harmony 鸿蒙Docking to the Soft Keyboard
Docking to the Soft Keyboard
By docking the Web component to the soft keyboard, you can manage the display and interaction of the soft keyboard in your application, and can also customize its features to suit your specific needs. The main scenarios are as follows:
- Bringing up the system soft keyboard to enter text: When a user taps a text box on a web page, the default soft keyboard (input method) is displayed at the bottom of the screen. The user can enter text using the soft keyboard, and the entered content is displayed in the text box.
- Customizing the Enter key type of the system soft keyboard: The application specifies the web page text box to pull up different types of Enter keys on the soft keyboard. For example, Confirm, Next, and Submit.
- Specifying the soft keyboard avoidance mode: On a mobile device, the input method is usually fixed at the lower part of the screen. The application can set different soft keyboard avoidance modes for web pages. For example, relocating, resizing, or no avoidance.
- Defining a custom soft keyboard: On a mobile device, applications can use a self-drawing soft keyboard to replace the system soft keyboard.
W3C Standard Attributes for the Interaction Between the Web Page Text Box and the Soft Keyboard
To support the interaction between the web page and the system soft keyboard and custom soft keyboard, ArkWeb complies with and implements the following input component attributes in the W3C specifications: - type
The type attribute defines the type of the input element, which affects the input validation, display mode, and keyboard type. The common type values are as follows.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| text | Default value. Common text. |
| number | Number. |
| Email address. | |
| password | Password. |
| tel | Telephone number. |
| url | URL. |
| date | Date picker. |
| time | Time picker. |
| checkbox | Check box. |
| radio | Radio button. |
| file | File upload. |
| submit | Submit button. |
| reset | Reset button. |
| button | Common button. |
- inputmode
The inputmode attribute is used to configure the input method type. It accepts the values listed below.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| decimal | Numeric keyboard, usually with a comma key. |
| Text keyboard with keys usually used for email addresses, such as @. | |
| none | No keyboard. |
| numeric | Numeric keypad. |
| search | Text keyboard. The Enter key is displayed as Go. |
| tel | Numeric keyboard with +, *****, and # keys. |
| text | Default value. Text keyboard. |
| url | Text keyboard with keys used for websites such as the ., /, and .com keys, or other domain name terminators used locally. |
- enterkeyhint
The enterkeyhint attribute specifies the display mode of the Enter key on the virtual keyboard of the mobile device. It accepts the values listed below.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| enter | Displays the default Enter key. |
| done | Indicates that the input is complete. |
| go | Indicates to jump or execute. |
| next | Goes to the next input field. |
| previous | Goes to the previous input field. |
| search | Searches for information. |
| send | Sends a message. |
NOTE
When a user taps a web page input box, the default soft keyboard (input method) is displayed at the bottom of the screen, and the user can enter text on the screen.
The type attribute affects not only the keyboard display, but also the input validation and element appearance.
The inputmode is mainly used to optimize the keyboard input experience on mobile devices and does not change the basic input behavior or verification.
Setting the Avoidance Mode for the Soft Keyboard
On a mobile device, you can set the avoidance mode for the soft keyboard on the web page.
Call setKeyboardAvoidMode() of UIContext in your application code to set the avoidance mode, which can be Resize or Offset for the Web component.
In the Resize mode, the height of the application window can be reduced to avoid the soft keyboard, and the Web component is re-arranged with ArkUI.
In the Offset mode (the default mode), the height of the application window remains unchanged, and the Web component performs avoidance based on its own avoidance mode.
(1) Set the soft keyboard avoidance mode of UIContext in the application code.
// EntryAbility.ets
import { KeyboardAvoidMode } from '@kit.ArkUI';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) {
hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'Ability onWindowStageCreate');
windowStage.loadContent('pages/Index', (err, data) => {
let keyboardAvoidMode = windowStage.getMainWindowSync().getUIContext().getKeyboardAvoidMode();
// When the soft keyboard is displayed, the application window is resized to its original height minus the keyboard height.
windowStage.getMainWindowSync().getUIContext().setKeyboardAvoidMode(KeyboardAvoidMode.RESIZE);
if (err.code) {
hilog.error(0x0000, 'testTag', 'Failed to load the content. Cause: %{public}s', JSON.stringify(err) ?? '');
return;
}
hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'Succeeded in loading the content. Data: %{public}s', JSON.stringify(data) ?? '');
});
}
(2) Enable the soft keyboard in the Web component.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test Web Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>DEMO</h1>
<input type="text" id="input_a">
</body>
</html>
//Index.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct KeyboardAvoidExample {
controller: web_webview.WebviewController = new web_webview.WebviewController();
build() {
Column() {
Row().height("50%").width("100%").backgroundColor(Color.Gray)
Web({ src: $rawfile("index.html"),controller: this.controller})
Text("I can see the bottom of the page").width("100%").textAlign(TextAlign.Center).backgroundColor(Color.Pink).layoutWeight(1)
}.width('100%').height("100%")
}
}
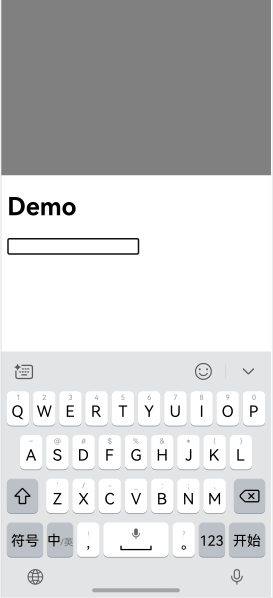
In this case, the Web component is re-arranged with ArkUI, as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
Figure 1 Soft keyboard in the default avoidance mode
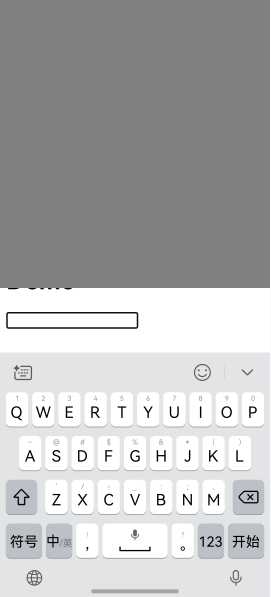
Figure 2 Soft keyboard following the avoidance mode of the ArkUI soft keyboard
When the keyboard avoidance mode of UIContext is Offset, the application can set the keyboard avoidance mode of the Web component through the WebKeyboardAvoidMode() API of the Web component. This API is at a higher priority than virtualKeyboard.overlayContens on the W3C side and accepts the following values:
RESIZE_VISUAL: Only the size of the visual viewport is adjusted, and the size of the layout viewport is not adjusted.
RESIZE_CONTENT: The size of both the visual viewport and the layout viewport is adjusted.
OVERLAYS_CONTENT: No viewport size is adjusted, and the soft keyboard overlays the content of the web page.
NOTE
The visual viewport refers to the area of the web page that the user is viewing, and the width of this area is equal to the width of the browser window of the mobile device.
The layout viewport refers to the width of the web page itself.
(1) Set the soft keyboard avoidance mode of the Web component in the application code.
// Index.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct KeyboardAvoidExample {
controller: web_webview.WebviewController = new web_webview.WebviewController();
build() {
Column() {
Row().height("50%").width("100%").backgroundColor(Color.Gray)
Web({ src: $rawfile("index.html"),controller: this.controller})
.keyboardAvoidMode (WebKeyboardAvoidMode.OVERLAYS_CONTENT) // The Web component does not adjust the size of any viewport.
Text("I can see the bottom of the page").width("100%").textAlign(TextAlign.Center).backgroundColor(Color.Pink).layoutWeight(1)
}.width('100%').height("100%")
}
}
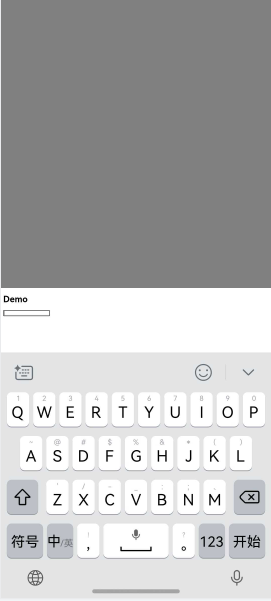
In this case, the Web component performs avoidance based on its own avoidance mode settings, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Soft keyboard avoidance mode of the Web component page
The following are overlapping scenarios with other Web component behaviors.
| Overlapping Scenario | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Same-layer rendering component | The soft keyboard avoidance behavior of the same-layer Web component is the same as that in common scenarios. The soft keyboard avoidance behavior of the same-layer native component is implemented by ArkUI. |
| Offscreen component creation | By default, the soft keyboard avoidance mode used in non-offscreen creation is used. You can set other avoidance modes before attaching the component to the tree. |
| customDialog | The customDialog component avoids the keyboard by itself. |
| Foldable device | The soft keyboard avoidance behavior is the same as that in common scenarios. The soft keyboard is opened and closed based on the screen status. |
| Soft keyboard docking | The soft keyboard avoidance behavior is the same as that in common scenarios. |
| Web nested scrolling | In the nested scrolling scenario, the soft keyboard avoidance mode of the Web component is not recommended, including RESIZE_VISUAL and RESIZE_CONTENT. |
Blocking System Soft Keyboard and Custom Soft Keyboard
The application can invoke onInterceptKeyboardAttach to block the system soft keyboard. On a web page, when an editable element such as the input tag is about to trigger the display of the soft keyboard, onInterceptKeyboardAttach is called. This allows you to manage the soft keyboard and use any of the following options:
- The system soft keyboard with default settings
- The system soft keyboard with a custom Enter key
- The custom soft keyboard of the application
// xxx.ets
import { webview } from '@kit.ArkWeb';
import { inputMethodEngine } from '@kit.IMEKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct WebComponent {
controller: webview.WebviewController = new webview.WebviewController();
webKeyboardController: WebKeyboardController = new WebKeyboardController()
inputAttributeMap: Map<string, number> = new Map([
['UNSPECIFIED', inputMethodEngine.ENTER_KEY_TYPE_UNSPECIFIED],
['GO', inputMethodEngine.ENTER_KEY_TYPE_GO],
['SEARCH', inputMethodEngine.ENTER_KEY_TYPE_SEARCH],
['SEND', inputMethodEngine.ENTER_KEY_TYPE_SEND],
['NEXT', inputMethodEngine.ENTER_KEY_TYPE_NEXT],
['DONE', inputMethodEngine.ENTER_KEY_TYPE_DONE],
['PREVIOUS', inputMethodEngine.ENTER_KEY_TYPE_PREVIOUS]
])
/**
* Builder for a custom keyboard component
*/
@Builder
customKeyboardBuilder() {
// Implement a custom keyboard component and connect it to WebKeyboardController to implement operations such as input, deletion, and close.
Row() {
Text("Finish")
.fontSize(20)
.fontColor(Color.Blue)
.onClick(() => {
this.webKeyboardController.close();
})
// Insert characters.
Button("insertText").onClick(() => {
this.webKeyboardController.insertText('insert ');
}).margin({
bottom: 200,
})
// Delete characters from the end to the beginning for the length specified by the length parameter.
Button("deleteForward").onClick(() => {
this.webKeyboardController.deleteForward(1);
}).margin({
bottom: 200,
})
// Delete characters from the beginning to the end for the length specified by the length parameter.
Button("deleteBackward").onClick(() => {
this.webKeyboardController.deleteBackward(1);
}).margin({
left: -220,
})
// Insert a function key.
Button("sendFunctionKey").onClick(() => {
this.webKeyboardController.sendFunctionKey(6);
})
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Web({ src: $rawfile('index.html'), controller: this.controller })
.onInterceptKeyboardAttach((KeyboardCallbackInfo) => {
// Initialize option. By default, the default keyboard is used.
let option: WebKeyboardOptions = {
useSystemKeyboard: true,
};
if (!KeyboardCallbackInfo) {
return option;
}
// Save the WebKeyboardController. When a custom keyboard is used, this handler is required to control behaviors such as input, deletion, and closing of the keyboard.
this.webKeyboardController = KeyboardCallbackInfo.controller
let attributes: Record<string, string> = KeyboardCallbackInfo.attributes
// Traverse attributes.
let attributeKeys = Object.keys(attributes)
for (let i = 0; i < attributeKeys.length; i++) {
console.log('WebCustomKeyboard key = ' + attributeKeys[i] + ', value = ' + attributes[attributeKeys[i]])
}
if (attributes) {
if (attributes['data-keyboard'] == 'customKeyboard') {
// Determine the soft keyboard to use based on the attributes of editable HTML elements. For example, if the attribute includes data-keyboard and its value is customKeyboard, use a custom keyboard.
console.log('WebCustomKeyboard use custom keyboard')
option.useSystemKeyboard = false;
// Set the custom keyboard builder.
option.customKeyboard = () => {
this.customKeyboardBuilder()
}
return option;
}
if (attributes['keyboard-return'] != undefined) {
// Determine the soft keyboard to use based on the attributes of editable HTML elements. For example, if the attribute includes keyboard-return, use the system keyboard and specify the type of the system soft keyboard's Enter key.
option.useSystemKeyboard = true;
let enterKeyType: number|undefined = this.inputAttributeMap.get(attributes['keyboard-return'])
if (enterKeyType != undefined) {
option.enterKeyType = enterKeyType
}
return option;
}
}
return option;
})
}
}
}
<!-- index.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,minimum-scale=1.0,maximum-scale=1.0">
</head>
<body>
<p style="font-size:12px">input tag. Original default behavior: </p>
<input type="text" style="width: 300px; height: 20px"><br>
<hr style="height:2px;border-width:0;color:gray;background-color:gray">
<p style="font-size:12px">input tag. System keyboard with enterKeyType as UNSPECIFIED: </p>
<input type="text" keyboard-return="UNSPECIFIED" style="width: 300px; height: 20px"><br>
<hr style="height:2px;border-width:0;color:gray;background-color:gray">
<p style="font-size:12px">input tag. System keyboard with enterKeyType as GO: </p>
<input type="text" keyboard-return="GO" style="width: 300px; height: 20px"><br>
<hr style="height:2px;border-width:0;color:gray;background-color:gray">
<p style="font-size:12px">input tag. System keyboard with enterKeyType as SEARCH: </p>
<input type="text" keyboard-return="SEARCH" style="width: 300px; height: 20px"><br>
<hr style="height:2px;border-width:0;color:gray;background-color:gray">
<p style="font-size:12px">input tag. System keyboard with enterKeyType as SEND: </p>
<input type="text" keyboard-return="SEND" style="width: 300px; height: 20px"><br>
<hr style="height:2px;border-width:0;color:gray;background-color:gray">
<p style="font-size:12px">input tag. System keyboard with enterKeyType as NEXT: </p>
<input type="text" keyboard-return="NEXT" style="width: 300px; height: 20px"><br>
<hr style="height:2px;border-width:0;color:gray;background-color:gray">
<p style="font-size:12px">input tag. System keyboard with enterKeyType as DONE: </p>
<input type="text" keyboard-return="DONE" style="width: 300px; height: 20px"><br>
<hr style="height:2px;border-width:0;color:gray;background-color:gray">
<p style="font-size:12px">input tag. System keyboard with enterKeyType as PREVIOUS: </p>
<input type="text" keyboard-return="PREVIOUS" style="width: 300px; height: 20px"><br>
<hr style="height:2px;border-width:0;color:gray;background-color:gray">
<p style="font-size:12px">input tag. Custom keyboard: </p>
<input type="text" data-keyboard="customKeyboard" style="width: 300px; height: 20px"><br>
</body>
</html>
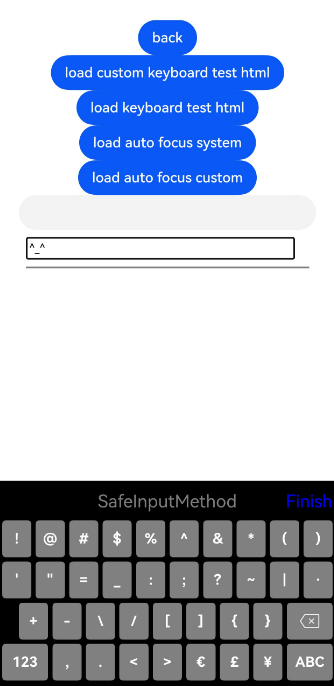
Figure 4, Figure 5, and Figure 6 show the ArkWeb custom keyboard examples.
Figure 4 Custom numeric keyboard
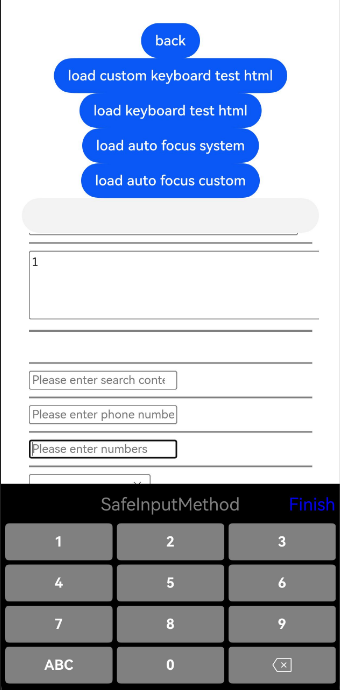
Figure 5 Custom alphabetic keyboard
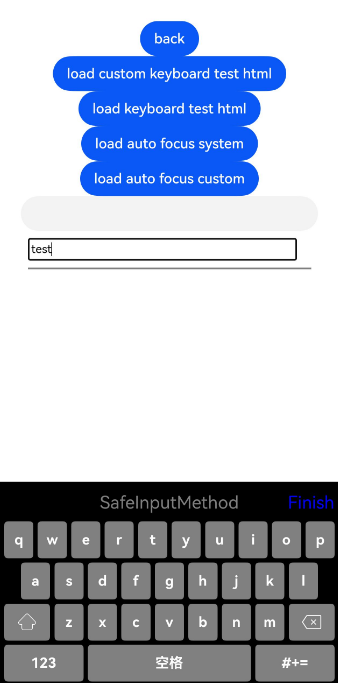
Figure 6 Custom symbol keyboard
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Taking Over the Media Playback on Web Pages
harmony 鸿蒙Mutual Invoking Between the Application and the Frontend Page (C/C++)
harmony 鸿蒙Establishing a Data Channel Between the Application and the Frontend Page (C/C++)
harmony 鸿蒙Enabling Ads Blocking
harmony 鸿蒙Establishing a Data Channel Between the Application and the Frontend Page
harmony 鸿蒙Migrating Web Components Between Different Windows
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to ArkWeb
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: