harmony 鸿蒙Regulator
Regulator
Overview
Regulator
The regulator module controls the voltage and current supplies of some devices in the system. In an embedded system (especially a mobile phone), it is important to control the power consumption, which directly affects the battery endurance. You can use a regulator to shut down the power supply to an idle module in the system or reduce the voltage and current for the module. The regulator APIs provide a set of methods for managing a regulator, including those for:
- Opening or closing a regulator device handle
- Setting the output voltage and current for a regulator
- Enabling or disabling a regulator
- Obtaining the voltage, current, and status of a regulator
Basic Concepts
- Calibrator
Software used to maintain stable output voltage when the output load is different from the input voltage.
- Consumer
The devices served by the regulator are called consumers. Consumers are classified into the following:
Static consumer: Only the power needs to be turned on or off for this type of consumers. The voltage and current do not need to be changed. Generally, the consumers are set in the bootloader, firmware, and kernel board phases.
Dynamic consumer: The voltage and current need to be changed based on operation requirements for this type of consumers.
Power Management IC (PMIC)
Power management chipset provides efficient, reliable, and safe voltage regulation.
Working Principles
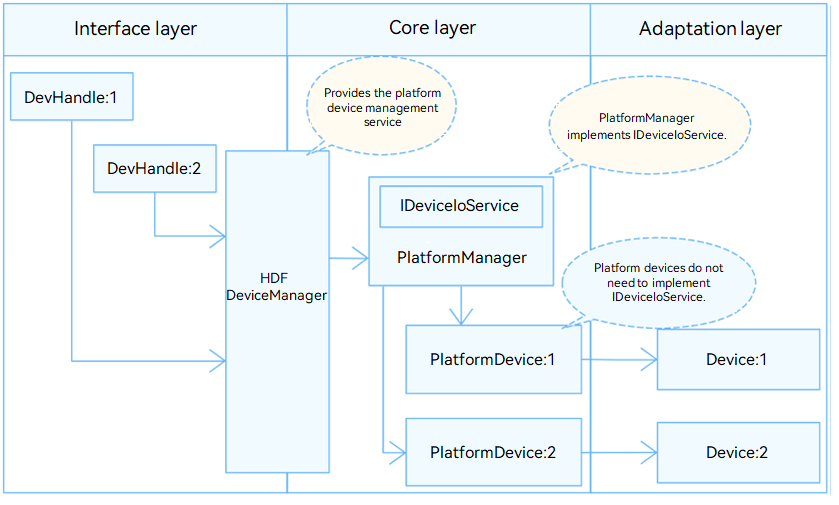
In the Hardware Driver Foundation (HDF), the regulator module uses the unified service mode for API adaptation. In this mode, a device service is used as the regulator manager to handle external access requests in a unified manner, which is reflected in the configuration file. The unified service mode applies to the scenario where there are many device objects of the same type, for example, when the regulator has more than 10 controllers. If the independent service mode is used, more device nodes need to be configured and more memory resources will be consumed by services.
The regulator module is divided into the following layers:
- The interface layer provides APIs for opening or closing a device and writing data.
- The core layer provides the capabilities of binding, initializing, and releasing devices.
- The adaptation layer implements other functions.
NOTE
The core layer can call the functions of the interface layer and uses the hook to call functions of the adaptation layer. In this way, the adaptation layer can indirectly call the functions of the interface layer, but the interface layer cannot call the functions of the adaptation layer.
Figure 1 Unified service mode
Constraints
Currently, the regulator module supports only the kernels (LiteOS) of mini and small systems.
Development Guidelines
When to Use
Regulators are used to:
- Control the voltage/current supplies of some devices in the system.
- Manage regulated power supplies.
Available APIs
Table 1 Regulator module APIs
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| RegulatorOpen | Opens the regulator device handle. |
| RegulatorClose | Closes the regulator device handle. |
| RegulatorEnable | Enables a regulator. |
| RegulatorDisable | Disables a regulator. |
| RegulatorForceDisable | Forcibly disables a regulator. |
| RegulatorSetVoltage | Sets the regulator output voltage. |
| RegulatorGetVoltage | Obtains the regulator output voltage. |
| RegulatorSetCurrent | Sets the regulator output current. |
| RegulatorGetCurrent | Obtains the regulator output current. |
| RegulatorGetStatus | Obtains the regulator status. |
How to Develop
During the OS startup process, the driver management module loads the regulator driver based on the configuration file. Then, the regulator driver detects the regulator devices and initializes the driver.
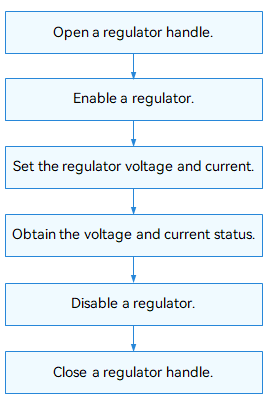
The figure below illustrates how to use the APIs.
Figure 2 Using regulator driver APIs
Opening a Regulator Device Handle
Before operating a regulator, call RegulatorOpen to open the device handle of the regulator. This function returns the device handle of the regulator.
DevHandle RegulatorOpen(const char *name);
Table 2 Description of RegulatorOpen
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| name | Name of the target regulator. |
| Return Value | Description |
| handle | The regulator device handle is returned if the operation is successful. |
| NULL | The operation failed. |
/* Regulator device name */
const char *name = "regulator_virtual_1";
DevHandle handle = NULL;
/* Open the regulator device handle. */
handle = RegulatorOpen(name);
if (handle == NULL) {
/* Error handling. */
}
Closing a Regulator Device Handle
Call RegulatorClose to close the regulator device handle to release resources.
void RegulatorClose(DevHandle handle);
Table 3 Description of RegulatorClose
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | Device handle of the target regulator. |
/* Close the regulator device handle. */
RegulatorClose(handle);
Enabling a Regulator
Call RegulatorEnable() to enable a regulator.
int32_t RegulatorEnable(DevHandle handle);
Table 4 Description of RegulatorEnable
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | Device handle of the target regulator. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
int32_t ret;
/* Enable the regulator. */
ret = RegulatorEnable(handle);
if (ret != 0) {
/* Error handling. */
}
Disabling a Regulator
Call RegulatorDisable() to disable a regulator. The operation will fail if the regulator status is set to always on or a child node of the regulator is not disabled.
int32_t RegulatorDisable(DevHandle handle);
Table 5 Description of RegulatorDisable
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | Device handle of the target regulator. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
int32_t ret;
/* Disable the regulator. */
ret = RegulatorDisable(handle);
if (ret != 0) {
/* Error handling. */
}
Forcibly Disabling a Regulator
Call RegulatorForceDisable() to forcibly disable a regulator. The regulator will be disabled even if its status is set to always on or its child node is still enabled.
int32_t RegulatorForceDisable(DevHandle handle);
Table 6 Description of RegulatorForceDisable
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | Device handle of the target regulator. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
int32_t ret;
/* Forcibly disable the regulator. /*
ret = RegulatorForceDisable(handle);
if (ret != 0) {
/* Error handling. */
}
Setting the Output Voltage Range
Call RegulatorSetVoltage to set the output voltage range for a regulator.
int32_t RegulatorSetVoltage(DevHandle handle, uint32_t minUv, uint32_t maxUv);
Table 7 Description of RegulatorSetVoltage
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | Device handle of the target regulator. |
| minUv | Minimum voltage to set. |
| maxUv | Maximum voltage to set. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
int32_t ret;
int32_t minUv = 0; // The minimum voltage is 0 µV.
int32_t maxUv = 20000; // The maximum voltage is 20000 µV.
/* Set the output voltage range of the regulator. */
ret = RegulatorSetVoltage(handle, minUv, maxUv);
if (ret != 0) {
/* Error handling. */
}
Obtaining the Regulator Voltage
Call RegulatorGetVoltage() to obtain the regulator voltage.
int32_t RegulatorGetVoltage(DevHandle handle, uint32_t *voltage);
Table 8 Description of RegulatorGetVoltage
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | Device handle of the target regulator. |
| *voltage | Pointer to the regulator voltage information. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
int32_t ret;
uint32_t voltage;
/* Obtain the regulator voltage. */
ret = RegulatorGetVoltage(handle, &voltage);
if (ret != 0) {
/* Error handling. */
}
Setting the Output Current Range
Call RegulatorSetCurrent() to set the output current range of the regulator.
int32_t RegulatorSetCurrent(DevHandle handle, uint32_t minUa, uint32_t maxUa);
Table 9 Description of RegulatorSetCurrent
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | Device handle of the target regulator. |
| minUa | Minimum current to set. |
| maxUa | Maximum current to set. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
int32_t ret;
int32_t minUa = 0; // The minimum current is 0 μA.
int32_t maxUa = 200; // The maximum current is 200 μA.
/* Set the output current range of the regulator. */
ret = RegulatorSetCurrent(handle, minUa, maxUa);
if (ret != 0) {
/* Error handling. */
}
Obtaining the Regulator Current
Call RegulatorGetCurrent() to obtain the current of the regulator.
int32_t RegulatorGetCurrent(DevHandle handle, uint32_t *regCurrent);
Table 10 Description of RegulatorGetCurrent
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | Device handle of the target regulator. |
| *regCurrent | Pointer to the regulator current information. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
int32_t ret;
uint32_t regCurrent;
/* Obtain the current of the regulator. */
ret = RegulatorGetCurrent(handle, ®Current);
if (ret != 0) {
/* Error handling. */
}
Obtaining the Regulator Status
Call RegulatorGetStatus() to obtain the regulator status.
int32_t RegulatorGetStatus(DevHandle handle, uint32_t *status);
Table 11 Description of RegulatorGetStatus
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| handle | Device handle of the target regulator. |
| *status | Pointer to the regulator status information. |
| Return Value | Description |
| 0 | The operation is successful. |
| Negative value | The operation failed. |
int32_t ret;
uint32_t status;
/* Obtain the regulator status. */
ret = RegulatorGetStatus(handle, &status);
if (ret != 0) {
/* Error handling. */
}
Development Example
The following is an example of using a regulator.
void RegulatorTestSample(void)
{
int32_t ret;
/* Regulator device name */
const char *name = "regulator_virtual_1";
DevHandle handle = NULL;
/* Open the regulator device handle. */
handle = RegulatorOpen(name);
if (handle == NULL) {
HDF_LOGE("RegulatorOpen: failed!\n");
return;
}
/* Enable the regulator. */
ret = RegulatorEnable(handle);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("RegulatorEnable: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
int32_t minUv = 0; // The minimum voltage is 0 µV.
int32_t maxUv = 20000; // The maximum voltage is 20000 µV.
/* Set the output voltage range of the regulator. */
ret = RegulatorSetVoltage(handle, minUv, maxUv);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("RegulatorSetVoltage: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
uint32_t voltage;
/* Obtain the regulator voltage. */
ret = RegulatorGetVoltage(handle, &voltage);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("RegulatorGetVoltage: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
uint32_t status;
/* Obtain the regulator status. */
ret = RegulatorGetStatus(handle, &status);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("RegulatorGetStatus: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
/* Disable the regulator. */
ret = RegulatorDisable(handle);
if (ret != 0) {
HDF_LOGE("RegulatorDisable: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
goto _ERR;
}
_ERR:
/* Close the regulator device handle. */
RegulatorClose(handle);
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙HDF Driver Development Process
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: