harmony 鸿蒙DistributedDataManager Subsystem
DistributedDataManager Subsystem
Introduction
The DistributedDataManager subsystem implements persistence of a variety of structured data on a single device and data sync and sharing across devices. It allows application data to be seamlessly processed across devices, ensuring consistent user experience for the same application across devices.
The following figure shows the architecture of the DistributedDataManager subsystem.
Figure 1 Architecture
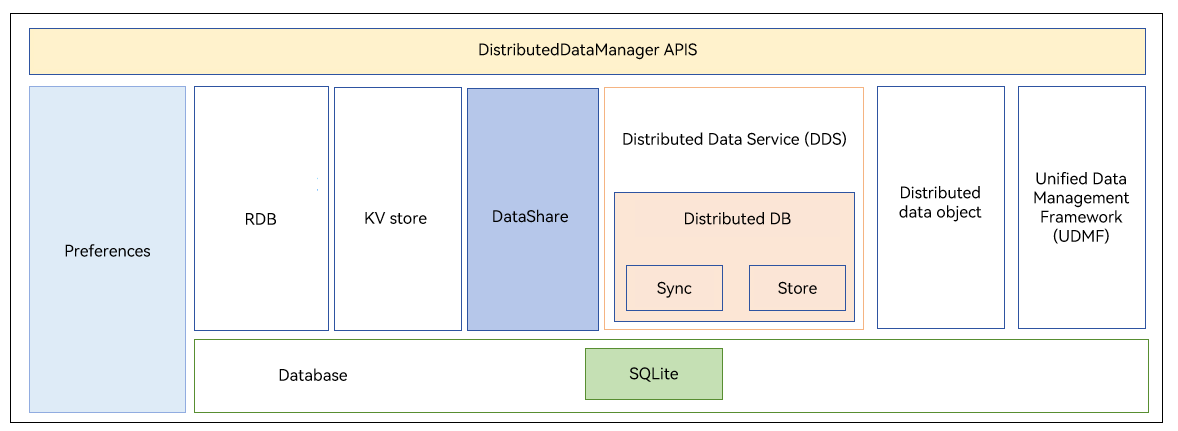
Directory Structure
Level 1 and 2 directories of the DistributedDataManager subsystem:
distributeddatamgr/ # DistributedDataManager subsystem
├── data_object # Distributed data object
└── data_share # DataShare
└── datamgr_service # Distributed data service (DDS)
└── kv_store # Key-value (KV) store
└── preferences # Preferences
└── relational_store # Relational Database (RDB) store
└── udmf # Unified Data Management Framework (UDMF)
third_party/ # Open-source software
├── bounds_checking_function # bounds_checking_function code
└── cJSON # cJSON code
└── flatbuffers # FlatBuffers code
└── googletest # GoogleTest code
└── jsoncpp # JsonCpp code
└── icu # ICU code
└── libuv # libuv code
└── openssl # OpenSSL code
└── sqlite # SQLite code
└── zlib # zlib code
Component Description
Distributed Data Object
As an object-oriented in-memory data management framework, the distributed data object framework provides APIs for basic data object management, including creating, querying, deleting, modifying, and subscribing to in-memory objects. Moreover, it provides distributed capabilities to implement data object collaboration for the same application between multiple devices that form a Super Device.
JS APIs are provided to help you use distributed data objects like using local data objects. A variety of data types are supported, including basic data types such as number, string, and Boolean, as well as complex data types such as array and nested basic data types.
DataShare
The DataShare module allows an application to share data with other applications. It allows data to be shared across different applications on the same device.
DDS
The DDS implements database collaboration across devices for applications. Data of different devices is isolated based on a triplet of the account, application, and database. The DDS synchronizes data between trusted devices, delivering a consistent data access experience on different devices.
KV Store
The distributed KV store provides distributed collaboration of KV stores across devices. By calling the APIs of distributedKVStore, applications can save data to distributed KV stores and perform operations, such as adding, deleting, modifying, querying, and synchronizing data in distributed KV stores.
The distributedKVStore module provides the following functions:
- KVManager: provides a KVManager instance for obtaining KV store information.
- KVStoreResultSet: provides APIs for accessing the result obtained from a KV store.
- Query: provides APIs for setting predicates for data query.
- SingleKVStore: provides APIs for querying and syncing data in single KV stores, which manage data without distinguishing devices.
- DeviceKVStore: provides APIs for querying and syncing data in device KV stores, which inherit from SingleKVStore and manage data by device.
Preferences
The Preferences module allows quick access to data in KV pairs and storage of a small amount of data for local applications. The data is stored in local files in KV pairs and loaded in memory, which allows for faster access and higher processing efficiency. Preferences provides non-relational data storage and is not suitable for storing a large amount of data.
- The Preferences module provides APIs for preferences operations.
- You can use getPreferences() to load the data of a file to a Preferences instance. Each file has only one Preferences instance. The system stores the instance data in memory through a static container until the application removes the instance from the memory or deletes the file.
- After obtaining a Preferences instance, the application can call Preferences APIs to read data from or write data to the Preferences instance, and call flush() to save the instance data to a file.
RDB Store
The RDB store manages data based on relational models. The OpenHarmony RDB store provides a complete mechanism for managing a local database based on the underlying SQLite.
With the SQLite as the persistence engine, the RDB store supports all SQLite features, including transactions, indexes, views, triggers, foreign keys, parameterized queries, prepared SQL statements, and more.
UDMF
The UDMF provides standard data channels for many-to-many data sharing across applications and provides standard APIs for data access. It also provides standard definitions for data types, such as text and image, to streamline data interaction between different applications and minimize the workload of data type adaptation.
Repositories Involved
DistributedDataManager
distributeddatamgr_data_object
distributeddatamgr_datamgr_service
distributeddatamgr_preferences
distributeddatamgr_relational_store
third_party_bounds_checking_function
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙System Ability Manager
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: