harmony 鸿蒙Audio
Audio
Audio Driver Overview
A multimedia system is an indispensable part in Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Audio is an important module of the multimedia system, and building an audio driver model is particularly important in device development.
This document describes the audio driver architecture and functional modules and how to develop audio drivers based on the Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF). You can develop your own drivers and call Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) APIs based on this driver architecture.
Audio Driver Architecture
The audio driver framework is implemented based on the HDF. The following figure illustrates the audio driver architecture.
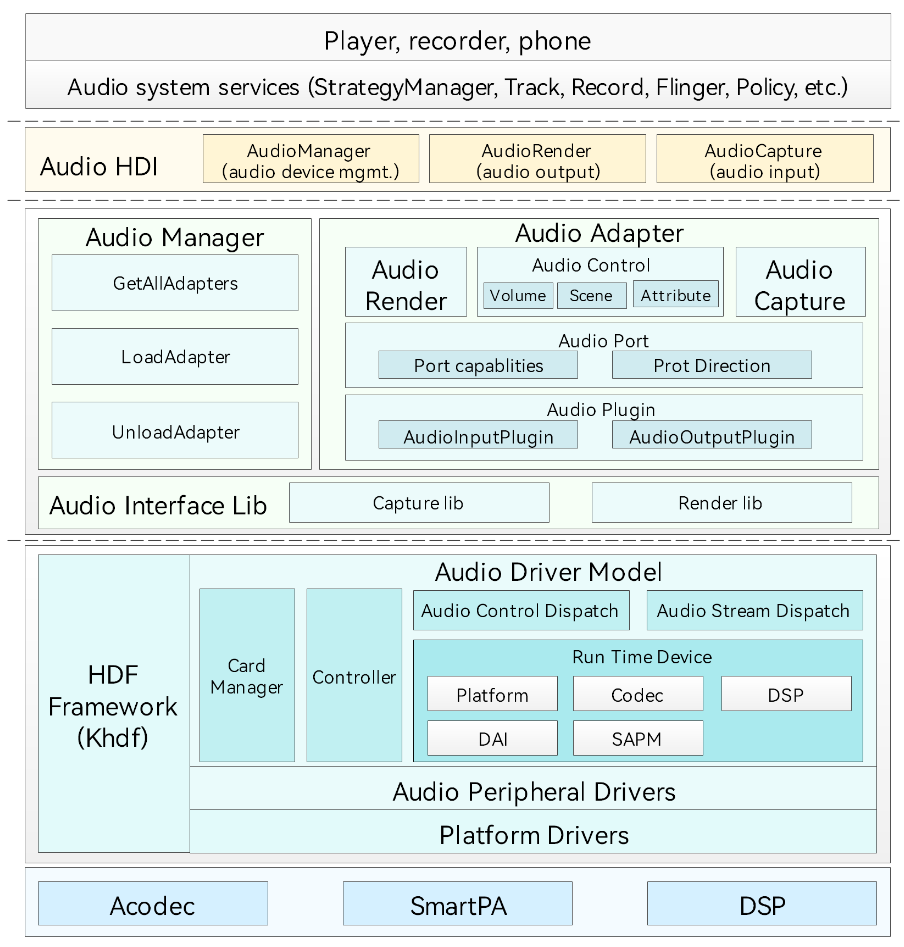
The driver architecture consists of the following: - Hardware Device Interface (HDI) adapter: implements the audio HAL driver (for HDI adaptation) and provides hardware driver APIs for audio services (frameworks). The HDI adapter provides API objects such as AudioManager, AudioAdapter, AudioControl, AudioCapture, and AudioRender. - Audio Interface Lib: works with the Audio Driver Model (ADM) in the kernel to control audio hardware, read recording data, and write playback data. The Stream_ctrl_common in the Audio Interface Lib interacts with the Audio HDI Adapter layer. - ADM: helps system developers to develop scenario-specific applications for the multimedia audio subsystem. With the ADM, codec and DSP device vendors can adapt their driver code based on the APIs provided by the ADM and implement quick development and easy adaptation to the OpenHarmony system. - Audio Control Dispatch: dispatches the control instructions from the Audio Interface Lib to the driver layer. - Audio Stream Dispatch: dispatches the data from the Audio Interface Lib to the driver layer.
- Card Manager: manages multiple audio adapters. Each audio adapter consists of the digital audio interface (DAI), platform, codec, DSP, and Smart Audio Power Manager (SAPM) modules.
- Platform Drivers: driver adaptation layer.
- SAPM: optimizes the power consumption policy of the ADM.
Audio Driver Development
The following uses the Hi3516D V300 as an example to describe how to develop drivers based on the audio driver architecture.
Audio ADM Architecture
The audio driver provides the hdf_audio_render, hdf_audio_capture, and hdf_audio_control services for the HDI layer. The driver service nodes in the dev directory of the development board are as follows:
# ls -l hdf_audio*
crw-rw---- 1 system system 247, 6 1970-01-01 00:00 hdf_audio_capture // Voice recording service.
crw-rw---- 1 root root 247, 4 1970-01-01 00:00 hdf_audio_codec_primary_dev0 // Audio adapter device 0.
crw-rw---- 1 root root 247, 4 1970-01-01 00:00 hdf_audio_codec_primary_dev11 // Audio adapter device 1.
crw-rw---- 1 system system 247, 5 1970-01-01 00:00 hdf_audio_control // Audio control service.
crw-rw---- 1 system system 247, 7 1970-01-01 00:00 hdf_audio_render // Audio playback service.
The audio adapters have the following driver services:
hdf_audio_codec_primary_dev0
- dma_service_0: DMA service
- dai_service: CPU DAI service
- codec_service_0: codec service (which can be smartPA)
- dsp_service_0: DSP service (optional)
hdf_audio_codec_primary_dev11
- dma_service_0: DMA service
- dai_service: CPU DAI service
- codec_service_1: codec service (which can be smartPA)
- dsp_service_0: DSP service (optional)
Startup Process
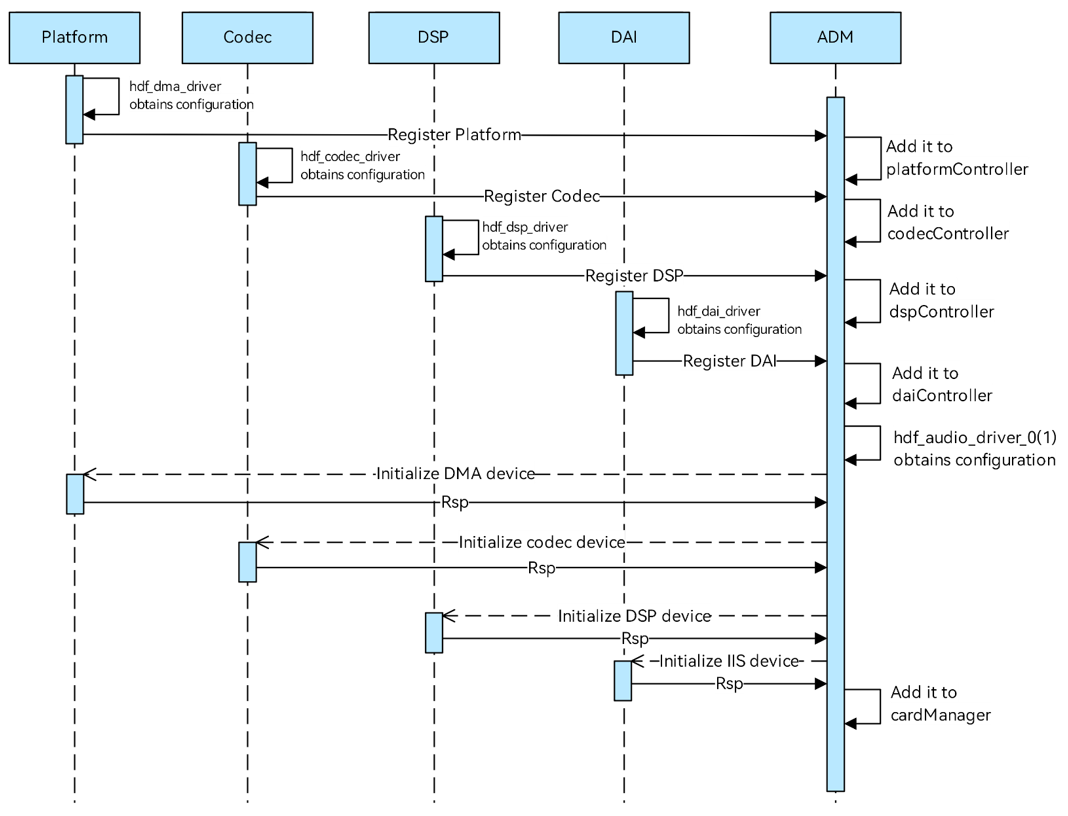
When the system starts, the platform, codec, DSP, and DAI drivers of the audio module are loaded first. Each driver obtains the configuration information from its configuration file and saves the obtained information to the data structs.
Each driver module calls the ADM registration interface to add itself to the linked list of the driver module.
The ADM obtains the hdf_audio_driver_0 and hdf_audio_driver_1 configuration and loads the devices of each module.
The ADM module initializes each module device by calling the initialization API of the respective module.
The initialized audio devices are added to the cardManager linked list.
Playback Process
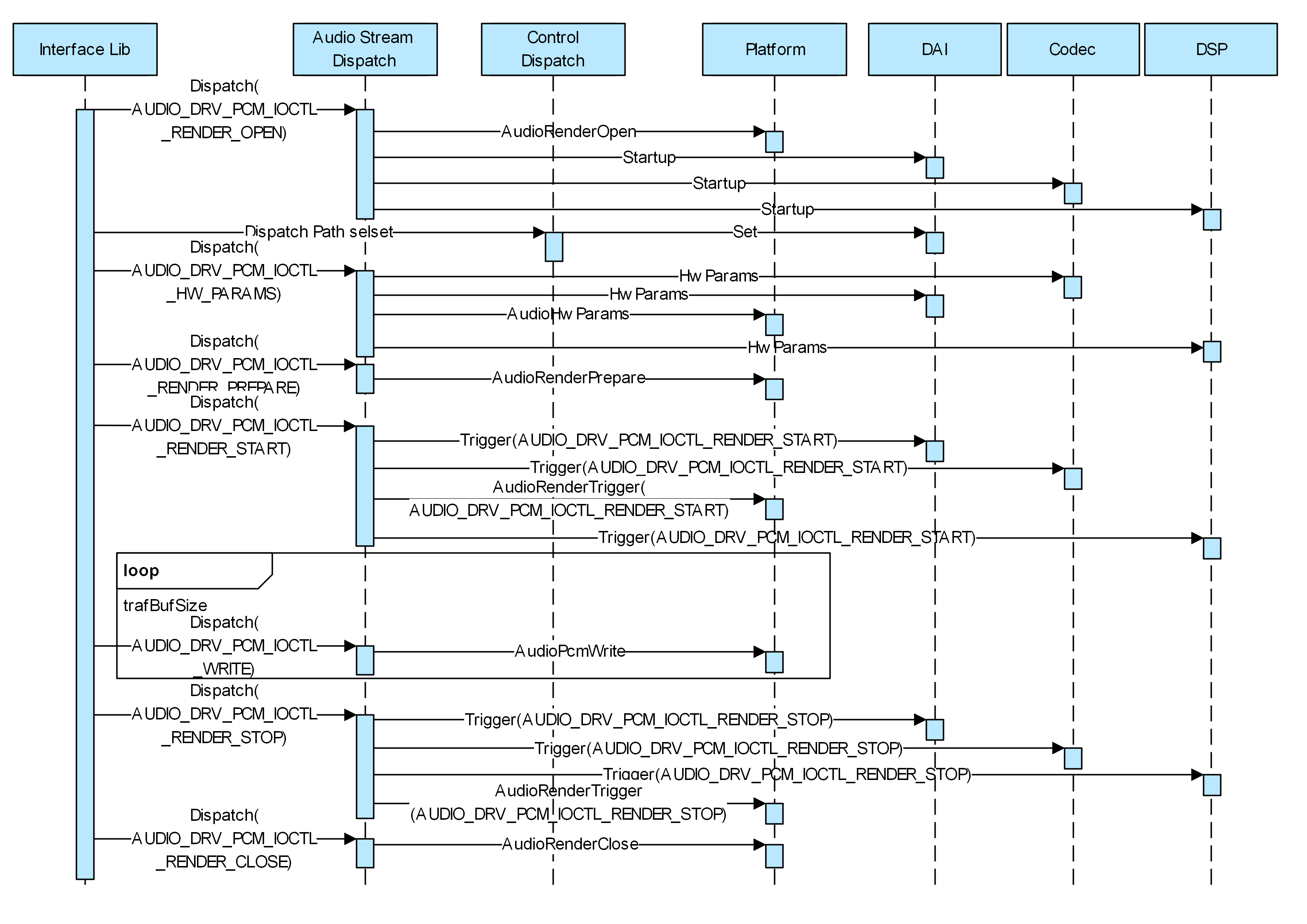
The Audio Interface Lib sends the Render Open instruction to the Audio Stream Dispatch service. The Audio Stream Dispatch service calls the API of each module to deliver the instruction.
The Audio Interface Lib sends a path select instruction to the Control Dispatch service. The Control Dispatch service calls the DAI API to set the path.
The Audio Interface Lib sends hardware parameters to the Audio Stream Dispatch service. The Audio Stream Dispatch service calls the API of each module to set the hardware parameters.
The Audio Interface Lib sends the start playing instruction to the Audio Stream Dispatch service. The Audio Stream Dispatch service calls the API of each module to perform related settings for each module.
The Audio Interface Lib sends audio data to the Audio Stream Dispatch service. The Audio Stream Dispatch service calls the Platform AudioPcmWrite API to send the audio data to DMA.
The Audio Interface Lib sends the stop playing instruction to the Audio Stream Dispatch service. The Audio Stream Dispatch service calls the stop API of each module to perform related stop settings for each module.
The Audio Interface Lib sends the Render Close instruction to the Audio Stream Dispatch service. The Audio Stream Dispatch service calls the Platform AudioRenderClose API to release resources.
Control Process
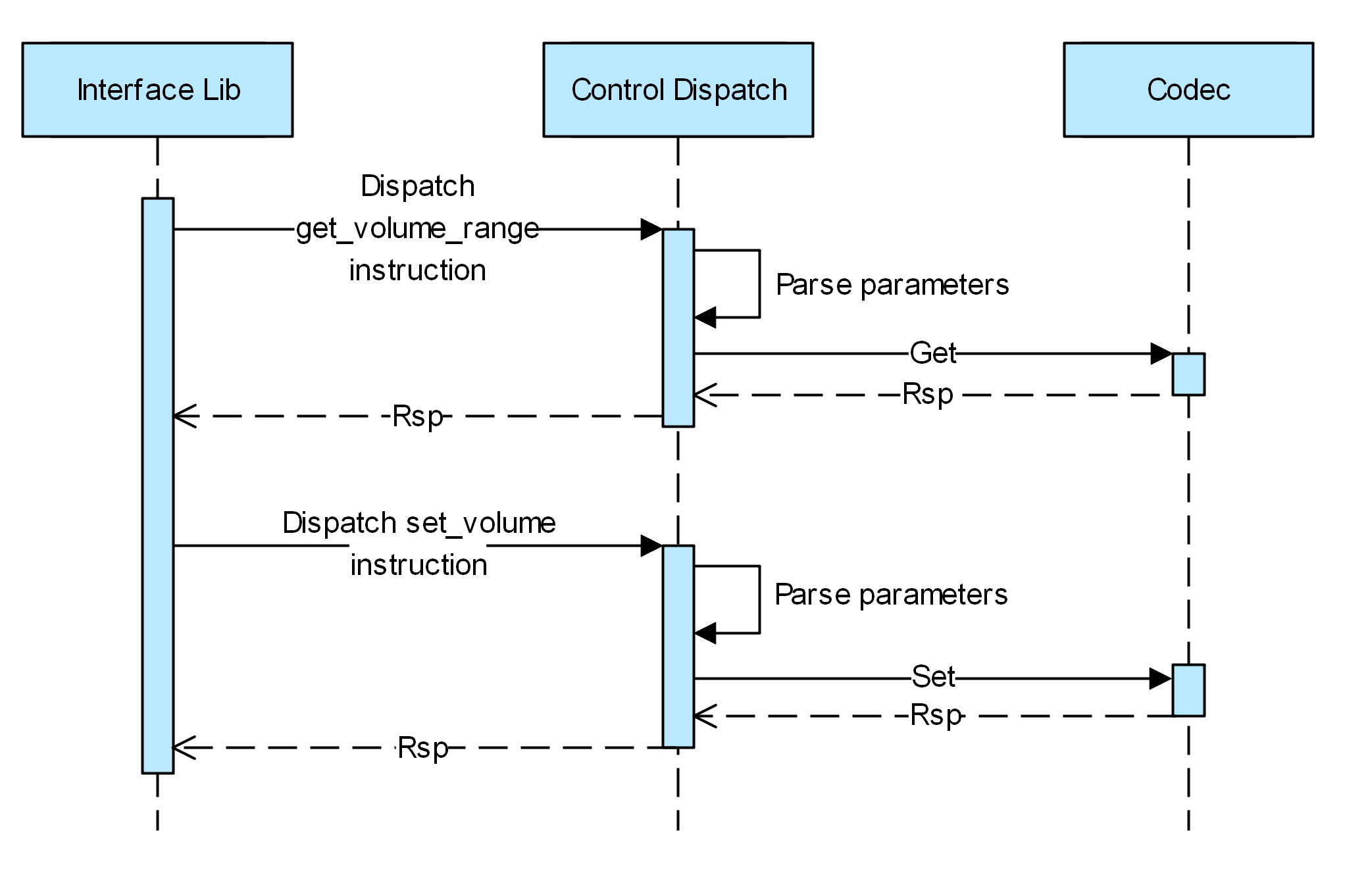
- When the volume needs to be adjusted, the Audio Interface Lib sends an instruction for obtaining the volume range to the Control Dispatch service. The Control Dispatch service parses the instruction and calls get() of the codec module to obtain the volume range.
- The Audio Interface Lib sends an instruction for setting the volume to the Control Dispatch service. The Control Dispatch service parses the instruction and calls Set() of the codec module to set the volume.
Common Audio Driver Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| CodecDeviceReadReg | Reads data from a codec register. |
| CodecDeviceWriteReg | Writes data to a codec register. |
| CodecDaiRegI2cRead | Reads data from a codec register over an I2C interface to a codec DAI. |
| CodecDaiRegI2cWrite | Writes data to a codec register over an I2C interface from a codec DAI. |
| CodecDeviceRegI2cRead | Reads data from a codec register over an I2C interface to a codec device. |
| CodecDeviceRegI2cWrite | Write data to a codec register over an I2C interface from a codec device. |
| CodecDeviceInitRegConfig | Initializes codec. |
| CodecDaiDeviceStartupRegConfig | Starts a codec device. |
| CodecSetCtlFunc | Sets the set() and get() functions. |
| CodecSetConfigInfoOfControls | Sets the codec control function and register information. |
| CodecGetConfigInfo | Obtains the code HDF configuration source (HCS). |
| CodecGetDaiName | Obtains the DAI name in the HCS. |
| CodecGetServiceName | Obtains the service name in the HCS. |
| DaiDeviceReadReg | Reads data from a DAI register. |
| DaiDeviceWriteReg | Writes data to a DAI register. |
| DaiSetConfigInfoOfControls | Sets the DAI control function and register information. |
| DaiGetConfigInfo | Obtains the DAI HCS. |
Audio Driver Development Procedure
Development on an Adapted Platform
The following figure shows the process for developing the codec or SmartPA driver on a chip platform (Hi3516D V300) to which the ADM has adapted.
Add register information to the private HDF configuration source (HCS) of the codec or SmartPA based on the chip description.
If the workflow of the newly added codec or SmartPA is the same as that of the existing codec or SmartPA, you do not need to implement the operation function set or configure the compilation file for the newly added codec or SmartPA.
Perform build, debugging, and testing.
Development on a New Platform
The following figure shows the driver development process if the ADM has not adapted to the platform.
The codec (optional), DAI, DMA, DSP (optional), and SmartPA (optional) modules of the audio adapter need to be adapted to the new platform.
Add register information of each module driver to the private configuration file of the respective module according to the chip description.
Implement the operation function set of each module.
Modify the compilation file of the audio module.
Perform build, debugging, and testing.
Audio Driver Development Examples
Code path: device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers
The following uses Hi3516D V300 as an example to describe how to develop the codec driver, DAI driver, and Platform driver.
Codec Driver Development Example
Code path: device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/codec/hi3516
The major steps for developing the codec driver are as follows:
- Define and fill in a codec instance.
- Implement callbacks for the codec instance.
- Register and bind the codec instance to the HDF.
- Configure the HCS and makefile.
Filling in Codec Data Structs
Fill in the following data structs for the codec module:
g_codecData: operation function set and private data set of the codec device.
g_codecDaiDeviceOps: codec DAI device operation function set, including APIs for starting transmission and setting parameters.
g_codecDaiData: operation function set and private data set of the digital audio interface of the codec.
struct CodecData g_codecData = {
.Init = CodecDeviceInit, // Initialize the codec device (need to be implemented for a new platform).
.Read = AudioDeviceReadReg, // Read the register (available in the existing framework).
.Write = AudioDeviceWriteReg, // Write the register (available in the existing framework).
};
struct AudioDaiOps g_codecDaiDeviceOps = {
.Startup = CodecDaiStartup, // Start transmission (need to be implemented for a new platform).
.HwParams = CodecDaiHwParams, // Set parameters (need to be implemented for a new platform).
};
struct DaiData g_codecDaiData = {
.DaiInit = CodecDaiDeviceInit,// Initialize the codec DAI device (need to be implemented for a new platform).
.ops = &g_codecDaiDeviceOps, // Codec DAI device operation function set.
};
Initializing codecDevice and codecDai
CODECDeviceInit sets audio input/audio output (AIAO), initializes registers, inserts g_audioControls into the controller linked list, initializes the power management, and selects a path.
int32_t CodecDeviceInit(struct AudioCard *audioCard, struct CodecDevice *codec)
{
...
/* Register set() and get() of the AIAO module on the Hi3516. */
CodecSetCtlFunc(codec->devData, AudioCodecAiaoGetCtrlOps, AudioCodecAiaoSetCtrlOps)
...
/* Hi3516 codec register IoRemap. */
CodecHalSysInit();
...
/* Initialize the codec registers of the Hi3516. */
CodecRegDefaultInit(codec->devData->regCfgGroup);
...
/* Add g_audioControls of the Hi3516 to the controller linked list.*/
AudioAddControls(audioCard, codec->devData->controls, codec->devData->numControls);
...
/* Load the codec of the Hi3516 to the SAPM. */
AudioSapmNewComponents(audioCard, codec->devData->sapmComponents, codec->devData->numSapmComponent);
...
/* Add the codec of the Hi3516 to the audioRoutes linked list. */
AudioSapmAddRoutes(audioCard, g_audioRoutes, HDF_ARRAY_SIZE(g_audioRoutes);
...
AudioSapmNewControls(audioCard);
...
/* Hi3516 codec power management. */
AudioSapmSleep(audioCard);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
CodecDaiDeviceInit initializes the codec DAI device. This API is not used on the Hi3516 and is reserved.
int32_t CodecDaiDeviceInit(struct AudioCard *card, const struct DaiDevice *device)
{
...
AUDIO_DRIVER_LOG_DEBUG("codec dai device name: %s\n", device->devDaiName);
(void)card;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Implementing the Codec Operation Function Set
The codec module is encapsulated with the read() and write() functions of the read and write registers at the operating system abstraction layer (OSAL).
If the new platform cannot use the OSAL read() and write() functions to operate registers, you should implement them.
int32_t AudioDeviceReadReg(unsigned long virtualAddress, uint32_t reg, uint32_t *val)
{
...
*val = OSAL_READL((void *)((uintptr_t)(virtualAddress + reg)));
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
int32_t AudioDeviceWriteReg(unsigned long virtualAddress, uint32_t reg, uint32_t value)
{
OSAL_WRITEL(value, (void *)((uintptr_t)(virtualAddress + reg)));
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
CodecDaiStartup completes startup settings.
int32_t CodecDaiStartup(const struct AudioCard *card, const struct DaiDevice *device)
{
int32_t ret;
...
(void)card;
ret = CodecSetAdcTuneEnable(device->devData->regCfgGroup);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
CodecDaiHwParams sets parameters, including the sampling rate and bit width.
int32_t CodecDaiHwParams(const struct AudioCard *card, const struct AudioPcmHwParams *param)
{
unsigned int bitWidth;
struct CodecDaiParamsVal codecDaiParamsVal;
...
int ret = AudioFormatToBitWidth(param->format, &bitWidth);
...
codecDaiParamsVal.frequencyVal = param->rate;
codecDaiParamsVal.formatVal = bitWidth;
ret = CodecDaiParamsUpdate(card->rtd->codecDai->devData->regCfgGroup, codecDaiParamsVal);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Registering and Binding Codec to HDF
The following implementation depends on the driver implementation mode of the HDF. For details, see HDF.
Fill in the g_codecDriverEntry struct. Ensure that the value of moduleName is the same as that in device_info.hcs. Implement the pointers to the Bind, Init, and Release functions.
device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/codec/hi3516/src/hi3516_codec_adapter.c
struct HdfDriverEntry g_codecDriverEntry = {
.moduleVersion = 1,
.moduleName = "CODEC_HI3516",
.Bind = CodecDriverBind,
.Init = CodecDriverInit,
.Release = CodecDriverRelease,
};
HDF_INIT(g_codecDriverEntry);
CodecDriverBind binds the device in the HDF to the codec and registers the codec service with the HDF.
static int32_t CodecDriverBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
struct CodecHost *codecHost = (struct CodecHost *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*codecHost));
...
codecHost->device = device;
device->service = &codecHost->service;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
CodecDriverInit obtains the codecService name and private register configuration, and inserts them into the linked list by using AudioRegisterCodec.
static int32_t CodecDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
...
CodecGetConfigInfo(device, &g_codecData);
CodecSetConfigInfo(&g_codecData, &g_codecDaiData);
CodecGetServiceName(device, &g_codecData.drvCodecName);
CodecGetDaiName(device, &g_codecDaiData.drvDaiName);
AudioRegisterCodec(device, &g_codecData, &g_codecDaiData);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
CodecDriverRelease releases driver resources.
static void CodecDriverRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
codecHost = (struct CodecHost *)device->service;
OsalMemFree(codecHost);
}
Configuring HCS
Configure the driver node, loading sequence, and service name in the .hcs file. For details about the HCS syntax, see Configuration Management of the HDF.
Path of the standard-system configuration file:
vendor/hisilicon/hispark_taurus_standard/hdf_config/khdf/
Path of the small-system configuration file:
vendor/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/hdf_config/
Configuring Codec Device Information in device_info.hcs
Add codec node configuration. Modify moduleName in the configuration file. The value must be the same as moduleName in the HdfDriverEntry struct. Generally, the value should present the hardware platform. For example, moduleName = “CODEC_HI3516”.
The code snippet is as follows:
audio :: host {
device_codec :: device {
device0 :: deviceNode {
policy = 1; // The codec module provides services only for the kernel.
priority = 50; // The codec module must be loaded before the load of the HDF_AUDIO module.
preload = 0;
permission = 0666;
moduleName = "CODEC_HI3516"; // The value must be the same as moduleName in HdfDriverEntry.
serviceName = "codec_service_0"; // Name of the service provided externally.
deviceMatchAttr = "hdf_codec_driver"; // Name of the private attribute, which is used to match the corresponding private data (including the register configuration).
}
}
Configuring Dependencies in audio_config.hcs
Configure the dependency between the codec, platform, DAI, and DSP on which the audio_card device depends.
The code snippet is as follows:
root {
platform {
...
controller_0x120c1001 :: card_controller {
// Set the private data attribute name, which must be the same as the deviceMatchAttr in device_info.hcs.
match_attr = "hdf_audio_driver_1";
serviceName = "hdf_audio_codec_primary_dev11"; // Name of the service provided externally.
codecName = "codec_service_1"; // Codec service name.
platformName = "dma_service_0"; // DMA service.
cpuDaiName = "dai_service"; // CPU DAI service.
codecDaiName = "tfa9879_codec_dai"; // Codec DAI service.
dspName = "dsp_service_0"; // DSP service name.
dspDaiName = "dsp_dai"; // DSP DAI.
}
}
}
Configuring Private Registers in codec_config.hcs
The configuration matches deviceMatchAttr of the codec configured in device_info.hcs. It includes the register configuration.
Binding the control functionality configuration is to configure the control functionalities and their register parameters in the .hcs file according to unified struct specifications. The configuration can be obtained and parsed, and added to the controller linked list.
regConfig: register and control functionality configuration.
ctrlParamsSeqConfig: register configuration for a function. The items in ctrlParamsSeqConfig must be in the same sequence as the items in controlsConfig.
daiStartupSeqConfig: DAI startup configuration.
daiParamsSeqConfig: playback parameter configuration.
resetSeqConfig: reset process register configuration.
initSeqConfig: initialization process register configuration.
controlsConfig: control function configuration. The array index (specific service scenario) and iface (same as that in the HAL) have fixed values.
sapmConfig: power management and control function configuration. The values of array index (specific service scenario) and iface (consistent with the HAL) have fixed values.
ctrlSapmParamsSeqConfig: register configuration of the power management and control function.
sapmComponent: power management component configuration.
array index:
The array index in controlsConfig is the element ID in the g_audioCodecControlsList array in the audio_codec_base.c file.
The array index in sapmConfig is the element ID in the g_audioSapmCfgNameList array in the audio_codec_base.c file.
The compNameIndex in sapmComponent is the element ID in the g_audioSapmCompNameList array in the audio_codec_base.c file.
- iface: 2 for the virtual mixer device.
root {
platform {
template codec_controller {
match_attr = "";
serviceName = "";
codecDaiName = "";
}
controller_0x120c1030 :: codec_controller {
match_attr = "hdf_codec_driver";
serviceName = "codec_service_0";
codecDaiName = "codec_dai";
/* Base address of Hi3516 registers. */
idInfo {
chipName = "hi3516"; // Codec name.
chipIdRegister = 0x113c0000; // Codec base address.
chipIdSize = 0x1000; // Codec address offset.
}
/* Register configuration, including configuration of registers. */
regConfig {
/* reg: register address
rreg: register address
shift: shift bits
rshift: rshift bits
min: min value
max: max value
mask: mask of value
invert: enum InvertVal 0-uninvert 1-invert
value: value
*/
/* reg, value */
initSeqConfig = [
0x14, 0x04000002,
0x18, 0xFD200004,
0x1C, 0x00180018,
0x20, 0x83830028,
0x24, 0x00005C5C,
0x28, 0x00130000,
0x30, 0xFF035A00,
0x34, 0x08000001,
0x38, 0x06062424,
0x3C, 0x1E1EC001,
0x14, 0x04000002
];
/* Control functionality configuration.
array index, iface, mixer/mux, enable, */
0, 2, 0, 0,
1, 2, 0, 1,
2, 2, 0, 1,
3, 2, 0, 1,
4, 2, 0, 1,
5, 2, 0, 1,
8, 2, 0, 0,
9, 2, 0, 0,
];
/* Control functionality register configuration
reg, rreg, shift, rshift, min, max, mask, invert, value */
ctrlParamsSeqConfig = [
0x3c, 0x3c, 24, 24, 0x0, 0x57, 0x7F, 1, 0, // "Main Capture Volume"
0x38, 0x38, 31, 31, 0x0, 0x1, 0x1, 0, 0, // "Playback Mute"
0x3c, 0x3c, 31, 31, 0x0, 0x1, 0x1, 0, 0, // "Capture Mute"
0x20, 0x20, 16, 16, 0x0, 0xF, 0x1F, 0, 0, // "Mic Left Gain"
0x20, 0x20, 24, 24, 0x0, 0xF, 0x1F, 0, 0, // "Mic Right Gain"
0x2000, 0x2000, 16, 16, 0x0, 0x7, 0x7, 0, 0, // "Render Channel Mode"
0x1000, 0x1000, 16, 16, 0x0, 0x7, 0x7, 0, 0 // "Capture Channel Mode"
];
/* After the upper layer delivers parameters, write audio-related data to registers.
reg, rreg, shift, rshift, min, max, mask, invert, value */
daiParamsSeqConfig = [
0x30, 0x30, 13, 13, 0x0, 0x1F, 0x1F, 0, 0x0, // i2s_frequency
0x1C, 0x1C, 6, 6, 0x0, 0x3, 0x3, 0, 0x0, // adc_mode_sel
0x30, 0x30, 22, 22, 0x0, 0x3, 0x3, 0, 0x0, // i2s_datawith
];
/* Configuration of the power management function register.
reg, rreg, shift, rshift, min, max, mask, invert, value */
ctrlSapmParamsSeqConfig = [
0x20, 0x20, 23, 23, 0x0, 0x1, 0x1, 0, 0, // LPGA MIC 0 -- connect MIC
0x20, 0x20, 31, 31, 0x0, 0x1, 0x1, 0, 0, // RPGA MIC 0 -- connect MIC
0x30, 0x30, 27, 27, 0x0, 0x1, 0x1, 0, 0, // dacl to dacr mixer
0x30, 0x30, 26, 26, 0x0, 0x1, 0x1, 0, 0 // dacr to dacl mixer
];
/*
Power management component configuration.
sapmType, compNameIndex, reg, mask, shift, invert, kcontrolNews, kcontrolsNum
reg = 0xFFFF: component has no sapm register bit
*/
sapmComponent = [
10, 0, 0x20, 0x1, 15, 1, 0, 0, // ADCL
10, 1, 0x20, 0x1, 14, 1, 0, 0, // ADCR
11, 2, 0x14, 0x1, 11, 1, 0, 0, // DACL
11, 3, 0x14, 0x1, 12, 1, 0, 0, // DACR
17, 4, 0x20, 0x1, 13, 1, 1, 1, // LPGA
17, 5, 0x20, 0x1, 12, 1, 2, 1, // RPGA
15, 6, 0xFFFF, 0xFFFF, 0, 0, 0, 0, // SPKL
15, 7, 0xFFFF, 0xFFFF, 0, 0, 0, 0, // SPKR
17, 52, 0xFFFF, 0xFFFF, 0, 0, 3, 1, // SPKL PGA
17, 53, 0xFFFF, 0xFFFF, 0, 0, 4, 1, // SPKR PGA
13, 40, 0xFFFF, 0xFFFF, 0, 0, 0, 0, // MIC1
13, 41, 0xFFFF, 0xFFFF, 0, 0, 0, 0 // MIC2
];
/* Power management function configuration.
array index, iface, mixer/mux, enable
*/
sapmConfig = [
0, 2, 0, 1,
1, 2, 0, 1,
2, 2, 0, 1,
3, 2, 0, 1
];
}
}
}
}
Read the .hcs files in the C code to obtain register configuration.
static int32_t CodecDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
...
CodecGetConfigInfo(device, &g_codecData) ;
CodecSetConfigInfo(&g_codecData, &g_codecDaiData);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
When the codec is registered, the input parameter device contains controller_0x120c1030 node information. You only need to parse the node to obtain the configuration information.
int32_t CodecGetConfigInfo(const struct HdfDeviceObject *device, struct CodecData *codecData)
{
codecData->regConfig = (struct AudioRegCfgData *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*(codecData->regConfig)));
CodecGetRegConfig(device, codecData->regConfig);
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Obtain the node configuration to configure the node.
int32_t CodecGetRegConfig(const struct HdfDeviceObject *device, struct AudioRegCfgData *configData)
{
...
drsOps = DeviceResourceGetIfaceInstance(HDF_CONFIG_SOURCE);
...
idNode = drsOps->GetChildNode(root, "idInfo");
ParseAudioAttr(drsOps, idNode, &configData->audioIdInfo);
regCfgNode = drsOps->GetChildNode(root, "regConfig");
...
DEV_RES_NODE_FOR_EACH_ATTR(regCfgNode, regAttr) {
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Obtain and use the configuration of the regConfig node. After the configuration files are parsed, the register information in the code can be directly updated.
int32_t CodecDeviceInit(struct AudioCard *audioCard, struct CodecDevice *codec)
{
...
if (CodecRegDefaultInit(codec->devData->regCfgGroup) != HDF_SUCCESS) {
AUDIO_DRIVER_LOG_ERR("CodecRegDefaultInit failed.");
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
SmartPA Driver Development Example
Code path: device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/codec/tfa9879
The SmartPA is a type of codec driver. The development process is as follows:
- Define and fill in a codec instance.
- Implement callbacks for the codec instance.
- Register and bind the codec instance to the HDF.
- Configure the HCS and makefile.
Filling in the Codec Data Structs
Fill in the following data structs for the codec module:
g_tfa9879Data: operation function set of the codec device. It contains the configuration in the .hcs file, and defines and maps the functions for initializing the codec device and reading and writing registers.
g_tfa9879DaiDeviceOps: DAI data set that defines and maps the operations of the codec device DAI.
g_tfa9879DaiData: DAI data set that defines and maps the driver name, initialization, and operations of the data access interfaces of the codec device.
struct CodecData g_tfa9879Data = {
.Init = Tfa9879DeviceInit,
.Read = CodecDeviceRegI2cRead,
.Write = CodecDeviceRegI2cWrite,
};
struct AudioDaiOps g_tfa9879DaiDeviceOps = {
.Startup = Tfa9879DaiStartup,
.HwParams = Tfa9879DaiHwParams,
};
struct DaiData g_tfa9879DaiData = {
.drvDaiName = "tfa9879_codec_dai",
.DaiInit = Tfa9879DaiDeviceInit,
.ops = &g_tfa9879DaiDeviceOps,
.Read = CodecDaiRegI2cRead,
.Write = CodecDaiRegI2cWrite,
};
Initializing codecDevice and codecDai
As the entry function for device initialization, Tfa9879DeviceInit sets the address of the SmartPA I2C device, obtains configuration data, initializes (including resets) the device registers, and adds the control functionality to the controller linked list. The current demo also includes the initialization of the registers related to the Hi3516D V300 device, such as initialization of GPIO pins.
int32_t Tfa9879DeviceInit(struct AudioCard *audioCard, const struct CodecDevice *device)
{
int32_t ret;
...
// Initialize GPIO pins.
ret = Hi35xxGpioPinInit();
...
// Set I2C parameters.
g_transferParam.i2cBusNumber = TFA9879_I2C_BUS_NUMBER;
g_transferParam.i2cDevAddr = TFA9879_I2C_DEV_ADDR;
g_transferParam.i2cRegDataLen = TFA9879_I2C_REG_DATA_LEN;
device->devData->privateParam = &g_transferParam;
...
// Initialize device registers.
ret = CodecDeviceInitRegConfig(device);
...
// Bind the control functionality configuration.
if (AudioAddControls(audioCard, device->devData->controls, device->devData->numControls) !=
HDF_SUCCESS) {
AUDIO_DRIVER_LOG_ERR("add controls failed.");
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
...
}
Common functions of the I2C read/write registers:
int32_t CodecDeviceRegI2cRead(const struct CodecDevice *codec, uint32_t reg, uint32_t *val)
{
int32_t ret;
struct AudioAddrConfig regAttr;
struct I2cTransferParam *i2cTransferParam = NULL;
...
i2cTransferParam = (struct I2cTransferParam *)codec->devData->privateParam;
...
regAttr.addr = (uint8_t)reg;
regAttr.value = 0;
ret = CodecI2cTransfer(i2cTransferParam, ®Attr, I2C_FLAG_READ);
...
*val = regAttr.value;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
int32_t CodecDeviceRegI2cWrite(const struct CodecDevice *codec, uint32_t reg, uint32_t value)
{
int32_t ret;
struct AudioAddrConfig regAttr;
struct I2cTransferParam *i2cTransferParam = NULL;
...
i2cTransferParam = (struct I2cTransferParam *)codec->devData->privateParam;
...
regAttr.addr = (uint8_t)reg;
regAttr.value = (uint16_t)value;
ret = CodecI2cTransfer(i2cTransferParam, ®Attr, 0);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
int32_t CodecDaiRegI2cRead(const struct DaiDevice *dai, uint32_t reg, uint32_t *value)
{
...
ret = CodecI2cTransfer(i2cTransferParam, ®Attr, I2C_FLAG_READ);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
int32_t CodecDaiRegI2cWrite(const struct DaiDevice *dai, uint32_t reg, uint32_t value)
{
...
ret = CodecI2cTransfer(i2cTransferParam, ®Attr, 0);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Implementing the Codec Operation Function Set
Tfa9879DaiStartup performs startup settings. The code snippet is as follows:
int32_t Tfa9879DaiStartup(const struct AudioCard *card, const struct DaiDevice *device)
{
int ret;
(void)card;
(void)device;
// Set the register for starting the SmartPA.
ret = CodecDaiDeviceStartupRegConfig(device);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Tfa9879DaiHwParams delivers playback parameters. The code snippet is as follows:
int32_t Tfa9879DaiHwParams(const struct AudioCard *card, const struct AudioPcmHwParams *param)
{
int32_t ret;
uint16_t frequency, bitWidth;
struct DaiParamsVal daiParamsVal;
(void)card;
...
// Set the sampling rate.
ret = Tfa9879FrequencyParse(param->rate, &frequency);
...
// Set the bit width.
ret = Tfa9879FormatParse(param->format, &bitWidth);
...
daiParamsVal.frequencyVal = frequency;
daiParamsVal.formatVal = bitWidth;
daiParamsVal.channelVal = param->channels; // Set the audio channel.
ret = Tfa9879DaiParamsUpdate(card->rtd->codecDai, daiParamsVal);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Registering and Binding Codec to HDF
The following implementation depends on the driver implementation mode of the HDF. For details, see HDF.
Fill in the g_tfa9879DriverEntry struct. Ensure that the value of moduleName is the same as that in device_info.hcs. Implement the pointers to the Bind, Init, and Release functions.
device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/codec/tfa9879/src/tfa9879_accessory_adapter.c
static int32_t Tfa9879DriverBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
(void)device;
AUDIO_DRIVER_LOG_INFO("success!");
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
static int32_t Tfa9879DriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
int32_t ret;
...
// Obtain configuration data from .hcs files.
ret = CodecGetConfigInfo(device, &g_tfa9879Data);
...
// Set the interface functions and register information related to codec control.
ret = CodecSetConfigInfoOfControls(&g_tfa9879Data, &g_tfa9879DaiData);
...
ret = CodecGetServiceName(device, &g_tfa9879Data.drvCodecName);
...
ret = CodecGetDaiName(device, &g_tfa9879DaiData.drvDaiName);
...
// Register the codec with the audio adapter.
ret = AudioRegisterCodec(device, &g_tfa9879Data, &g_tfa9879DaiData);
....
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
/* HdfDriverEntry definitions */
struct HdfDriverEntry g_tfa9879DriverEntry = {
.moduleVersion = 1,
.moduleName = "CODEC_TFA9879",
.Bind = Tfa9879DriverBind,
.Init = Tfa9879DriverInit,
.Release = NULL,
};
HDF_INIT(g_tfa9879DriverEntry);
Configuring HCS
For details about the configuration process, see Configuring HCS in Codec Driver Development Example.
Platform Driver Development Example
Code path: device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/soc
In audio driver development, the Platform module is configured to adapt to the DMA driver. The major steps for developing the platform driver are as follows:
- Define and fill in a platform instance.
- Implement callbacks for the platform instance.
- Register and bind the codec instance to the HDF.
- Configure the HCS and makefile.
Filling in Platform Data Structures
Fill in the following structs for the platform module:
g_platformData: private configuration of the platform device, including the initialization and operation functions of the platform device.
g_dmaDeviceOps: DMA device operation function set, including the encapsulation of some common DMA APIs.
struct AudioDmaOps g_dmaDeviceOps = {
.DmaBufAlloc = Hi3516DmaBufAlloc, // Apply for memory for the DMA device.
.DmaBufFree = Hi3516DmaBufFree, // Release the memory of the DMA device.
.DmaRequestChannel = Hi3516DmaRequestChannel, // Request a DMA channel.
.DmaConfigChannel = Hi3516DmaConfigChannel, // Configure the DMA channel.
.DmaPrep = Hi3516DmaPrep, // Prepare for DMA.
.DmaSubmit = Hi3516DmaSubmit, // Submit a DMA request.
.DmaPending = Hi3516DmaPending, // Pend DMA.
.DmaPause = Hi3516DmaPause, // Pause or stop the DMA service.
.DmaResume = Hi3516DmaResume, // Resume the DMA service.
.DmaPointer = Hi3516DmaPointer, // Obtain the current playing or recording position.
};
struct PlatformData g_platformData = {
.PlatformInit = AudioDmaDeviceInit, // Initialize the DMA device.
.ops = &g_dmaDeviceOps,
};
Initializing dmaDevice
AudioDmaDeviceInit initializes the DMA device, including setting the Hi3516 AIAO module.
int32_t AudioDmaDeviceInit(const struct AudioCard *card, const struct PlatformDevice *platformDevice)
{
...
AiaoHalSysInit();
/* PIN MUX */
AiaoSysPinMux();
/* CLK reset */
AiaoClockReset();
/* AIAO initialization */
AiaoDeviceInit(chnId);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Implementing the DMA Operation Function Set
The DMA device operation function set includes the encapsulation of DMA common APIs. If the common APIs cannot meet development requirements, you can implement new DMA callbacks.
int32_t AudioDmaDeviceInit(const struct AudioCard *card, const struct PlatformDevice *platform);
int32_t Hi3516DmaBufAlloc(struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType);
int32_t Hi3516DmaBufFree(struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType);
int32_t Hi3516DmaRequestChannel(const struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType);
int32_t Hi3516DmaConfigChannel(const struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType);
int32_t Hi3516DmaPrep(const struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType);
int32_t Hi3516DmaSubmit(const struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType);
int32_t Hi3516DmaPending(struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType);
int32_t Hi3516DmaPause(struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType);
int32_t Hi3516DmaResume(const struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType);
int32_t Hi3516DmaPointer(struct PlatformData *data, const enum AudioStreamType streamType, uint32_t *pointer);
Registering and Binding Platform to HDF
The following implementation depends on the driver implementation mode of the HDF. For details, see HDF.
- Fill in the g_platformDriverEntry struct.
- Ensure that the value of moduleName is the same as that in device_info.hcs.
- Implement the pointers to the Bind, Init, and Release functions.
device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/soc/src/hi3516_dma_adapter.c
static int32_t Hi3516DmaDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
...
OsalMutexInit(&g_platformData.renderBufInfo.buffMutex);
OsalMutexInit(&g_platformData.captureBufInfo.buffMutex);
g_platformData.platformInitFlag = false;
ret = AudioSocRegisterPlatform(device, &g_platformData);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
static void Hi3516DmaDriverRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
struct PlatformHost *platformHost = NULL;
...
platformHost = (struct PlatformHost *)device->service;
...
OsalMutexDestroy(&g_platformData.renderBufInfo.buffMutex);
OsalMutexDestroy(&g_platformData.captureBufInfo.buffMutex);
OsalMemFree(platformHost);
}
/* HdfDriverEntry definitions */
struct HdfDriverEntry g_platformDriverEntry = {
.moduleVersion = 1,
.moduleName = "DMA_HI3516",
.Bind = Hi3516DmaDriverBind,
.Init = Hi3516DmaDriverInit,
.Release = Hi3516DmaDriverRelease,
};
HDF_INIT(g_platformDriverEntry);
Configuring HCS
For details about the configuration process, see Configuring HCS in Codec Driver Development Example.
DAI Driver Development Example
Code path: device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/soc
The major steps for developing the DAI driver are as follows:
- Define and fill in a DAI instance.
- Implement callbacks for the DAI instance.
- Register and bind the codec instance to the HDF.
- Configure the HCS and makefile.
Filling in DAI Data Structures
Fill in the following structs for the DAI module:
g_daiData: private configuration of the DAI device, including the initialization of the DAI device, read/write of registers, and operation functions.
g_daiDeviceOps: DAI device operation function set, including setting DAI parameters and triggering and starting the DAI device.
struct AudioDaiOps g_daiDeviceOps = {
.HwParams = DaiHwParams,
.Trigger = DaiTrigger,
.Startup = DaiStartup,
};
struct DaiData g_daiData = {
.DaiInit = DaiDeviceInit,
.Read = AudioDeviceReadReg,
.Write = AudioDeviceWriteReg,
.ops = &g_daiDeviceOps,
};
Initializing daiDevice
DaiDeviceInit initializes DAI configuration and adds the information to the controller linked list.
int32_t DaiDeviceInit(struct AudioCard *audioCard, const struct DaiDevice *dai)
{
...
struct DaiData *data = dai->devData;
struct AudioRegCfgData *regConfig = dai->devData->regConfig;
...
g_regCodecBase = OsalIoRemap(CODEC_REG_BASE, CODEC_MAX_REG_SIZE);
...
data->regVirtualAddr = (uintptr_t)g_regCodecBase;
DaiSetConfigInfo(data);
AudioAddControls(audioCard, data->controls, data->numControls);
I2c6PinInit();
...
data->daiInitFlag = true;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Implementing the DAI Operation Function Set
AudioDeviceReadReg and AudioDeviceWriteReg are not used on the Hi3516 and are reserved.
DaiHwParams sets PCM stream information.
int32_t DaiHwParams(const struct AudioCard *card, const struct AudioPcmHwParams *param)
{
uint32_t bitWidth;
struct DaiDevice *device = card->rtd->cpuDai;
...
DaiCheckSampleRate(param->rate);
struct DaiData *data = DaiDataFromCard(card);
data->pcmInfo.channels = param->channels;
...
AudioFormatToBitWidth(param->format, &bitWidth);
...
data->pcmInfo.bitWidth = bitWidth;
data->pcmInfo.rate = param->rate;
data->pcmInfo.streamType = param->streamType;
data->regVirtualAddr = (uintptr_t)g_regDaiBase;
...
DaiParamsUpdate(device);
data->regVirtualAddr = (uintptr_t)g_regCodecBase;
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
DaiTrigger is not used on the Hi3516 and is reserved.
DaiStartup updates the register configuration and configures the I2S.
int32_t DaiStartup(const struct AudioCard *card, const struct DaiDevice *device)
{
struct AudioMixerControl *regCfgItem = NULL;
...
regCfgItem = device->devData->regConfig->audioRegParams[AUDIO_DAI_STARTUP_PATAM_GROUP]->regCfgItem;
itemNum = device->devData->regConfig->audioRegParams[AUDIO_DAI_STARTUP_PATAM_GROUP]->itemNum;
device->devData->regVirtualAddr = (uintptr_t)g_regDaiBase;
for (int i = 0; i < itemNum; i++) {
int ret = AudioUpdateDaiRegBits(device, ®CfgItem[i], regCfgItem[i].value);
if (ret != HDF_SUCCESS) {
AUDIO_DRIVER_LOG_ERR("set frequency fail.");
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
}
device->devData->regVirtualAddr = (uintptr_t)g_regCodecBase;
if (I2sPinInit() != HDF_SUCCESS) {
AUDIO_DRIVER_LOG_ERR("I2sPinInit fail.");
}
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
Registering and Binding DAI to HDF
The following implementation depends on the driver implementation mode of the HDF. For details, see HDF.
- Fill in the g_daiDriverEntry struct.
- Ensure that the value of moduleName is the same as that in device_info.hcs.
- Implement the pointers to the Bind, Init, and Release functions.
device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/soc/src/hi3516_dai_adapter.c
static int32_t DaiDriverBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
...
struct DaiHost *daiHost = (struct DaiHost *)OsalMemCalloc(sizeof(*daiHost));
...
daiHost->device = device;
device->service = &daiHost->service;
g_daiData.daiInitFlag = false;
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
static int32_t DaiDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
...
DaiGetConfigInfo(device, &g_daiData);
DaiGetServiceName(device);
...
OsalMutexInit(&g_daiData.mutex);
AudioSocRegisterDai(device, &g_daiData);
...
return HDF_SUCCESS;
}
static void DaiDriverRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *device)
{
...
OsalMutexDestroy(&g_daiData.mutex);
...
struct DaiHost *daiHost = (struct DaiHost *)device->service;
...
OsalMemFree(daiHost);
}
/* HdfDriverEntry definitions */
struct HdfDriverEntry g_daiDriverEntry = {
.moduleVersion = 1,
.moduleName = "DAI_HI3516",
.Bind = DaiDriverBind,
.Init = DaiDriverInit,
.Release = DaiDriverRelease,
};
HDF_INIT(g_daiDriverEntry);
Configuring HCS
For details about the configuration process, see Configuring HCS in Codec Driver Development Example.
Adding Compilation Configuration to Makefile
Add the newly added files to the Makefile file to link them to the kernel image.
Standard system (Linux): device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/Makefile
obj-$(CONFIG_DRIVERS_HDF_AUDIO_HI3516CODEC) += \
codec/tfa9879/src/tfa9879_codec_adapter.o \
codec/tfa9879/src/tfa9879_codec_ops.o \
codec/hi3516/src/hi3516_codec_adapter.o \
codec/hi3516/src/hi3516_codec_impl.o \
codec/hi3516/src/hi3516_codec_ops.o \
dsp/src/dsp_adapter.o \
dsp/src/dsp_ops.o \
soc/src/hi3516_dai_adapter.o \
soc/src/hi3516_dai_ops.o \
soc/src/hi3516_aiao_impl.o \
soc/src/hi3516_dma_ops.o \
soc/src/hi3516_dma_adapter.o
Small system (LiteOS): drivers/adapter/khdf/liteos/model/audio/Makefile
LOCAL_SRCS += \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/codec/tfa9879/src/tfa9879_codec_adapter.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/codec/tfa9879/src/tfa9879_codec_ops.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/codec/hi3516/src/hi3516_codec_adapter.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/codec/hi3516/src/hi3516_codec_impl.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/codec/hi3516/src/hi3516_codec_ops.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/dsp/src/dsp_adapter.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/dsp/src/dsp_ops.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/soc/src/hi3516_dai_adapter.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/soc/src/hi3516_dai_ops.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/soc/src/hi3516_aiao_impl.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/soc/src/hi3516_dma_ops.c \
$(KHDF_AUDIO_HI3516DV300_DIR)/soc/src/hi3516_dma_adapter.c
Source Code Structure and Directory
The development example implements the functions in the header file of the driver interface. The following uses Hi3516 as an example to describe the directory struct.
Path of the driver implementation sample code: device/board/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/audio_drivers/
.
├── codec
│ ├── hi3516
│ │ ├── include
│ │ │ ├── hi3516_codec_impl.h
│ │ │ └── hi3516_codec_ops.h
│ │ └── src
│ │ │ ├── hi3516_codec_adapter.c // Codec driver entry
│ │ │ ├── hi3516_codec_impl.c // Implementation of codec hardware operations
│ │ │ └── hi3516_codec_ops.c // Implementation of codec driver APIs
│ └── tfa9879
│ ├── include
│ │ └── tfa9879_codec_ops.h
│ └── src
│ ├── tfa9879_codec_adapter.c
│ └── tfa9879_codec_ops.c
├── dsp
│ ├── include
│ │ └── dsp_ops.h
│ └── src
│ ├── dsp_adapter.c // DSP driver entry
│ └── dsp_ops.c
├── LICENSE
├── Makefile
└── soc
├── include
│ ├── hi3516_aiao_impl.h
│ ├── hi3516_dai_ops.h
│ └── hi3516_dma_ops.h
└── src
├── hi3516_aiao_impl.c
├── hi3516_dai_adapter.c // DAI driver entry
├── hi3516_dai_ops.c
├── hi3516_dma_adapter.c // DMA driver entry
└── hi3516_dma_ops.c
HCS Files and Directory
Standard system:
vendor/hisilicon/hispark_taurus_standard/
└── hdf_config
└── khdf
├── audio
│ ├── audio_config.hcs
│ ├── codec_config.hcs
│ ├── dai_config.hcs
│ ├── dma_config.hcs
│ └── dsp_config.hcs
├── device_info
│ └── device_info.hcs
└── hdf.hcs
Small system:
vendor/hisilicon/hispark_taurus/
├── config.json
└── hdf_config
├── audio
│ ├── audio_config.hcs
│ ├── codec_config.hcs
│ ├── dai_config.hcs
│ ├── dma_config.hcs
│ └── dsp_config.hcs
├── device_info
│ └── device_info.hcs
└── hdf.hcs
HAL-based Development Procedure and Example
The Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) provides the following function:
- Provides audio HDIs for audio services to implement basic audio features on applications.
- Provides standard interfaces for device developers to comply with the HDI adapter standards. This promises a healthy evolution of the ecosystem.
Code path: drivers_interface/audio/v1_0
Development procedure

Call GetAudioManagerFuncs() to obtain methods.
Use GetAllAdapters() to obtain information about the supported audio adapter, and call LoadAdapter() to load the audio adapter.
Create a Render class by calling CreateRender() or create a recorder class and deliver audio attributes.
Call the methods hooked in the Render class created. For example, call render->Start() to start the playback, and call render->RenderFrame() to deliver audio data cyclically.
During the playback, call control commands to control the playback service, for example, call render->SetVolume() to adjust the volume, call render->Pause() to pause the playback, and call render->Resume() to resume the playback.
After the playback is complete, call render->Stop() to stop the playback, call adapter->DestroyRender() to destroy the playback instance, and call audioManagerIns->UnloadAdapter() to unload the audio adapter.
HAL Usage Example
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "v1_0/audio_types.h"
#include "v1_0/iaudio_manager.h"
struct IAudioRender *g_render = NULL;
struct IAudioAdapter *g_adapter = NULL;
struct AudioDeviceDescriptor g_devDesc;
struct AudioSampleAttributes g_attrs;
struct AudioHeadInfo g_wavHeadInfo;
bool g_isDirect = false; //IPC Loading
uint32_t g_renderId = 0;
static int32_t FrameStart(const struct StrPara *param)
{
...
/* Initialize parameters. */
char *frame = param->frame;
int32_t bufferSize = param->bufferSize;
size_t remainingDataSize = g_wavHeadInfo.riffSize;
/* Send audio data cyclically. */
do {
uint64_t replyBytes = 0;
size_t readSize = (remainingDataSize > bufferSize) ? (size_t)bufferSize : remainingDataSize;
numRead = fread(frame, 1, readSize, g_file);
if (numRead > 0) {
int32_t ret = render->RenderFrame(render, (int8_t *)frame, numRead, &replyBytes);
if (ret == HDF_ERR_INVALID_OBJECT) {
AUDIO_FUNC_LOGE("Render already stop!");
break;
}
remainingDataSize -= numRead;
}
/* Pause the playback and wait. */
while (g_waitSleep) {
printf("music pause now.\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&g_functionCond, &g_mutex);
printf("music resume now.\n");
}
} while (!g_closeEnd && numRead > 0 && remainingDataSize > 0);
...
}
static void *hal_main()
{
int32_t adapterIndex = 0;
struct AudioPort *renderPort;
/* Call IAudioManagerGet() to obtain the entry function. */
struct IAudioManager *audioManagerIns = IAudioManagerGet(g_isDirect);
if (audioManagerIns == NULL) {
AUDIO_FUNC_LOGE("Get Audio Manager Fail");
return HDF_FAILURE;
}
/* Obtain the audio adapter list. */
struct AudioAdapterDescriptor *descs = (struct AudioAdapterDescriptor *)OsalMemCalloc(
sizeof(struct AudioAdapterDescriptor) * (MAX_AUDIO_ADAPTER_DESC));
uint32_t adapterNum = MAX_AUDIO_ADAPTER_DESC;
int32_t ret = audioManagerIns->GetAllAdapters(audioManagerIns, descs, &adapterNum);
/* Locate the audio adapter and port based on the specified audio adapter name and port description. */
SelectAudioCard(descs, adapterNum, &adapterIndex);
strcpy_s(g_adapterName, PATH_LEN, descs[adapterIndex - 1].adapterName);
SwitchAudioPort(&descs[adapterIndex - 1], PORT_OUT, renderPort); // The port type is OUT, which means playback.
/* Load the audio adapter based on the matched audio adapter information. */
audioManagerIns->LoadAdapter(audioManagerIns, &descs[adapterIndex - 1], &g_adapter); // Load the audio adapter and obtain the related instances.
/* Create a Render class. */
uint32_t portId = renderPort->portId;
InitDevDesc(&g_devDesc, portId); // Initialize the parameters for setting the device.
InitAttrs(&g_attrs); // Initialize audio attribute parameters.
CheckWavFileHeader(g_file, &g_wavHeadInfo, &g_attrs); // Parse the audio file and set attributes.
g_adapter->CreateRender(g_adapter, &g_devDesc, &g_attrs, &g_render, &g_renderId);
/* Deliver the number of the audio to be played. */
g_render->Start((void *)g_render); // Send the start command to start the playback.
pthread_create(&g_tids, &tidsAttr, (void *)(&FrameStart), &g_str); // Start the thread to play the music.
/* Send the control instructions. */
g_render->Pause((void *)g_render); // Pause the playback.
g_render->Resume((void *)g_render); // Resume the playback.
g_render->SetVolume((void *)g_render, 0.5); // Set the volume.
/* Stop playback and destroy the Render class. */
g_render->Stop((void *)g_render);
g_adapter->DestroyRender(g_adapter, g_renderId);
/* Unload the audio adapter. */
audioManagerIns->UnloadAdapter(audioManagerIns, g_adapterName);
}
Summary
This document provides all the key adaptations involved in the audio driver development. It elaborates how to adapt the audio driver and use HDI APIs. You can conduct development based on the chip you use. After reading this document, you will be able to master the audio driver development based on the HDF.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙HDF Driver Development Process
harmony 鸿蒙Facial Authentication
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: