harmony 鸿蒙Interactive Tool User Guide
Interactive Tool User Guide
Introduction
You can use Bindgen and CXX to implement the interaction between Rust and C/C++. Bindgen enables Rust to call C by converting C interfaces into Rust interfaces. CXX implement interaction between C++ and Rust by generating bindings between C interfaces and Rust interfaces.
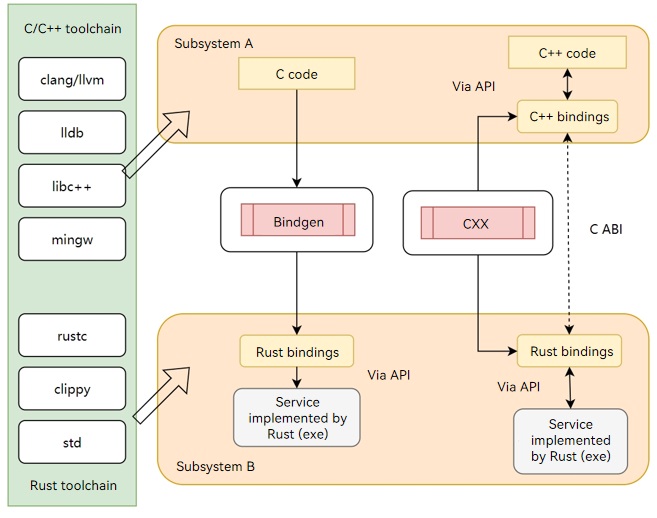
Using Bindgen
Procedure
The following example shows how to use Bindgen to implement invocation of C by Rust.
- In the header file lib.h, define two interfaces FuncAAddB and SayHello in C. The FuncAAddB interface calculates the sum of two numbers, and the SayHello interface prints strings.
#ifndef BUILD_RUST_TESTS_BINDGEN_TEST_LIB_H_
#define BUILD_RUST_TESTS_BINDGEN_TEST_LIB_H_
#include <stdint.h>
#include "build/rust/tests/test_bindgen_test/test_for_hello_world/lib2.h"
uint32_t FuncAAddB(uint32_t a, uint32_t b);
void SayHello(const char *message);
#endif // BUILD_RUST_TESTS_BINDGEN_TEST_LIB_H_
- Add the implementation of the two interfaces to lib.c.
#include "build/rust/tests/test_bindgen_test/test_for_hello_world/lib.h"
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void SayHello(const char *message)
{
printf("This is a test for bindgen hello world:\n");
printf("%s\n", message);
}
uint32_t FuncAAddB(uint32_t a, uint32_t b)
{
printf("This is a test for bindgen of a + b:\n");
return a + b;
}
- Create the main.rs file to call C interfaces through c_ffi using Rust. Note that insecure interfaces called by Rust must be encapsulated by using unsafe.
//! bindgen test for hello world
#![allow(clippy::approx_constant)]
mod c_ffi {
#![allow(dead_code)]
#![allow(non_upper_case_globals)]
#![allow(non_camel_case_types)]
include!(env!("BINDGEN_RS_FILE"));
}
/// pub fn add_two_numbers_in_c
pub fn add_two_numbers_in_c(a: u32, b: u32) -> u32 {
unsafe { c_ffi::FuncAAddB(a, b) }
}
use std::ffi::c_char;
use std::ffi::CString;
/// fn main()
fn main() {
println!("{} + {} = {}", 3, 7, add_two_numbers_in_c(3, 7));
let c_str = CString::new("This is a message from C").unwrap();
let c_world: *const c_char = c_str.as_ptr() as *const c_char;
unsafe {
c_ffi::SayHello(c_world);
}
}
- Create the BUILD.gn file to define the dependency of the Rust module on the C module.
import("//build/ohos.gni")
ohos_shared_library("c_lib") {
sources = [ "lib.c" ]
defines = [ "COMPONENT_IMPLEMENTATION" ]
}
rust_bindgen("c_lib_bindgen") {
header = "lib.h"
}
ohos_rust_executable("bindgen_test") {
deps = [ ":c_lib" ]
deps += [ ":c_lib_bindgen" ]
sources = [ "main.rs" ]
bindgen_output = get_target_outputs(":c_lib_bindgen")
inputs = bindgen_output
rustenv = [ "BINDGEN_RS_FILE=" + rebase_path(bindgen_output[0]) ]
crate_root = "main.rs"
}
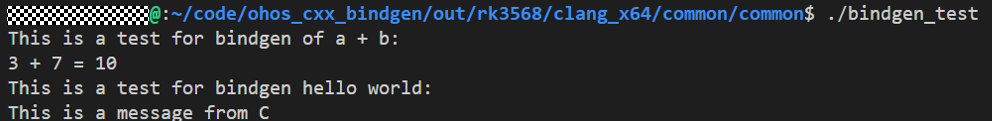
Verification
Using CXX
Calling Rust Interfaces by C++
- In the Rust lib.rs file, add the C++ interfaces to be called in mod ffi, and add the interfaces in extern “Rust” to expose them to C++.
//! #[cxx::bridge]
#[cxx::bridge]
mod ffi{
#![allow(dead_code)]
#[derive(Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq, PartialOrd, Ord)]
struct Shared {
z: usize,
}
extern "Rust"{
fn print_message_in_rust();
fn r_return_primitive() -> usize;
fn r_return_shared() -> Shared;
fn r_return_rust_string() -> String;
fn r_return_sum(_: usize, _: usize) -> usize;
}
}
fn print_message_in_rust(){
println!("Here is a test for cpp call Rust.");
}
fn r_return_shared() -> ffi::Shared {
println!("Here is a message from Rust,test for ffi::Shared:");
ffi::Shared { z: 1996 }
}
fn r_return_primitive() -> usize {
println!("Here is a message from Rust,test for usize:");
1997
}
fn r_return_rust_string() -> String {
println!("Here is a message from Rust,test for String");
"Hello World!".to_owned()
}
fn r_return_sum(n1: usize, n2: usize) -> usize {
println!("Here is a message from Rust,test for {} + {} is:",n1 ,n2);
n1 + n2
}
- Include lib.rs.h (converted from lib.rs by the CXX tool) in C++ code.
#include <iostream>
#include "build/rust/tests/test_cxx/src/lib.rs.h"
int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
int a = 2021;
int b = 4;
print_message_in_rust();
std::cout << r_return_primitive() << std::endl;
std::cout << r_return_shared().z << std::endl;
std::cout << std::string(r_return_rust_string()) << std::endl;
std::cout << r_return_sum(a, b) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
- Create the BUILD.gn file. The underlying rust_cxx calls the CXX tool to convert the lib.rs file into lib.rs.h and lib.rs.cc. ohos_rust_static_ffi implements compilation of the Rust source code, and ohos_executable implements compilation of the C++ code.
import("//build/ohos.gni")
import("//build/templates/rust/rust_cxx.gni")
rust_cxx("test_cxx_exe_gen") {
sources = [ "src/lib.rs" ]
}
ohos_rust_static_ffi("test_cxx_examp_rust") {
sources = [ "src/lib.rs" ]
deps = [ "//build/rust:cxx_rustdeps" ]
}
ohos_executable("test_cxx_exe") {
sources = [ "main.cpp" ]
sources += get_target_outputs(":test_cxx_exe_gen")
include_dirs = [ "${target_gen_dir}" ]
deps = [
":test_cxx_examp_rust",
":test_cxx_exe_gen",
"//build/rust:cxx_cppdeps",
]
}
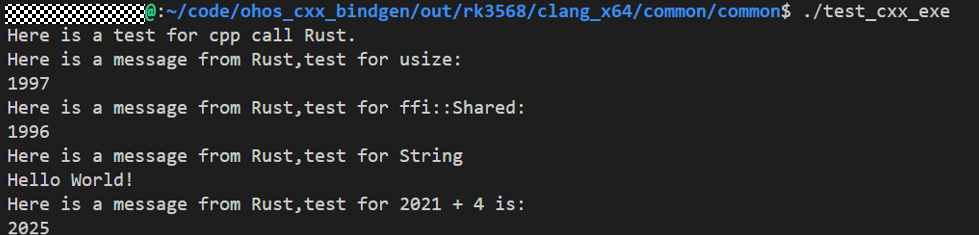
Verification
Calling C++ by Rust
- Create the header file client_blobstore.h.
#ifndef BUILD_RUST_TESTS_CLIENT_BLOBSTORE_H
#define BUILD_RUST_TESTS_CLIENT_BLOBSTORE_H
#include <memory>
#include "third_party/rust/cxx/include/cxx.h"
namespace nsp_org {
namespace nsp_blobstore {
struct MultiBufs;
struct Metadata_Blob;
class client_blobstore {
public:
client_blobstore();
uint64_t put_buf(MultiBufs &buf) const;
void add_tag(uint64_t blobid, rust::Str add_tag) const;
Metadata_Blob get_metadata(uint64_t blobid) const;
private:
class impl;
std::shared_ptr<impl> impl;
};
std::unique_ptr<client_blobstore> blobstore_client_new();
} // namespace nsp_blobstore
} // namespace nsp_org
#endif
- Create the client_blobstore.cpp file.
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <set>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include "src/main.rs.h"
#include "build/rust/tests/test_cxx_rust/include/client_blobstore.h"
namespace nsp_org {
namespace nsp_blobstore {
// Toy implementation of an in-memory nsp_blobstore.
//
// The real implementation of client_blobstore could be a large complex C++
// library.
class client_blobstore::impl {
friend client_blobstore;
using Blob = struct {
std::string data;
std::set<std::string> tags;
};
std::unordered_map<uint64_t, Blob> blobs;
};
client_blobstore::client_blobstore() : impl(new class client_blobstore::impl) {}
// Upload a new blob and return a blobid that serves as a handle to the blob.
uint64_t client_blobstore::put_buf(MultiBufs &buf) const
{
std::string contents;
// Traverse the caller's res_chunk iterator.
//
// In reality there might be sophisticated batching of chunks and/or parallel
// upload implemented by the nsp_blobstore's C++ client.
while (true) {
auto res_chunk = next_chunk(buf);
if (res_chunk.size() == 0) {
break;
}
contents.append(reinterpret_cast<const char *>(res_chunk.data()), res_chunk.size());
}
// Insert into map and provide caller the handle.
auto res = std::hash<std::string> {} (contents);
impl->blobs[res] = {std::move(contents), {}};
return res;
}
// Add add_tag to an existing blob.
void client_blobstore::add_tag(uint64_t blobid, rust::Str add_tag) const
{
impl->blobs[blobid].tags.emplace(add_tag);
}
// Retrieve get_metadata about a blob.
Metadata_Blob client_blobstore::get_metadata(uint64_t blobid) const
{
Metadata_Blob get_metadata {};
auto blob = impl->blobs.find(blobid);
if (blob != impl->blobs.end()) {
get_metadata.size = blob->second.data.size();
std::for_each(blob->second.tags.cbegin(), blob->second.tags.cend(),
[&](auto &t) { get_metadata.tags.emplace_back(t); });
}
return get_metadata;
}
std::unique_ptr<client_blobstore> blobstore_client_new()
{
return std::make_unique<client_blobstore>();
}
} // namespace nsp_blobstore
} // namespace nsp_org
- In ffi of the main.rs file, use the macro includes! to import the header file client_blobstore.h. Then, the main() function of Rust can call the C++ interfaces in ffi mode.
//! test_cxx_rust
#[cxx::bridge(namespace = "nsp_org::nsp_blobstore")]
mod ffi {
// Shared structs with fields visible to both languages.
struct Metadata_Blob {
size: usize,
tags: Vec<String>,
}
// Rust types and signatures exposed to C++.
extern "Rust" {
type MultiBufs;
fn next_chunk(buf: &mut MultiBufs) -> &[u8];
}
// C++ types and signatures exposed to Rust.
unsafe extern "C++" {
include!("build/rust/tests/test_cxx_rust/include/client_blobstore.h");
type client_blobstore;
fn blobstore_client_new() -> UniquePtr<client_blobstore>;
fn put_buf(&self, parts: &mut MultiBufs) -> u64;
fn add_tag(&self, blobid: u64, add_tag: &str);
fn get_metadata(&self, blobid: u64) -> Metadata_Blob;
}
}
// An iterator over contiguous chunks of a discontiguous file object.
//
// Toy implementation uses a Vec<Vec<u8>> but in reality this might be iterating
// over some more complex Rust data structure like a rope, or maybe loading
// chunks lazily from somewhere.
/// pub struct MultiBufs
pub struct MultiBufs {
chunks: Vec<Vec<u8>>,
pos: usize,
}
/// pub fn next_chunk
pub fn next_chunk(buf: &mut MultiBufs) -> &[u8] {
let next = buf.chunks.get(buf.pos);
buf.pos += 1;
next.map_or(&[], Vec::as_slice)
}
/// fn main()
fn main() {
let client = ffi::blobstore_client_new();
// Upload a blob.
let chunks = vec![b"fearless".to_vec(), b"concurrency".to_vec()];
let mut buf = MultiBufs { chunks, pos: 0 };
let blobid = client.put_buf(&mut buf);
println!("This is a test for Rust call cpp:");
println!("blobid = {}", blobid);
// Add a add_tag.
client.add_tag(blobid, "rust");
// Read back the tags.
let get_metadata = client.get_metadata(blobid);
println!("tags = {:?}", get_metadata.tags);
}
- Create the BUILD.gn file. Use CXX to convert main.rs into lib.rs.h and lib.rs.cc, which are used as the source code of test_cxx_rust_staticlib. Compile Rust main.rs, and add the dependency test_cxx_rust_staticlib.
import("//build/ohos.gni")
rust_cxx("test_cxx_rust_gen") {
sources = [ "src/main.rs" ]
}
ohos_static_library("test_cxx_rust_staticlib") {
sources = [ "src/client_blobstore.cpp" ]
sources += get_target_outputs(":test_cxx_rust_gen")
include_dirs = [
"${target_gen_dir}",
"//third_party/rust/cxx/v1/crate/include",
"include",
]
deps = [
":test_cxx_rust_gen",
"//build/rust:cxx_cppdeps",
]
}
ohos_rust_executable("test_cxx_rust") {
sources = [ "src/main.rs" ]
deps = [
":test_cxx_rust_staticlib",
"//build/rust:cxx_rustdeps",
]
}
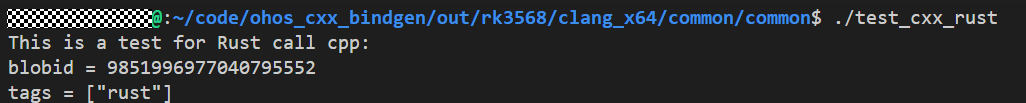
Verification
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙AI Framework Development Guide
harmony 鸿蒙Neural Network Runtime Device Access
harmony 鸿蒙Application Privilege Configuration
harmony 鸿蒙Setting Up a Development Environment
harmony 鸿蒙Development Guidelines
harmony 鸿蒙Application Framework Overview
harmony 鸿蒙ArkCompiler Development
harmony 鸿蒙Window Title Bar Customization Development (ArkTS)
0
赞
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: