harmony 鸿蒙Combo Solution – W800 Chip Porting Case
Combo Solution – W800 Chip Porting Case
The combo solution is developed based on the OpenHarmony LiteOS-M kernel. This document exemplifies how to port code of the Neptune100 development board powered by the W800 chip from Winner Micro. The porting architecture uses the solution where Board and SoC are separated. Compilation options can be graphically configured through KConfig. The porting of the ck804ef architecture is added to adapt subsystems and components such as HDF and XTS.
Adaptation Preparation
Prepare the ubuntu20.04 system environment and install the cross compilation toolchain csky-abiv2-elf-gcc.
Compilation and Building
Directory Planning
This solution designs the directory structure using the board and SoC decoupling idea.
The SoC adaptation directory is planned as follows:
device
├── board --- Board vendor directory
│ └── hihope --- Board vendor: HiHope
│ └── neptune100 --- Board name: Neptune100
└── soc --- SoC vendor directory
└── winnermicro --- SoC vendor: Winner Micro
└── wm800 --- SoC series: W800
The planned product demo directory is as follows:
vendor
└── hihope --- Vendor of the product demo.
├── neptune_iotlink_demo --- Product demo name: sample code of Neptune100
└── ...
Product Definition
The vendor/hihope/neptune_iotlink_demo/config.json file describes the kernel, board, and subsystem information used by the product. The kernel, board model, and board vendor are required by the precompilation command hb set and must be planned. Example:
{
"product_name": "neptune_iotlink_demo", --- Product name
"ohos_version": "OpenHarmony 3.1", --- OS version in use
"type":"mini", --- OS type: mini
"version": "3.0", --- OS version: 3.0
"device_company": "hihope", --- Board vendor: hihope
"board": "neptune100", --- Board name: neptune100
"kernel_type": "liteos_m", --- Kernel type: liteos_m
"kernel_version": "3.0.0", --- Kernel version: 3.0.0
"subsystems": [] --- Subsystem
}
The filled information corresponds to the planned directory. In the information, device_company and board are used to associate the device/board/<device_company>/ directory.
Board Configuration
In the associated <board> directory, place the config.gni file to the device/board/hihope/neptune100/liteos_m directory. This file is used to describe the board information, including the CPU model, cross compilation toolchain, global compilation, and link parameters.
# Kernel type, e.g. "linux", "liteos_a", "liteos_m".
kernel_type = "liteos_m"
# Kernel version.
kernel_version = "3.0.0"
# Board CPU type, e.g. "cortex-a7", "riscv32".
board_cpu = "ck804ef"
# Board arch, e.g. "armv7-a", "rv32imac".
board_arch = "ck803"
# Toolchain name used for system compiling.
# E.g. gcc-arm-none-eabi, arm-linux-harmonyeabi-gcc, ohos-clang, riscv32-unknown-elf.
# Note: The default toolchain is "ohos-clang". It's not mandatory if you use the default toolchain.
board_toolchain = "csky-elfabiv2-gcc"
#use_board_toolchain = true
# The toolchain path installed, it's not mandatory if you have added toolchain path to your ~/.bashrc.
board_toolchain_path = ""
# Compiler prefix.
board_toolchain_prefix = "csky-elfabiv2-"
# Compiler type, "gcc" or "clang".
board_toolchain_type = "gcc"
# config.json parse
if (product_path != "") {
product_conf = read_file("${product_path}/config.json", "json")
product_name = product_conf.product_name
bin_list = product_conf.bin_list
}
# Board related common compile flags.
board_cflags = [
"-mcpu=ck804ef",
"-mhard-float",
"-DGCC_COMPILE=1",
"-DTLS_CONFIG_CPU_XT804=1",
"-DNIMBLE_FTR=1",
"-D__CSKY_V2__=1",
"-DCPU_CK804",
"-O2",
"-g3",
"-Wall",
"-ffunction-sections",
"-MMD",
"-MP",
]
board_cxx_flags = board_cflags
board_asmflags = [
"-mcpu=ck804ef",
"-DCPU_CK804",
]
board_ld_flags = []
# Board related headfiles search path.
board_include_dirs = []
# Board adapter dir for OHOS components.
board_adapter_dir = ""
# Sysroot path.
board_configed_sysroot = ""
# Board storage type, it used for file system generation.
storage_type = ""
Precompilation
Run the precompilation command hb set in the project root directory to show relevant product information, as shown below:
hb set
OHOS Which product do you need? (Use arrow keys)
hihope
> neptune_iotlink_demo
OHOS Which product do you need? neptune_iotlink_demo
After hb set is executed, an ohos_config.json file will be automatically generated in the root directory. The file lists the product information to be compiled.
Run the hb env command to view the selected precompilation environment variables.
[OHOS INFO] root path: /home/xxxx/openharmony_w800
[OHOS INFO] board: neptune100
[OHOS INFO] kernel: liteos_m
[OHOS INFO] product: neptune_iotlink_demo
[OHOS INFO] product path: /home/xxxx/openharmony_w800/vendor/hihope/neptune_iotlink_demo
[OHOS INFO] device path: /home/xxxx/openharmony_w800/device/board/hihope/neptune100/liteos_m
[OHOS INFO] device company: hihope
So far, the precompilation adaptation is complete. However, the project cannot be compiled by running hb build. You also need to prepare for the subsequent LiteOS-M kernel porting.
Kernel Porting
Kconfig Adaptation
During the compilation of kernel/liteos_m, you need to use the Kconfig file for indexing in the corresponding board and SoC directory.
Create a kernel_configs directory in the
vendor/hihope/neptune_iotlink_demodirectory, and create an emptydebug.configfile.Open the
kernel/liteos_m/Kconfigfile. MultipleKconfigfiles indevice/boardanddevice/sochave been imported using the orsource command in this file. You need to create and modify these files later.
orsource "../../device/board/*/Kconfig.liteos_m.shields"
orsource "../../device/board/$(BOARD_COMPANY)/Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig.boards"
orsource "../../device/board/$(BOARD_COMPANY)/Kconfig.liteos_m.boards"
orsource "../../device/soc/*/Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig"
orsource "../../device/soc/*/Kconfig.liteos_m.series"
orsource "../../device/soc/*/Kconfig.liteos_m.soc"
- Create corresponding
Kconfigfiles indevice/board/hihope.
├── neptune100 --- neptune100 board configuration directory.
│ ├── Kconfig.liteos_m.board --- Board configuration options.
│ ├── Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig.board --- Default board configuration options.
│ └── liteos_m
│ └── config.gni --- Board configuration file.
├── Kconfig.liteos_m.boards --- Board configuration information of the board vendor.
└── Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig.boards --- Default board configuration information of the board vendor.
- Modify the
Kconfigfile in theBoarddirectory.
Add the following content to neptune100/Kconfig.liteos_m.board:
config BOARD_NEPTUNE100
bool "select board neptune100"
depends on SOC_WM800
Configure that BOARD_NEPTUNE100 can be selected only when SOC_WM800 is selected.
Add the following content to neptune100/Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig.board:
```
if BOARD_NEPTUNE100
endif #BOARD_NEPTUNE100
```
This content is used to add the default configuration of **BOARD_NEPTUNE100**.
- Create corresponding
Kconfigfiles indevice/soc/winnermicro.
├── wm800 --- W800 series.
│ ├── Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig.wm800 --- Default W800 SoC configuration.
│ ├── Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig.series --- Default configuration of the W800 series.
│ ├── Kconfig.liteos_m.series --- Configuration of the W800 series.
│ └── Kconfig.liteos_m.soc --- W800 SoC configuration.
├── Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig --- Default SoC configuration.
├── Kconfig.liteos_m.series --- Series configuration.
└── Kconfig.liteos_m.soc --- SoC configuration.
- Modify the
Kconfigfile in theSocdirectory.
Add the following content to wm800/Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig.wm800:
config SOC
string
default "wm800"
depends on SOC_WM800
Add the following content to wm800/Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig.series:
if SOC_SERIES_WM800
rsource "Kconfig.liteos_m.defconfig.wm800"
config SOC_SERIES
string
default "wm800"
endif
Add the following content to wm800/Kconfig.liteos_m.series:
config SOC_SERIES_WM800
bool "winnermicro 800 Series"
select ARM
select SOC_COMPANY_WINNERMICRO --- Select SOC_COMPANY_WINNERMICRO.
select CPU_XT804
help
Enable support for winnermicro 800 series
SOC_WM800 in the wm800/Kconfig.liteos_m.soc file can be selected only after SOC_SERIES_WM800 is selected.
choice
prompt "Winnermicro 800 series SoC"
depends on SOC_SERIES_WM800
config SOC_WM800 --- Select SOC_WM800.
bool "SoC WM800"
endchoice
In conclusion, to compile BOARD_NEPTUNE100, you need to select SOC_COMPANY_WINNERMICRO, SOC_SERIES_WM800, and SOC_WM800.
7. Run make menuconfig in kernel/liteos_m for configuration selection. The SoC series can be selected.
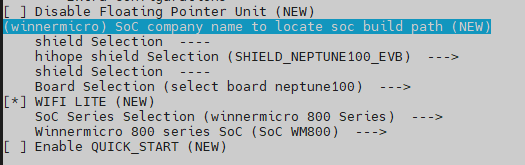
The configured file is saved to vendor/hihope/neptune_iotlink_demo/kernel_configs/debug.config by default. You can also directly configure debug.config.
LOSCFG_PLATFORM_QEMU_CSKY_SMARTL=y
LOSCFG_SOC_SERIES_WM800=y
Modular Compilation
The compilation of Board and SoC adopts the modular compilation method, starting from kernel/liteos_m/BUILD.gn and increasing by level. The adaptation process of this solution is as follows:
- Create the
BUILD.gnfile indevice/board/hihopeand add the following content to the file:
if (ohos_kernel_type == "liteos_m") {
import("//kernel/liteos_m/liteos.gni")
module_name = get_path_info(rebase_path("."), "name")
module_group(module_name) {
modules = [
"neptune100", --- Board module.
"shields",
]
}
}
In the preceding BUILD.gn file, neptune100 and shields are the module names organized by directory level.
- Create the
BUILD.gnfile indevice/soc/winnermicroand add the following content to the file:
if (ohos_kernel_type == "liteos_m") {
import("//kernel/liteos_m/liteos.gni")
module_name = get_path_info(rebase_path("."), "name")
module_group(module_name) {
modules = [
"hals",
"wm800",
]
}
}
- In the
device/soc/winnermicromodule at each level, add theBUILD.gnfile and compile the module. The following usesdevice/soc/winnermicro/wm800/board/platform/sys/BUILD.gnas an example:
import("//kernel/liteos_m/liteos.gni")
module_name = get_path_info(rebase_path("."), "name")
kernel_module(module_name) { --- Compiled module.
sources = [ --- Compiled source file.
"wm_main.c",
]
include_dirs = [ --- Header file used in the module.
".",
]
}
- To organize links and some compilation options, set the following parameters in
config("board_config")indevice/soc/winnermicro/wm800/board/BUILD.gn:
config("board_config") {
ldflags = [] --- Link parameters, including the Id file.
libs = [] --- Link library.
include_dirs = [] --- Common header file.
- To organize some product applications, this solution adds a corresponding list to the
config.jsonfile of the vendor. The following usesvendor/hihope/neptune_iotlink_demo/config.jsonas an example to describe how to add a corresponding list to theconfig.jsonfile:
"bin_list": [ --- demo list
{
"elf_name": "hihope",
"enable": "false", --- List switch.
"force_link_libs": [
"bootstrap",
"broadcast",
...
]
}
The demo is managed as a module. To enable or disable a demo, add or delete corresponding library files in bin_list. bin_list can be directly read in GN. You need to add the following content to device/board/hihope/neptune100/liteos_m/config.gni:
# config.json parse
if (product_path != "") {
product_conf = read_file("${product_path}/config.json", "json")
product_name = product_conf.product_name
bin_list = product_conf.bin_list
}
After reading the list, you can add related component libraries to the corresponding link options. Add the following content to //device/soc/winnermicro/wm800/BUILD.gn:
foreach(bin_file, bin_list) {
build_enable = bin_file.enable
...
if(build_enable == "true")
{
...
foreach(force_link_lib, bin_file.force_link_libs) {
ldflags += [ "-l${force_link_lib}" ]
}
...
}
}
Kernel Subsystem Adaptation
Add the kernel subsystem and relevant configuration to vendor/hihope/neptune_iotlink_demo/config.json, as shown below:
"subsystems": [
{
"subsystem": "kernel",
"components": [
{
"component": "liteos_m", "features":[]
}
]
},
Kernel Startup Adaptation
The Neptune100 development board uses the SoC architecture ck804ef, which is not supported by OpenHarmony. You need to port the architecture ck804ef. Adapt general files and function lists defined in kernel\liteos_m\arch\include, and place them to the kernel\liteos_m\arch\csky\v2\ck804\gcc directory.
The following is an example of kernel initialization:
osStatus_t ret = osKernelInitialize(); --- Kernel initialization.
if(ret == osOK)
{
threadId = osThreadNew((osThreadFunc_t)sys_init,NULL,&g_main_task); --- Create the init thread.
if(threadId!=NULL)
{
osKernelStart(); --- Thread scheduling.
}
}
Initialize necessary actions before board_main starts OHOS_SystemInit, as shown below:
...
UserMain(); --- Initialize the driver before starting OHOS_SystemInit of OpenHarmony.
...
OHOS_SystemInit(); --- Start OpenHarmony services and initialize components.
...
The UserMain function is in the device/soc/winnermicro/wm800/board/app/main.c file, as shown below:
...
if (DeviceManagerStart()) { --- HDF initialization.
printf("[%s] No drivers need load by hdf manager!",__func__);
}
...
HDF Framework Adaptation
HDF provides a set of unified APIs for applications to access hardware, simplifying application development. To add the HDF component, you need to add it to //vendor/hihope/neptune_iotlink_demo/kernel_configs:
LOSCFG_DRIVERS_HDF=y
LOSCFG_DRIVERS_HDF_PLATFORM=y
Driver adaptation files are stored in drivers/adapter/platform, including the gpio, i2c, pwm, spi, uart, and watchdog drivers. These files are loaded using the HDF mechanism. This section uses GPIO and UART as an example.
GPIO Adaptation
- The chip driver adaptation file is stored in the
drivers/adapter/platformdirectory. Add thegpio_wm.cfile to the gpio directory, and define the compilation adaptation of the W800 driver inBUILD.gn, as shown below:
...
if (defined(LOSCFG_SOC_COMPANY_WINNERMICRO)) {
sources += [ "gpio_wm.c" ]
}
...
- Define the driver description file in
gpio_wm.cas follows:
/* HdfDriverEntry definitions */
struct HdfDriverEntry g_GpioDriverEntry = {
.moduleVersion = 1,
.moduleName = "WM_GPIO_MODULE_HDF",
.Bind = GpioDriverBind,
.Init = GpioDriverInit,
.Release = GpioDriverRelease,
};
HDF_INIT(g_GpioDriverEntry);
- Add the GPIO hardware description information to
device/board/hihope/shields/neptune100/neptune100.hcs.
root {
platform {
gpio_config {
match_attr = "gpio_config";
groupNum = 1;
pinNum = 48;
}
}
}
- Obtain the hcs parameter from GpioDriverInit for initialization, as shown below:
...
gpioCntlr = GpioCntlrFromHdfDev(device); --- Obtain specific GPIO configurations through the **gpioCntlr** node variable.
if (gpioCntlr == NULL) {
HDF_LOGE("GpioCntlrFromHdfDev fail\r\n");
return HDF_DEV_ERR_NO_DEVICE_SERVICE;
}
...
UART Adaptation
- The chip driver adaptation file is stored in the
drivers/adapter/platformdirectory. Add theuart_wm.cfile to the uart directory, and define the compilation adaptation of the W800 driver inBUILD.gn, as shown below:
...
if (defined(LOSCFG_SOC_COMPANY_WINNERMICRO)) {
sources += [ "uart_wm.c" ]
}
...
- Define the driver description file in
uart_wm.cas follows:
/* HdfDriverEntry definitions */
struct HdfDriverEntry g_UartDriverEntry = {
.moduleVersion = 1,
.moduleName = "W800_UART_MODULE_HDF",
.Bind = UartDriverBind,
.Init = UartDriverInit,
.Release = UartDriverRelease,
};
/* Initialize HdfDriverEntry */
HDF_INIT(g_UartDriverEntry);
- Add the UART hardware description information to
device/board/hihope/shields/neptune100/neptune100.hcs.
root {
platform {
uart_config {
/*
uart0 {
match_attr = "uart0_config";
num = 0;
baudrate = 115200;
parity = 0;
stopBit = 1;
data = 8;
}*/
uart1 {
match_attr = "uart1_config";
num = 1;
baudrate = 115200;
parity = 0;
stopBit = 1;
data = 8;
}
}
}
}
- Obtain the hcs parameter from UartDriverInit for initialization, as shown below:
...
host = UartHostFromDevice(device);
if (host == NULL) {
HDF_LOGE("%s: host is NULL", __func__);
return HDF_ERR_INVALID_OBJECT;
}
...
OpenHarmony Subsystem Adaptation
Subsystem compilation options are configured in the config.json file of the corresponding product, for example, vendor/hihope/neptune_iotlink_demo/config.json.
wifi_lite Component
Add the wifi_lite component of the communication subsystem to the config.json file, as shown below:
{
"subsystem": "communication",
"components": [
{
"component": "wifi_lite",
"optional": "true"
}
]
},
The wifi_lite component is in the build/lite/components/communication.json file, which is described as follows:
{
"component": "wifi_lite",
"targets": [
"//foundation/communication/wifi_lite:wifi" --- Compilation target of the wifi_lite component.
]
},
In this case, the wifi adaptation source code can be checked in device/soc/winnermicro/wm800/board/src/wifi/wm_wifi.c, which is shown below:
int tls_wifi_netif_add_status_event(tls_wifi_netif_status_event_fn event_fn) --- Used to add the wifi event function.
{
u32 cpu_sr;
struct tls_wifi_netif_status_event *evt;
//if exist, remove from event list first.
tls_wifi_netif_remove_status_event(event_fn);
evt = tls_mem_alloc(sizeof(struct tls_wifi_netif_status_event));
if(evt==NULL)
return -1;
memset(evt, 0, sizeof(struct tls_wifi_netif_status_event));
evt->status_callback = event_fn;
cpu_sr = tls_os_set_critical();
dl_list_add_tail(&wifi_netif_status_event.list, &evt->list);
tls_os_release_critical(cpu_sr);
return 0;
}
systemabilitymgr Subsystem Adaptation
To adapt the systemabilitymgr subsystem, you need to add the samgr_lite component to the config.json file, as shown below:
{
"subsystem": "systemabilitymgr",
"components": [
{
"component": "samgr_lite"
}
]
},
utils Subsystem Adaptation
To adapt the utils subsystem, you need to add the kv_store and file components to the config.json file, as shown below:
{
"subsystem": "utils",
"components": [
{
"component": "kv_store",
"features": [
"enable_ohos_utils_native_lite_kv_store_use_posix_kv_api = true"
]
},
{ "component": "file", "features":[] }
]
},
When the kv_store component is adapted, key-value pairs will be written to the file. In the lite system, file operation APIs include POSIX and HalFiles.
The POSIX API is used for accessing the file system in the kernel. Therefore, you need to add enable_ohos_utils_native_lite_kv_store_use_posix_kv_api = true to features.
Startup Subsystem Adaptation
To adapt the startup subsystem, you need to add the bootstrap_lite and syspara_lite components to the config.json file, as shown below:
{
"subsystem": "startup",
"components": [
{
"component": "bootstrap_lite"
},
{
"component": "syspara_lite",
"features": [
"enable_ohos_startup_syspara_lite_use_posix_file_api = true",
"config_ohos_startup_syspara_lite_data_path = \"/data/\""
]
}
]
},
When adapting the bootstrap_lite component, you need to manually add the following content to the link script file device/soc/winnermicro/wm800/board/ld/w800/gcc_csky.ld:
.zinitcall_array :
{
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_core_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.core*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.core*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_core_end = .);
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_device_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.device*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.device*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_device_end = .);
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_bsp_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.bsp*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.bsp*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_bsp_end = .);
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_sys_service_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.sys.service*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.sys.service*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_sys_service_end = .);
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_app_service_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.app.service*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.app.service*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_app_service_end = .);
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_sys_feature_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.sys.feature*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.sys.feature*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_sys_feature_end = .);
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_app_feature_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.app.feature*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.app.feature*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_app_feature_end = .);
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_run_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.run*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.run*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_run_end = .);
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_test_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.test*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.test*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_test_end = .);
. = ALIGN(0x4) ;
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_exit_start = .);
KEEP (*(SORT(.zinitcall.exit*)))
KEEP (*(.zinitcall.exit*))
PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__zinitcall_exit_end = .);
} > REGION_RODATA
Adding the preceding content is because external APIs provided by bootstrap_init uses the segment injection mode and will be saved to the link segment. For details, see utils/native/lite/include/ohos_init.h. The following table lists the automatic initialization macros of main services.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| SYS_SERVICE_INIT(func) | Entry for initializing and starting a core system service. |
| SYS_FEATURE_INIT(func) | Entry for initializing and starting a core system feature. |
| APP_SERVICE_INIT(func) | Entry for initializing and starting an application-layer service. |
| APP_FEATURE_INIT(func) | Entry for initializing and starting an application-layer feature. |
The lib file compiled using the loaded components needs to be manually add to the forcible link.
If the bootstrap_lite component is configured in vendor/hihope/neptune_iotlink_demo/config.json:
{
"subsystem": "startup",
"components": [
{
"component": "bootstrap_lite"
},
...
]
},
The bootstrap_lite component will compile the base/startup/bootstrap_lite/services/source/bootstrap_service.c file. In this file, SYS_SERVICE_INIT is used to inject the Init function symbol to __zinitcall_sys_service_start and __zinitcall_sys_service_end. Since the Init function does not support explicit call, you need to forcibly link it to the final image, as shown below:
static void Init(void)
{
static Bootstrap bootstrap;
bootstrap.GetName = GetName;
bootstrap.Initialize = Initialize;
bootstrap.MessageHandle = MessageHandle;
bootstrap.GetTaskConfig = GetTaskConfig;
bootstrap.flag = FALSE;
SAMGR_GetInstance()->RegisterService((Service *)&bootstrap);
}
SYS_SERVICE_INIT(Init); --- Forcible link to the generated lib file is required if SYS_INIT is used for startup.
The base/startup/bootstrap_lite/services/source/BUILD.gn file describes libbootstrap.a generated in out/neptune100/neptune_iotlink_demo/libs, as shown below:
static_library("bootstrap") {
sources = [
"bootstrap_service.c",
"system_init.c",
]
...
When the syspara_lite component is adapted, system parameters will be written into the file for persistent storage. In the lite system, file operation APIs include POSIX and HalFiles.
The POSIX API is used for accessing the file system in the kernel. Therefore, you need to add enable_ohos_startup_syspara_lite_use_posix_file_api = true to the features field.
XTS Subsystem Adaptation
To adapt the XTS subsystem, add the following component options to config.json:
{
"subsystem": "xts",
"components": [
{
"component": "xts_acts",
"features":
[
"config_ohos_xts_acts_utils_lite_kv_store_data_path = \"/data\"",
"enable_ohos_test_xts_acts_use_thirdparty_lwip = true"
]
},
{ "component": "xts_tools", "features":[] }
]
}
The XTS function is also organized using list. You can add or delete relevant modules in the config.json file.
"bin_list": [
{
"enable": "true",
"force_link_libs": [
"module_ActsParameterTest",
"module_ActsBootstrapTest",
"module_ActsDfxFuncTest",
"module_ActsHieventLiteTest",
"module_ActsSamgrTest",
"module_ActsUtilsFileTest",
"module_ActsKvStoreTest",
"module_ActsWifiServiceTest"
]
}
],
The adaptation process of other components is similar to that of other vendors.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Combo Solution – ASR Chip Porting Case
harmony 鸿蒙Mini-System Devices with Screens – Bestechnic SoC Porting Case
harmony 鸿蒙IoT Solution - Chipsea CST85 Chip Porting Case
harmony 鸿蒙Standard System Solution – Rockchip RK3568 Porting Case
harmony 鸿蒙A Method for Rapidly Porting the OpenHarmony Linux Kernel
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: