harmony 鸿蒙Dual-Channel Preview (ArkTS)
Dual-Channel Preview (ArkTS)
Before developing a camera application, request permissions by following the instructions provided in Requesting Camera Development Permissions.
Dual-channel preview means that an application can use two preview streams at the same time. One preview stream is used for display on the screen, and the other is used for other operations such as image processing, so as to improve the processing efficiency.
The camera application controls the camera device to implement basic operations such as image display (preview), photo saving (photo capture), and video recording. The camera model is developed on the surface model, meaning that an application transfers data through the surface. Specifically, it obtains the photo stream data through the surface of an ImageReceiver object and the preview stream data through the surface of an XComponent.
To implement dual-channel preview (there are two preview streams instead of one preview stream plus one photo stream), you must create a previewOutput object through the surface of an ImageReceiver object. Other processes are the same as those of the photo stream and preview stream.
Read Camera for the API reference.
Constraints
- Currently, streams cannot be dynamically added. In other words, you cannot call addOutput to add streams without calling session.stop first.
- After an ImageReceiver object processes image data obtained, it must release the image buffer so that the buffer queue of the surface properly rotates.
API Calling Process
The figure below shows the recommended API calling process of the dual-channel preview solution.
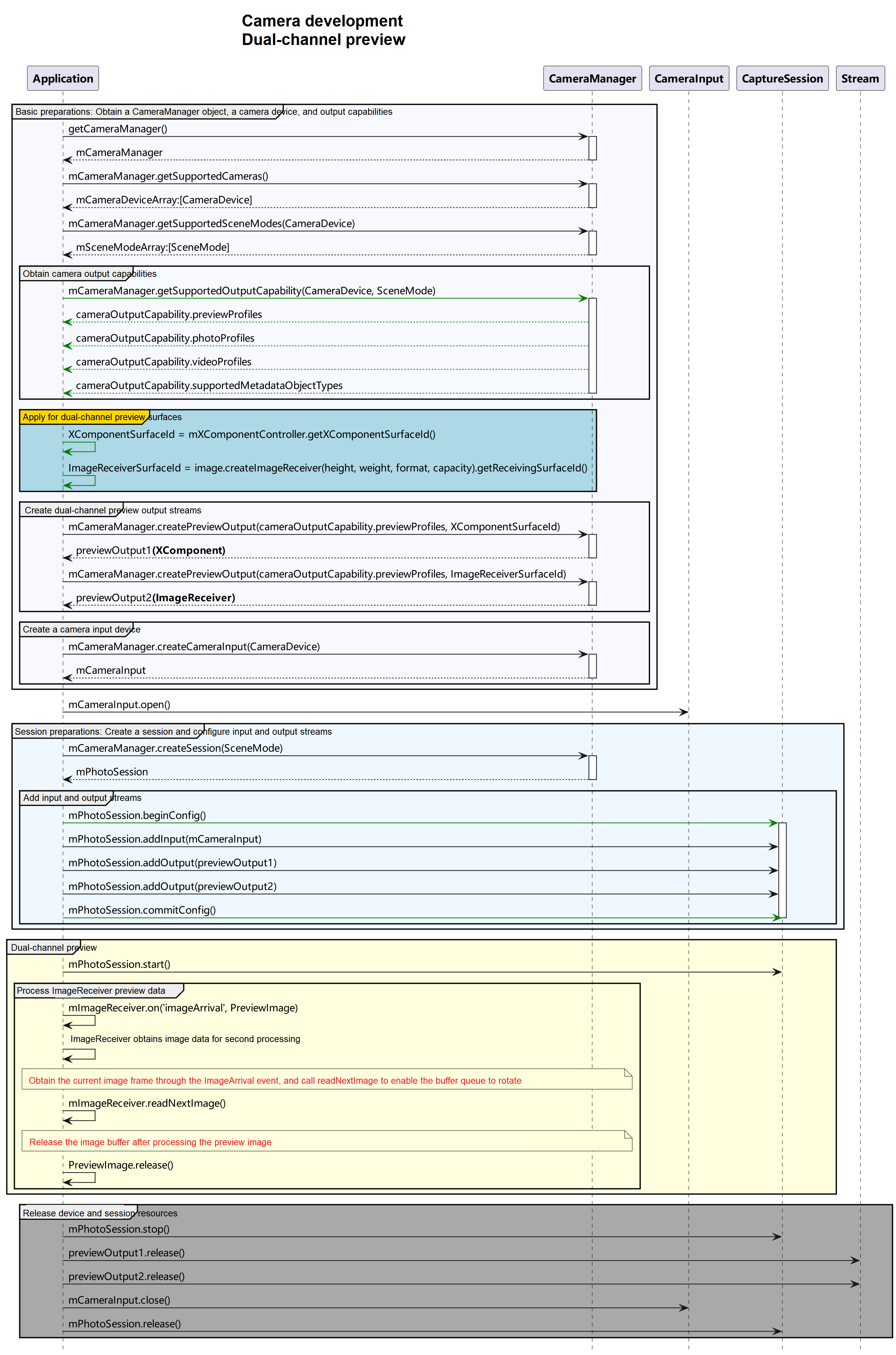
How to Develop
- For the first preview stream used for image processing, create an ImageReceiver object, obtain the surface ID to create the first preview stream, register an image listener, and process each frame of image data in the preview stream as required.
- For the second preview stream used for image display, create an XComponent, obtain the surface ID to create the second preview stream, and render the preview stream data in the component.
- To enable both preview streams to obtain data, configure a camera session for both preview streams, and start the session.
First Preview Stream Used for Image Processing
Import dependencies, including dependencies related to image and camera framework.
import { image } from '@kit.ImageKit'; import { camera } from '@kit.CameraKit'; import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';Obtain the surface ID for the first preview stream. Specifically, create an ImageReceiver object, and obtain the surface ID through the object.
let imageWidth: number = 1920; // Use the width in the profile size supported by the device. let imageHeight: number = 1080; // Use the height in the profile size supported by the device. async function initImageReceiver():Promise<void>{ // Create an ImageReceiver object. let size: image.Size = { width: imageWidth, height: imageHeight }; let imageReceiver = image.createImageReceiver(size, image.ImageFormat.JPEG, 8); // Obtain the surface ID for the first preview stream. let imageReceiverSurfaceId = await imageReceiver.getReceivingSurfaceId(); console.info(`initImageReceiver imageReceiverSurfaceId:${imageReceiverSurfaceId}`); }Register a listener to process each frame of image data in the preview stream. Specifically, use the imageArrival event in the ImageReceiver object to obtain the image data returned by the bottom layer. For details, see Image API Reference.
function onImageArrival(receiver: image.ImageReceiver): void { // Subscribe to the imageArrival event. receiver.on('imageArrival', () => { // Obtain an image. receiver.readNextImage((err: BusinessError, nextImage: image.Image) => { if (err||nextImage === undefined) { console.error('readNextImage failed'); return; } // Parse the image. nextImage.getComponent(image.ComponentType.JPEG, async (err: BusinessError, imgComponent: image.Component) => { if (err||imgComponent === undefined) { console.error('getComponent failed'); } if (imgComponent.byteBuffer) { // For details, see the description of parsing the image buffer data below. This example uses method 1. let width = nextImage.size.width; // Obtain the image width. let height = nextImage.size.height; // Obtain the image height. let stride = imgComponent.rowStride; // Obtain the image stride. console.debug(`getComponent with width:${width} height:${height} stride:${stride}`); // The value of stride is the same as that of width. if (stride == width) { let pixelMap = await image.createPixelMap(imgComponent.byteBuffer, { size: { height: height, width: width }, srcPixelFormat: 8, }) } else { // The value of stride is different from that of width. const dstBufferSize = width * height * 1.5 const dstArr = new Uint8Array(dstBufferSize) for (let j = 0; j < height * 1.5; j++) { const srcBuf = new Uint8Array(imgComponent.byteBuffer, j * stride, width) dstArr.set(srcBuf, j * width) } let pixelMap = await image.createPixelMap(dstArr.buffer, { size: { height: height, width: width }, srcPixelFormat: 8, }) } } else { console.error('byteBuffer is null'); } // Release the resource when the buffer is not in use. // If an asynchronous operation is performed on the buffer, call nextImage.release() to release the resource after the asynchronous operation is complete. nextImage.release(); }) }) }) }The following methods are available for parsing the image buffer data by using image.Component.
NOTE Check whether the width of the image is the same as rowStride. If they are different, perform the following operations:
Method 1: Remove the stride data from imgComponent.byteBuffer, obtain a new buffer by means of copy, and process the buffer by calling the API that does not support stride.
// For example, for NV21 (images in YUV_420_SP format), the formula for calculating the YUV_420_SP memory is as follows: YUV_420_SP memory = Width * Height + (Width * Height)/2. const dstBufferSize = width * height * 1.5; const dstArr = new Uint8Array(dstBufferSize); // Read the buffer data line by line. for (let j = 0; j < height * 1.5; j++) { // Copy the first width bytes of each line of data in imgComponent.byteBuffer to dstArr. const srcBuf = new Uint8Array(imgComponent.byteBuffer, j * stride, width); dstArr.set(srcBuf, j * width); } let pixelMap = await image.createPixelMap(dstArr.buffer, { size: { height: height, width: width }, srcPixelFormat: 8 });Method 2: Create a PixelMap based on the value of stride * height, and call cropSync of the PixelMap to crop redundant pixels.
// Create a PixelMap, with width set to the value of stride. let pixelMap = await image.createPixelMap(imgComponent.byteBuffer, { size:{height: height, width: stride}, srcPixelFormat: 8}); // Crop extra pixels. pixelMap.cropSync({size:{width:width, height:height}, x:0, y:0});Method 3: Pass imgComponent.byteBuffer and stride to the API that supports stride.
Second Preview Stream Used for Image Display
To obtain the surface ID of the second preview stream, you must first create an XComponent for displaying the preview stream. For details about how to obtain the surface ID, see getXcomponentSurfaceId. The XComponent capability is provided by the UI. For details, see XComponent.
@Component
struct example {
xComponentCtl: XComponentController = new XComponentController();
surfaceId:string = '';
imageWidth: number = 1920;
imageHeight: number = 1080;
private uiContext: UIContext = this.getUIContext();
build() {
XComponent({
id: 'componentId',
type: XComponentType.SURFACE,
controller: this.xComponentCtl
})
.onLoad(async () => {
console.info('onLoad is called');
this.surfaceId = this.xComponentCtl.getXComponentSurfaceId(); // Obtain the surface ID of the component.
// Use the surface ID to create a preview stream and start the camera. The component renders the preview stream data of each frame in real time.
})
// The width and height of the surface are opposite to those of the XComponent. Alternatively, you can use .renderFit(RenderFit.RESIZE_CONTAIN) to automatically adjust the display without manually setting the width and height.
.width(this.uiContext.px2vp(this.imageHeight))
.height(this.uiContext.px2vp(this.imageWidth))
}
}
Enabling a Preview Stream to Obtain Data
Create two preview outputs with two surface IDs, add the outputs to a camera session, and start the camera session to obtain the preview stream data.
function createDualPreviewOutput(cameraManager: camera.CameraManager, previewProfile: camera.Profile,
session: camera.Session, imageReceiverSurfaceId: string, xComponentSurfaceId: string): void {
// Create the first preview output by using imageReceiverSurfaceId.
let previewOutput1 = cameraManager.createPreviewOutput(previewProfile, imageReceiverSurfaceId);
if (!previewOutput1) {
console.error('createPreviewOutput1 error');
}
// Create the second preview output by using xComponentSurfaceId.
let previewOutput2 = cameraManager.createPreviewOutput(previewProfile, xComponentSurfaceId);
if (!previewOutput2) {
console.error('createPreviewOutput2 error');
}
// Add the output of the first preview stream.
session.addOutput(previewOutput1);
// Add the output of the second preview stream.
session.addOutput(previewOutput2);
}
Sample
import { camera } from '@kit.CameraKit';
import { image } from '@kit.ImageKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
import { abilityAccessCtrl, Permissions } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
private imageReceiver: image.ImageReceiver|undefined = undefined;
private imageReceiverSurfaceId: string = '';
private xComponentCtl: XComponentController = new XComponentController();
private xComponentSurfaceId: string = '';
@State imageWidth: number = 1920;
@State imageHeight: number = 1080;
private cameraManager: camera.CameraManager|undefined = undefined;
private cameras: Array<camera.CameraDevice>|Array<camera.CameraDevice> = [];
private cameraInput: camera.CameraInput|undefined = undefined;
private previewOutput1: camera.PreviewOutput|undefined = undefined;
private previewOutput2: camera.PreviewOutput|undefined = undefined;
private session: camera.VideoSession|undefined = undefined;
private uiContext: UIContext = this.getUIContext();
private context: Context|undefined = this.uiContext.getHostContext();
private cameraPermission: Permissions = 'ohos.permission.CAMERA'; // For details about how to request permissions, see the instructions provided at the beginning of this topic.
@State isShow: boolean = false;
async requestPermissionsFn(): Promise<void> {
let atManager = abilityAccessCtrl.createAtManager();
if (this.context) {
let res = await atManager.requestPermissionsFromUser(this.context, [this.cameraPermission]);
for (let i =0; i < res.permissions.length; i++) {
if (this.cameraPermission.toString() === res.permissions[i] && res.authResults[i] === 0) {
this.isShow = true;
}
}
}
}
aboutToAppear(): void {
this.requestPermissionsFn();
}
onPageShow(): void {
console.info('onPageShow');
this.initImageReceiver();
if (this.xComponentSurfaceId !== '') {
this.initCamera();
}
}
onPageHide(): void {
console.info('onPageHide');
this.releaseCamera();
}
/**
* Obtain the surface ID of the ImageReceiver object.
* @param receiver
* @returns
*/
async initImageReceiver(): Promise<void> {
if (!this.imageReceiver) {
// Create an ImageReceiver object.
let size: image.Size = { width: this.imageWidth, height: this.imageHeight };
this.imageReceiver = image.createImageReceiver(size, image.ImageFormat.JPEG, 8);
// Obtain the surface ID for the first preview stream.
this.imageReceiverSurfaceId = await this.imageReceiver.getReceivingSurfaceId();
console.info(`initImageReceiver imageReceiverSurfaceId:${this.imageReceiverSurfaceId}`);
// Register a listener to listen for and process the image data of each frame in the preview stream.
this.onImageArrival(this.imageReceiver);
}
}
/**
* Register a listener for the ImageReceiver object.
* @param receiver
*/
onImageArrival(receiver: image.ImageReceiver): void {
// Subscribe to the imageArrival event.
receiver.on('imageArrival', () => {
console.info('image arrival');
// Obtain an image.
receiver.readNextImage((err: BusinessError, nextImage: image.Image) => {
if (err||nextImage === undefined) {
console.error('readNextImage failed');
return;
}
// Parse the image.
nextImage.getComponent(image.ComponentType.JPEG, async (err: BusinessError, imgComponent: image.Component) => {
if (err||imgComponent === undefined) {
console.error('getComponent failed');
}
if (imgComponent.byteBuffer) {
// Parse the buffer data by referring to step 7. This example uses method 1 as an example.
let width = nextImage.size.width; // Obtain the image width.
let height = nextImage.size.height; // Obtain the image height.
let stride = imgComponent.rowStride; // Obtain the image stride.
console.debug(`getComponent with width:${width} height:${height} stride:${stride}`);
// The value of stride is the same as that of width.
if (stride == width) {
let pixelMap = await image.createPixelMap(imgComponent.byteBuffer, {
size: { height: height, width: width },
srcPixelFormat: 8,
})
} else {
// The value of stride is different from that of width.
const dstBufferSize = width * height * 1.5 // For example, for NV21 (images in YUV_420_SP format), the formula for calculating the YUV_420_SP memory is as follows: YUV_420_SP memory = Width * Height + (Width * Height)/2
const dstArr = new Uint8Array(dstBufferSize)
for (let j = 0; j < height * 1.5; j++) {
const srcBuf = new Uint8Array(imgComponent.byteBuffer, j * stride, width)
dstArr.set(srcBuf, j * width)
}
let pixelMap = await image.createPixelMap(dstArr.buffer, {
size: { height: height, width: width },
srcPixelFormat: 8,
})
}
} else {
console.error('byteBuffer is null');
}
// Release the resource when the buffer is not in use.
// If an asynchronous operation is performed on the buffer, call nextImage.release() to release the resource after the asynchronous operation is complete.
nextImage.release();
console.info('image process done');
})
})
})
}
build() {
Column() {
if (this.isShow) {
XComponent({
id: 'componentId',
type: XComponentType.SURFACE,
controller: this.xComponentCtl
})
.onLoad(async () => {
console.info('onLoad is called');
this.xComponentSurfaceId = this.xComponentCtl.getXComponentSurfaceId(); // Obtain the surface ID of the component.
// Initialize the camera. The component renders the preview stream data of each frame in real time.
this.initCamera()
})
.width(this.uiContext.px2vp(this.imageHeight))
.height(this.uiContext.px2vp(this.imageWidth))
}
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
}
// Initialize a camera.
async initCamera(): Promise<void> {
console.info(`initCamera imageReceiverSurfaceId:${this.imageReceiverSurfaceId} xComponentSurfaceId:${this.xComponentSurfaceId}`);
try {
// Obtain a camera manager instance.
this.cameraManager = camera.getCameraManager(this.context);
if (!this.cameraManager) {
console.error('initCamera getCameraManager');
}
// Obtain the list of cameras supported by the device.
this.cameras = this.cameraManager.getSupportedCameras();
if (!this.cameras) {
console.error('initCamera getSupportedCameras');
}
// Select a camera device and create a CameraInput object.
this.cameraInput = this.cameraManager.createCameraInput(this.cameras[0]);
if (!this.cameraInput) {
console.error('initCamera createCameraInput');
}
// Open the camera.
await this.cameraInput.open().catch((err: BusinessError) => {
console.error(`initCamera open fail: ${err}`);
})
// Obtain the profile supported by the camera device.
let capability: camera.CameraOutputCapability =
this.cameraManager.getSupportedOutputCapability(this.cameras[0], camera.SceneMode.NORMAL_VIDEO);
if (!capability) {
console.error('initCamera getSupportedOutputCapability');
}
// Select a supported preview stream profile based on service requirements.
let previewProfile: camera.Profile = capability.previewProfiles[0];
this.imageWidth = previewProfile.size.width; // Update the width of the XComponent.
this.imageHeight = previewProfile.size.height; // Update the height of the XComponent.
console.info(`initCamera imageWidth:${this.imageWidth} imageHeight:${this.imageHeight}`);
// Create the first preview output by using imageReceiverSurfaceId.
this.previewOutput1 = this.cameraManager.createPreviewOutput(previewProfile, this.imageReceiverSurfaceId);
if (!this.previewOutput1) {
console.error('initCamera createPreviewOutput1');
}
// Create the second preview output by using xComponentSurfaceId.
this.previewOutput2 = this.cameraManager.createPreviewOutput(previewProfile, this.xComponentSurfaceId);
if (!this.previewOutput2) {
console.error('initCamera createPreviewOutput2');
}
// Create a camera session in recording mode.
this.session = this.cameraManager.createSession(camera.SceneMode.NORMAL_VIDEO) as camera.VideoSession;
if (!this.session) {
console.error('initCamera createSession');
}
// Start configuration for the session.
this.session.beginConfig();
// Add a camera input.
this.session.addInput(this.cameraInput);
// Add the output of the first preview stream.
this.session.addOutput(this.previewOutput1);
// Add the output of the second preview stream.
this.session.addOutput(this.previewOutput2);
// Commit the session configuration.
await this.session.commitConfig();
// Start the configured input and output streams.
await this.session.start();
} catch (error) {
console.error(`initCamera fail: ${error}`);
}
}
// Release the camera.
async releaseCamera(): Promise<void> {
console.info('releaseCamera E');
try {
// Stop the session.
await this.session?.stop();
// Release the camera input stream.
await this.cameraInput?.close();
// Release the preview output stream.
await this.previewOutput1?.release();
// Release the photo output stream.
await this.previewOutput2?.release();
// Release the session.
await this.session?.release();
} catch (error) {
console.error(`initCamera fail: ${error}`);
}
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Basic Camera Animation (ArkTS)
harmony 鸿蒙Practices for Camera Recovery from the Background (ArkTS)
harmony 鸿蒙Deferred Photo Delivery Practices (ArkTS)
harmony 鸿蒙Deferred Photo Delivery (ArkTS)
harmony 鸿蒙Practices for High-Performance Photo Capture (for System Applications Only) (ArkTS)
harmony 鸿蒙High-Performance Photo Capture (for System Applications Only) (ArkTS)
harmony 鸿蒙Depth Data (for System Applications Only) (ArkTS)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: