默认会忽略 xml 文件,所以为了避免这种情况发生,我们需要在 pom.xml 文件中添加配置:
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
如果直接放在 resources 目录下,就不用担心打包时被忽略了,但放在 resources 目录下不会被 MyBatis 自动扫描到,所以需要在 application.yml 配置文件中告诉 MyBatis 具体的扫描路径:
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
第三步,在测试类中添加测试方法:
@Test
void testPostInsert() {
postMapper.insert(Posts.builder()
.postAuthor(1L)
.postTitle("沉默王二")
.postContent("123456")
.build());
log.info("查询所有:{}",postMapper.getAll().stream().toArray());
}
@Test
List<Posts> testPostQuery() {
List<Posts> all = postMapper.getAll();
log.info("查询所有:{}",all.stream().toArray());
return all;
}
@Test
void testPostUpdate() {
Posts one = postMapper.getOne(1L);
log.info("更新前{}", one);
one.setPostContent("沉默王二是沙比");
postMapper.update(one);
log.info("更新后{}", postMapper.getOne(1L));
}
@Test
void testPostDelete() {
log.info("删除前{}", postMapper.getAll().toArray());
postMapper.delete(1L);
log.info("删除后{}", postMapper.getAll().toArray());
}
可以看得出,注解版比较适合简单的 SQL 语句,一旦遇到比较复杂的 SQL 查询,比如说多表查询,xml 中写 SQL 语句会容易实现。
比如说编程喵🐱实战项目中有一个分页查询(首页展示,需要查询标签、作者名、文章信息等等),涉及到多张表,那么此时,xml 版本就更适合。
<select id="findByPageWithTagPaged" resultMap="PostsVoResultMapWithTagList">
SELECT a.*, pt.description, ptr.post_tag_id
FROM (
SELECT
<include refid="Base_Column_List_No_Content" />,
b.term_taxonomy_id,
c.user_nicename
FROM
posts a
LEFT JOIN term_relationships b ON a.posts_id = b.term_relationships_id
LEFT JOIN users c ON a.post_author = c.users_id
WHERE 1=1
<if test="searchTagId != null">
and a.posts_id in (select post_id from post_tag_relation where post_tag_id=#{searchTagId})
</if>
and ${ew.sqlSegment}
LIMIT #{pageStart}, #{pageSize}
) a
LEFT JOIN post_tag_relation ptr on a.posts_id = ptr.post_id
LEFT JOIN post_tag pt on pt.post_tag_id = ptr.post_tag_id
</select>
细心的小伙伴应该可以看到 ${ew.sqlSegment} 这样的表达式,它属于 MyBatis-Plus 中的内容。
通过 MyBatis-Plus 增强
MyBatis 属于半自动的 ORM 框架,实现一些简单的 CRUD 也是需要编写 SQL 语句,那如果想省掉这些步骤的话,可以选择 JPA,也可以选择国人开源的 MyBatis-Plus(简称 MP)。
MP 提供了诸多优秀的特性,比如说:
- 强大的 CRUD 操作:内置了通用的 mapper、service,可通过少量的配置实现大部分常用的 CRUD,不用再编写 SQL 语句。
- 支持主键自动生成
- 支持 ActiveRecord 模式:实体类只需继承 Model 类即可进行强大的 CRUD 操作
- 强大的代码生成器:可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码
- 内置分页插件
- 内置性能分析插件:可输出 SQL 语句以及其执行时间
我们直接进入实战。
第一步,在 pom.xml 文件中添加 MyBatis-Plus 的 starter。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
第二步,新建 PostTag 实体类。
@Data
public class PostTag {
private Long postTagId;
private String description;
}
对应的数据库表为 post-tag。
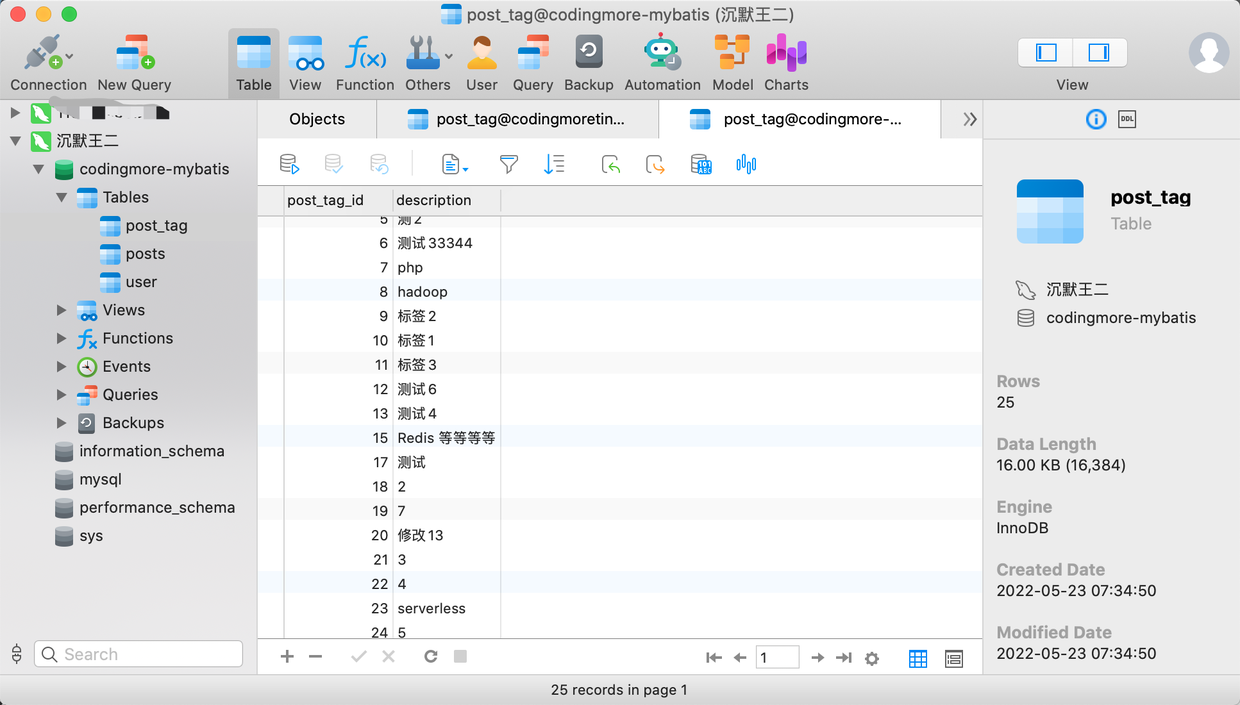
可以看得出,类名 PostTag,字段名 postTagId 和数据库表 post_tag、字段名 post_tag_id 并不一致,但 mp 自动帮我们做了映射关联。
第二步,新建 PostTagMapper 继承 BaseMapper,继承该接口后,无需编写 mapper.xml 文件,即可获得CRUD功能。
public interface PostTagMapper extends BaseMapper<PostTag> {}
BaseMapper里提供的方法如下:
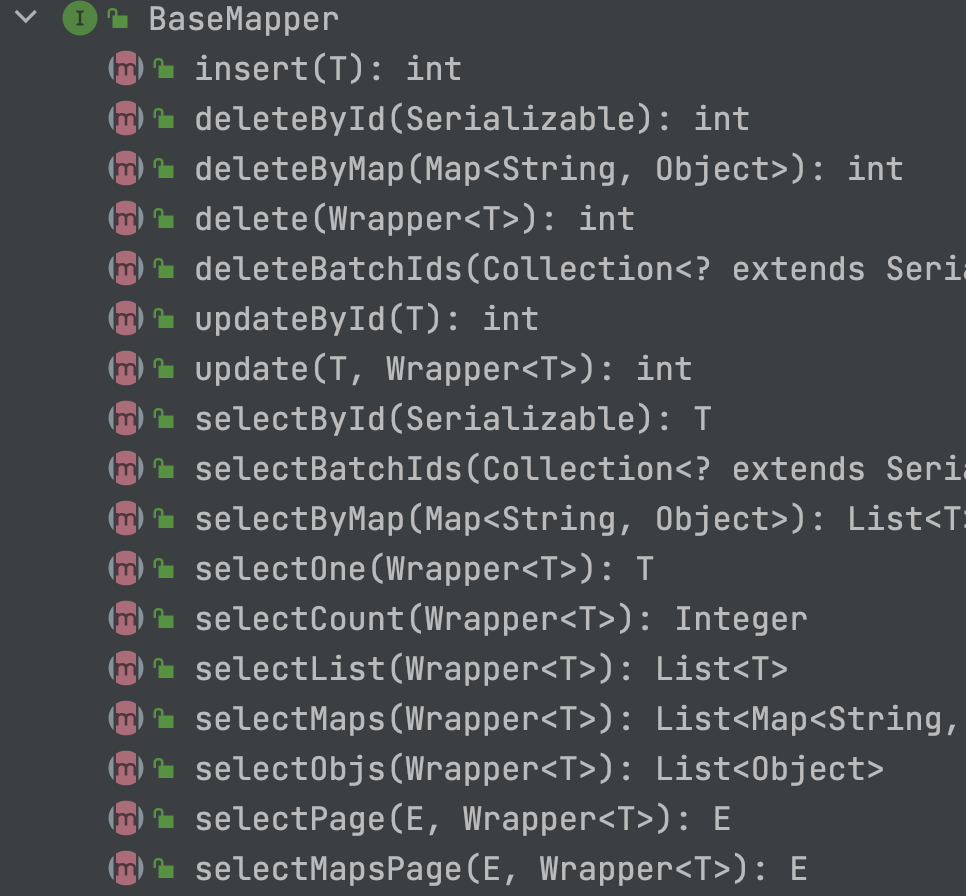
第三步,在测试类中添加查询方法。
更多内容,只针对《Java 程序员进阶之路》星球用户开放,需要的小伙伴可以戳链接🔗加入我们的星球,一起学习,一起卷。。编程喵🐱是一个 Spring Boot+Vue 的前后端分离项目,融合了市面上绝大多数流行的技术要点。通过学习实战项目,你可以将所学的知识通过实践进行检验、你可以拓宽自己的技术边界,你可以掌握一个真正的实战项目是如何从 0 到 1 的。
源码路径
- 编程喵:https://github.com/itwanger/coding-more
- codingmore-mybatis:https://github.com/itwanger/codingmore-learning