harmony 鸿蒙UIAbility Launch Type
UIAbility Launch Type
The launch type of the UIAbility component refers to the state of the UIAbility instance at startup. Three launch types are available:
NOTE
standard is the former name of multiton and provides the same effect as the multiton mode.
Singleton
singleton is the default launch type.
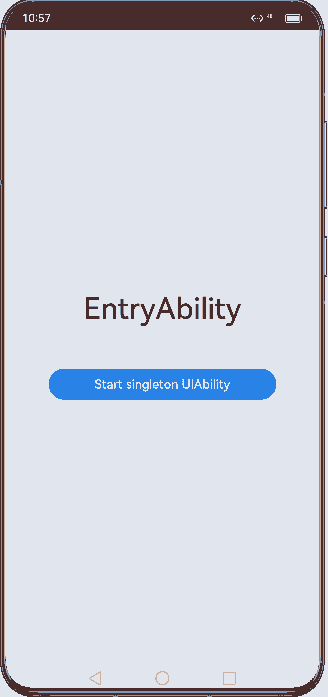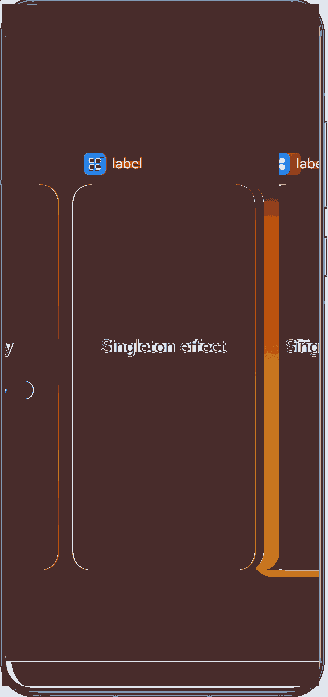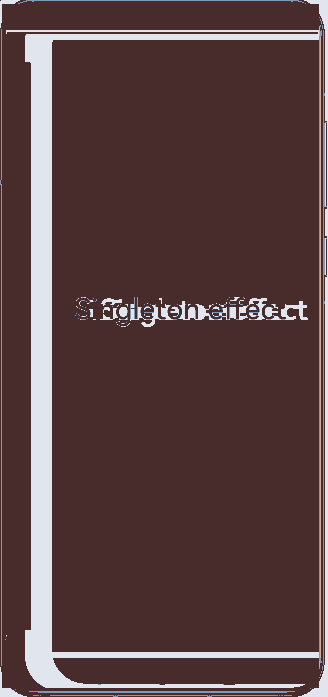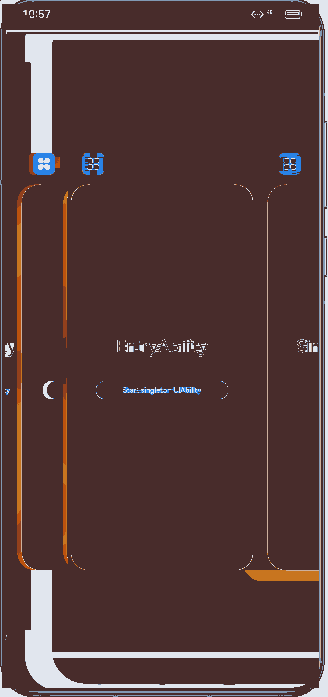
Each time startAbility() is called, if a UIAbility instance of this type already exists in the application process, the instance is reused. In other words, UIAbility of this type can have only one instance in the system, meaning that only one mission is displayed in the system application Recents.
Figure 1 Demonstration effect in singleton mode
NOTE
If startAbility() is called to start an existing UIAbility instance in singleton mode, that instance is started, and no new UIAbility instance is created. In this case, the onNewWant() callback is invoked, but the onCreate() and onWindowStageCreate() callbacks are not. If startAbility() is called to start an instance that is being started, error code 16000082 will be returned.
To use the singleton mode, set launchType in the module.json5 file to singleton.
{
"module": {
// ...
"abilities": [
{
"launchType": "singleton",
// ...
}
]
}
}
Multiton
In multiton mode, each time startAbility() is called, a new UIAbility instance is created in the application process. Multiple missions are displayed for UIAbility of this type in Recents.
Figure 2 Demonstration effect in multiton mode
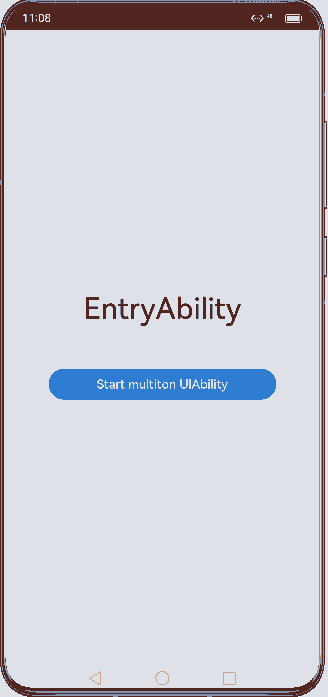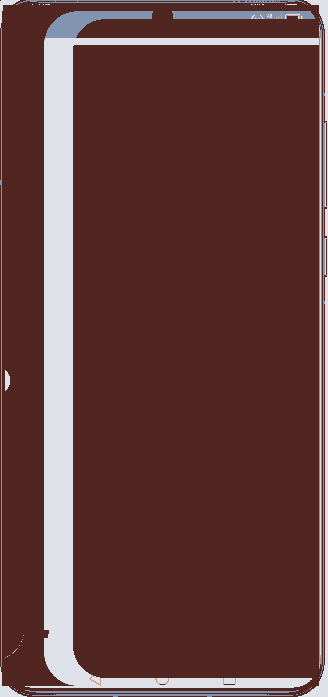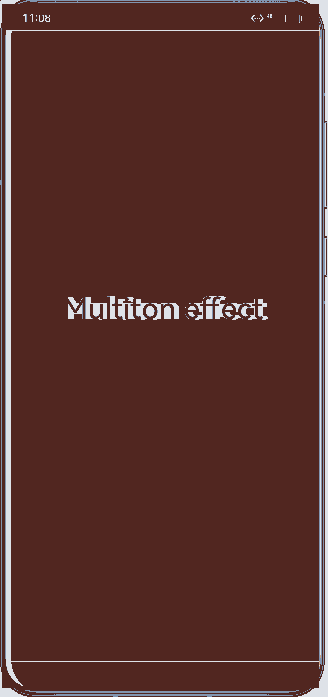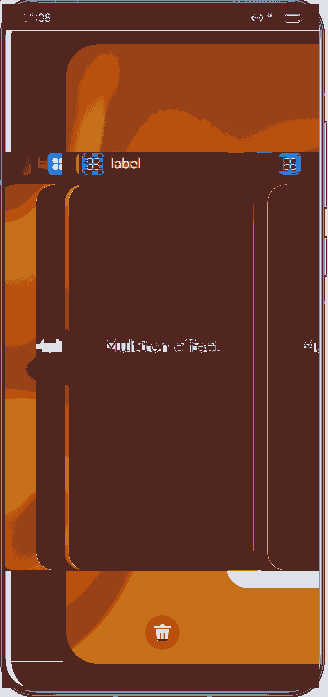
To use the multiton mode, set launchType in the module.json5 file to multiton.
{
"module": {
// ...
"abilities": [
{
"launchType": "multiton",
// ...
}
]
}
}
Specified
The specified mode is used in some special scenarios. For example, in a document application, you may want a document instance to be created each time you create a document, and you may also want to use the same document instance when you open an existing document.
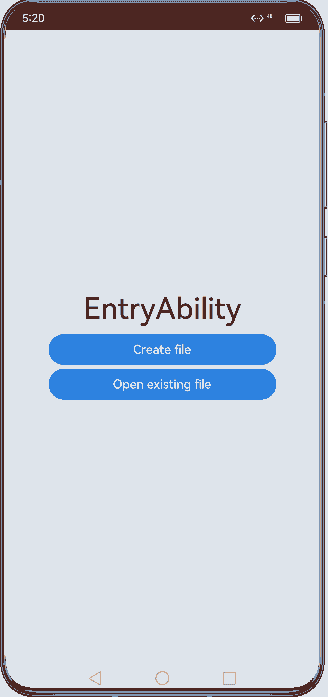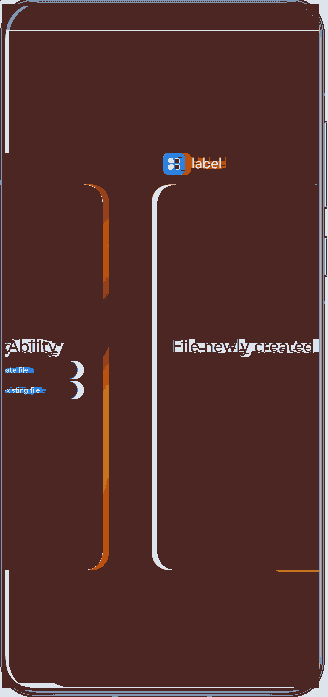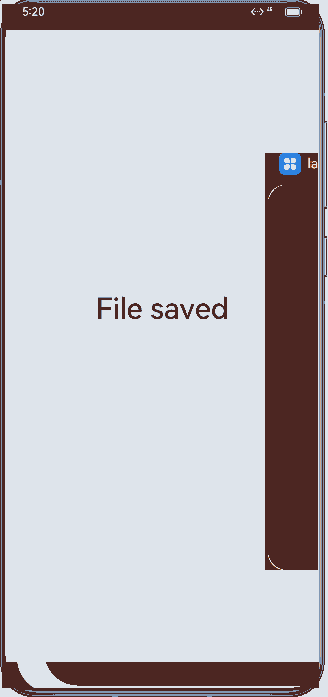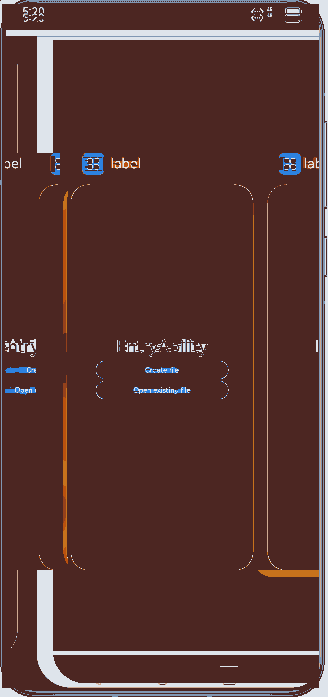
Figure 3 Principle in specified mode
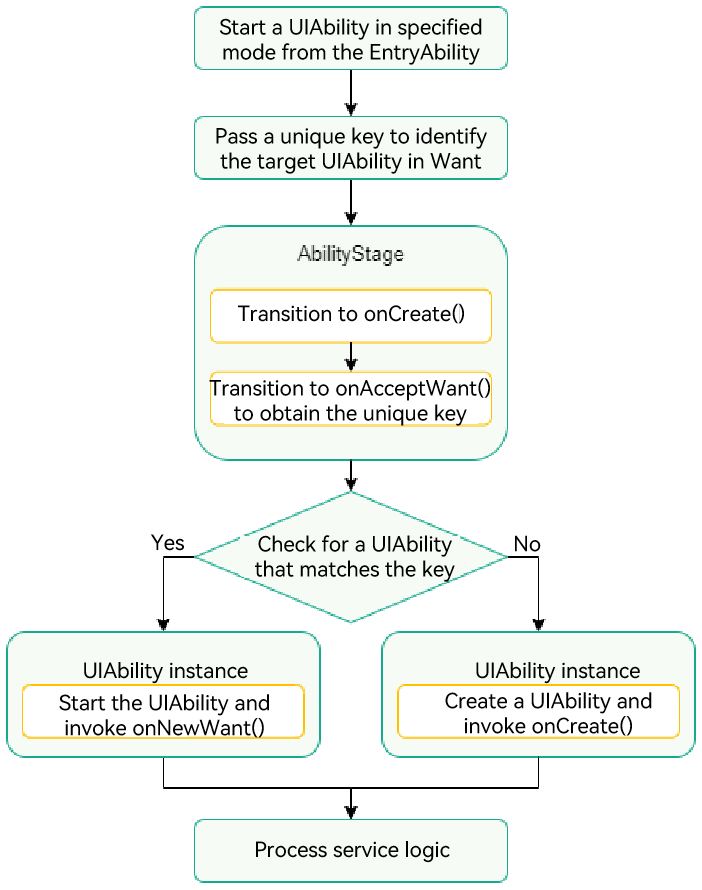
This section assumes that an application has two UIAbility instances: EntryAbility and SpecifiedAbility, and EntryAbility will start SpecifiedAbility in specified mode. The basic principle is as follows:
- EntryAbility calls startAbility() and sets a unique key in the parameters field of Want to identify SpecifiedAbility.
- Before starting SpecifiedAbility, the system invokes the onAcceptWant() lifecycle callback of the corresponding AbilityStage to obtain the key that identifies the target UIAbility.
- The system matches the UIAbility based on the key obtained.
- If a UIAbility instance is matched, that UIAbility instance is started, and its onNewWant() lifecycle callback is invoked.
- If no UIAbility instance is matched, a new UIAbility instance is created, and its onCreate() and onWindowStageCreate() lifecycle callbacks are invoked.
Figure 4 Demonstration effect in specified mode
- In SpecifiedAbility, set launchType in the module.json5 file to specified.
{
"module": {
// ...
"abilities": [
{
"launchType": "specified",
// ...
}
]
}
}
- In EntryAbility, pass the custom parameter instanceKey as the unique identifier into the want parameter in startAbility() to specify the target UIAbility instance. In the example, instanceKey is set to ‘KEY’.
// Configure a unique key for each UIAbility instance.
// For example, in the document usage scenario, use the document path as the key.
import { common, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
const TAG: string = '[Page_StartModel]';
const DOMAIN_NUMBER: number = 0xFF00;
function getInstance(): string {
return 'KEY';
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Page_StartModel {
private KEY_NEW = 'KEY';
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
// ...
Button()
.onClick(() => {
let context: common.UIAbilityContext = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext;
// context is the UIAbilityContext of the initiator UIAbility.
let want: Want = {
deviceId: '', // An empty deviceId indicates the local device.
bundleName: 'com.samples.stagemodelabilitydevelop',
abilityName: 'SpecifiedFirstAbility',
moduleName: 'entry', // moduleName is optional.
parameters: {
// Custom information.
instanceKey: this.KEY_NEW
}
};
context.startAbility(want).then(() => {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'Succeeded in starting SpecifiedAbility.');
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to start SpecifiedAbility. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`);
})
this.KEY_NEW = this.KEY_NEW + 'a';
})
// ...
Button()
.onClick(() => {
let context: common.UIAbilityContext = this.getUIContext().getHostContext() as common.UIAbilityContext;
// context is the UIAbilityContext of the initiator UIAbility.
let want: Want = {
deviceId: '', // An empty deviceId indicates the local device.
bundleName: 'com.samples.stagemodelabilitydevelop',
abilityName: 'SpecifiedSecondAbility',
moduleName: 'entry', // moduleName is optional.
parameters: {
// Custom information.
instanceKey: getInstance()
}
};
context.startAbility(want).then(() => {
hilog.info(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, 'Succeeded in starting SpecifiedAbility.');
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
hilog.error(DOMAIN_NUMBER, TAG, `Failed to start SpecifiedAbility. Code is ${err.code}, message is ${err.message}`);
})
this.KEY_NEW = this.KEY_NEW + 'a';
})
// ...
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
- Set the UIAbility identifier based on the onAcceptWant() lifecycle callback of SpecifiedAbility. In the example, the identifier is set to SpecifiedAbilityInstance_KEY.
import { AbilityStage, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
export default class MyAbilityStage extends AbilityStage {
onAcceptWant(want: Want): string {
// In the AbilityStage instance of the callee, a key string corresponding to a UIAbility instance is returned for UIAbility whose launch type is specified.
// In this example, SpecifiedAbility of module1 is returned.
if (want.abilityName === 'SpecifiedFirstAbility'||want.abilityName === 'SpecifiedSecondAbility') {
// The returned KEY string is a custom string.
if (want.parameters) {
return `SpecifiedAbilityInstance_${want.parameters.instanceKey}`;
}
}
// ...
return 'MyAbilityStage';
}
}
NOTE
- If startAbility() is called to start an existing UIAbility instance in specified mode, and the onAcceptWant() callback of AbilityStage matches that UIAbility instance, that instance is started, and no new UIAbility instance is created. In this case, the onNewWant() callback is invoked, but the onCreate() and onWindowStageCreate() callbacks are not.
- AbilityStage is not automatically generated by default in the project of DevEco Studio. For details about how to create an AbilityStage file, see AbilityStage Component Container.
For example, in the document application, different keys are bound to different document instances. Each time a document is created, a new key (for example, file path) is passed in, and a new UIAbility instance is created when the UIAbility is started in AbilityStage. However, when an existing document is opened, the same UIAbility instance is started again in AbilityStage.
The following steps are used as an example.
- Open file A. A UIAbility instance, UIAbility instance 1, is started.
- Close the process of file A in Recents. UIAbility instance 1 is destroyed. Return to the home screen and open file A again. A new UIAbility instance, UIAbility instance 2, is started.
- Return to the home screen and open file B. A new UIAbility instance, UIAbility instance 3, is started.
- Return to the home screen and open file A again. UIAbility instance 2 is started. This is because the system automatically matches the key with the UIAbility instance and starts the UIAbility instance that has a matching key. In this example, UIAbility instance 2 has the same key as file A. Therefore, the system pulls back UIAbility instance 2 and focuses it without creating a new instance.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Reasons for Abnormal Application Exits
harmony 鸿蒙UIAbility Backup and Restore
harmony 鸿蒙Using Explicit Want to Start an Application Component
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to Ability Kit
harmony 鸿蒙AbilityStage Component Container
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataAbility
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataShareExtensionAbility from the FA Model
harmony 鸿蒙Common action and entities Values (Not Recommended)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: