harmony 鸿蒙Dynamic Import
Dynamic Import
Dynamic imports support conditional loading and partial reflection, enhancing page load speed. It allows loading HSP modules, HAR modules, ohpm packages, and native libraries. It also enables module decoupling when only variables are dynamically imported between HAR modules.
When to Use
Dynamic imports can be used in application development when you need to import modules conditionally or on-demand, as an alternative to static import. The following are some cases where you might want to use dynamic import:
- Statically imported modules significantly slow the loading of your code and are rarely used or not immediately needed.
- Statically imported modules consume a large amount of system memory and are rarely used.
- The imported module does not exist at load time and needs to be fetched asynchronously.
- The import specifier string needs to be constructed dynamically. Static imports only support static specifiers.
- The imported module has side effects (which can be understood as code that runs directly in the module) that are only needed when certain conditions are triggered.
Service Expansion Scenarios
As aforementioned, in addition to conditional loading, dynamic imports can implement partial reflection. In the following example, an HAP dynamically imports a HAR package (harlibrary) and calls its static member function staticAdd(), instance member function instanceAdd(), and global function addHarlibrary().
// harlibrary's src/main/ets/utils/Calc.ets
export class Calc {
public static staticAdd(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am harlibrary in staticAdd, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
public instanceAdd(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am harlibrary in instanceAdd, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
}
export function addHarlibrary(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am harlibrary in addHarlibrary, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
// harlibrary's Index.ets
export { Calc, addHarlibrary } from './src/main/ets/utils/Calc'
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"harlibrary": "file:../harlibrary"
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('harlibrary').then((ns:ESObject) => {
ns.Calc.staticAdd(8, 9); // Call the static member function staticAdd().
let calc:ESObject = new ns.Calc(); // Instantiate the class Calc.
calc.instanceAdd(10, 11); // Call the instance member function instanceAdd().
ns.addHarlibrary(6, 7); // Call the global function addHarlibrary().
// Reflection using class, member function, and method names as strings.
let className = 'Calc';
let methodName = 'instanceAdd';
let staticMethod = 'staticAdd';
let functionName = 'addHarlibrary';
ns[className][staticMethod](12, 13); // Call the static member function staticAdd().
let calc1:ESObject = new ns[className](); // Instantiate the class Calc.
calc1[methodName](14, 15); // Call the instance member function instanceAdd().
ns[functionName](16, 17); // Call the global function addHarlibrary().
});
Implementation of Dynamic Import
A dynamic import expression accepts a constant or variable as its argument. The following table lists the specifications of dynamic import.
| Scenario | Module Specifier | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Local module | File path | The path must start with ./ or ../. |
| Local module | HSP module name | - |
| Local module | HSP module file path | Currently, dynamic imports with constants are supported, but not ones with variables. |
| Local module | HAR module name | - |
| Local module | HAR module file path | Currently, dynamic imports with constants are supported, but not ones with variables. |
| Remote module | Remote HAR module name | - |
| Remote module | ohpm package name | - |
| API | @system.* | - |
| API | @ohos.* | - |
| API | @arkui-x.* | - |
| Native library module | libNativeLibrary.so | - |
NOTE
- Module names used in all imports are the aliases defined under dependencies in the oh-package.json5 file.
- It is recommended that the alias configured under dependencies be the same as the values of moduleName and packageName, both of which indicate the name of the module to import. moduleName is set in the module.json5 file of the module, and packageName is set in the oh-package.json5 file.
- Importing a module by name is importing the module’s entry file, generally index.ets/ts.
Key Points in Dynamic Import Implementation
Dynamic Imports with Constant Expressions
Dynamic imports with constant expressions refer to scenarios where the input to import is a constant. The following examples show how to use this type of dynamic import to import a module or API into a HAP module.
Note: In the examples, the paths, such as the path to Index.ets, are set based on the current DevEco Studio module configuration and are subject to change.
- HAP dynamically imports a HAR module using a constant module name
// HAR's Index.ets
export function add(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am a HAR, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('myHar').then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info(ns.add(3, 5));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"myHar": "file:../myHar"
}
- HAP dynamically imports a HAR module using a constant file path
// HAR's Index.ets
export function add(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am a HAR, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('myHar/Index').then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info(ns.add(3, 5));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"myHar": "file:../myHar"
}
- HAP dynamically imports an HSP module using a constant module name
// HSP's Index.ets
export function add(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am a HSP, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('myHsp').then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info(ns.add(3, 5));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"myHsp": "file:../myHsp"
}
- HAP dynamically imports an HSP module using a constant file path
// HSP's Index.ets
export function add(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am a HSP, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('myHsp/Index').then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info(ns.add(3, 5));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"myHsp": "file:../myHsp"
}
- HAP dynamically imports a remote HAR module using a constant module name
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('@ohos/crypto-js').then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport @ohos/crypto-js: ' + ns.CryptoJS.MD5(123456));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"@ohos/crypto-js": "2.0.3-rc.0"
}
- HAP dynamically imports an ohpm package using a constant
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('json5').then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport json5');
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"json5": "1.0.2"
}
- HAP dynamically imports its own single file using a constant
// HAP's src/main/ets/Calc.ets
export function add(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am a HAP, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('../Calc').then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info(ns.add(3, 5));
});
- HAP dynamically imports its own native library using a constant
// libnativeapi.so's index.d.ts
export const add: (a:number, b:number) => number;
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('libnativeapi.so').then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport libnativeapi.so: ' + ns.default.add(2, 3));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"libnativeapi.so": "file:./src/main/cpp/types/libnativeapi"
}
- HAP dynamically imports APIs using a constant
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
import('@system.app').then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.terminate(); });
import('@system.router').then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.clear(); });
import('@ohos.curves').then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.springMotion(0.555, 0.75, 0.001); });
import('@ohos.matrix4').then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.identity(); });
import('@ohos.hilog').then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'DynamicImport @ohos.hilog.'); });
Dynamic Imports with Variable Expressions
In DevEco Studio, module dependencies are configured through dependencies in the oh-package.json5 file. By default, all modules listed under dependencies are installed (for local modules) or downloaded (for remote modules), but are not built. During a HAP/HSP build, the dependency relationship is searched from the entry file (generally Index.ets/ts), and only the dependencies found are added to the build. During compilation, static imports and dynamic imports with constant expressions can be identified and parsed by the packaging tool rollup and its plug-ins. This means that the related dependencies can be added to the dependency tree, participate in the build process, and finally generate Ark bytecode. However, dynamic imports with variable expressions cannot be resolved at compile-time because their values may depend on runtime calculations or external inputs. To add these dependencies to the build process, add runtimeOnly under buildOption and set it to the actual module name or file path pertaining to the variable.
Schema configuration format of the runtimeOnly field
If you are using dynamic imports with variable expressions to import modules or files, but not APIs, you need to add the runtimeOnly field under buildOption in the build-profile.json5 file of the HAP/HSP/HAR module. The following are some examples.
// Dynamically import a module based on the module name myHar.
let harName = 'myHar';
import(harName).then(......);
// Dynamically import a file of the module itself based on the file path src/main/ets/index.ets.
let filePath = './Calc';
import(filePath).then(......);
The corresponding runtimeOnly configuration is as follows:
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"packages": [ "myHar" ] // Set the name of the module to dynamically import. It must be the same as the one specified under dependencies.
"sources": ["./src/main/ets/utils/Calc.ets"] // Set the path of the file to dynamically import. The path is relative to the build-profile.json5 file of the module.
}
}
}
packages of runtimeOnly: name of the module to dynamically import. It must be the same as the one specified under dependencies. sources of runtimeOnly: path of the file to dynamically import. The path is relative to the build-profile.json5 file of the module.
Usage Examples
- HAP dynamically imports a HAR module using a variable module name
// HAR's Index.ets
export function add(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am a HAR, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
let packageName = 'myHar';
import(packageName).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info(ns.add(3, 5));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"myHar": "file:../myHar"
}
// HAP's build-profile.json5
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"packages": [
"myHar" // Applicable only when a variable is used to dynamically import a module or file.
]
}
}
}
- HAP dynamically imports an HSP module using a variable module name
// HSP's Index.ets
export function add(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am a HSP, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
let packageName = 'myHsp';
import(packageName).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info(ns.add(3, 5));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"myHsp": "file:../myHsp"
}
// HAP's build-profile.json5
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"packages": [
"myHsp" // Applicable only when a variable is used to dynamically import a module.
]
}
}
}
- HAP dynamically imports a remote HAR module using a variable module name
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
let packageName = '@ohos/crypto-js';
import(packageName).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport @ohos/crypto-js: ' + ns.CryptoJS.MD5(123456));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"@ohos/crypto-js": "2.0.3-rc.0"
}
// HAP's build-profile.json5
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"packages": [
"@ohos/crypto-js" // Applicable only when a variable is used to dynamically import a module.
]
}
}
}
- HAP dynamically imports an ohpm package using a variable
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
let packageName = 'json5';
import(packageName).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport json5');
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"json5": "1.0.2"
}
// HAP's build-profile.json5
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"packages": [
"json5" // Applicable only when a variable is used to dynamically import a module.
]
}
}
}
- HAP dynamically imports its own single file using a variable
// HAP's src/main/ets/Calc.ets
export function add(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am a HAP, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
let filePath = '../Calc';
import(filePath).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info(ns.add(3, 5));
});
// HAP's build-profile.json5
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"sources": [
"./src/main/ets/Calc.ets" // Applicable only when a variable is used to dynamically import a file of the module itself.
]
}
}
}
- HAP dynamically imports its own native library using a variable
// libnativeapi.so's index.d.ts
export const add: (a:number, b:number) => number;
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
let soName = 'libnativeapi.so';
import(soName).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport libnativeapi.so: ' + ns.default.add(2, 3));
});
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"libnativeapi.so": "file:./src/main/cpp/types/libnativeapi"
}
// HAP's build-profile.json5
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"packages": [
"libnativeapi.so" // Applicable only when a variable is used to dynamically import a module.
]
}
}
}
- HAP dynamically imports APIs using a variable
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
let packageName = '@system.app';
import(packageName).then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.terminate(); });
packageName = '@system.router';
import(packageName).then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.clear(); });
packageName = '@ohos.curves';
import(packageName).then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.springMotion(0.555, 0.75, 0.001); });
packageName = '@ohos.matrix4';
import(packageName).then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.identity(); });
packageName = '@ohos.hilog';
import(packageName).then((ns:ESObject) => { ns.default.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'DynamicImport @ohos.hilog.'); });
You do not need to set runtimeOnly when dynamically importing APIs with variables.
Decoupling Dynamic Imports Between HAR Modules
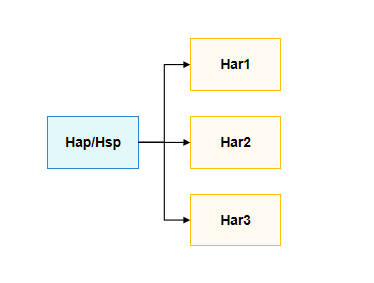
When an application contains multiple HAR packages with complex dependency relationships, circular dependencies may occur when configuring dependencies in DevEco Studio. If the dependencies between HAR packages are only through dynamic imports with variable expressions, the direct dependency relationships between HAR packages can be transferred to the HAP/HSP configuration. This decouples the dependencies between HAR packages, as shown in the figure below.
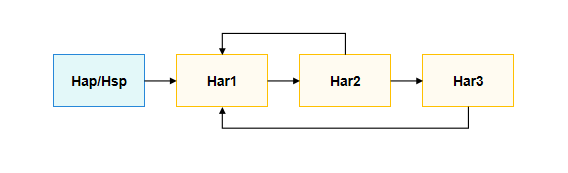
The figure shows the dependency graph after dependency conversion.
Constraints - This workaround is only applicable when circular dependencies occur between local HAR packages. - The transferred dependencies between HAR packages can only be through dynamic imports with variable expressions, not static imports or dynamic imports with constant expressions. - When transferring dependencies, both dependencies and runtimeOnly configurations must be transferred simultaneously. - HSP does not support transferring dependencies. For example, in the chain HAP -> HSP1 -> HSP2 -> HSP3, dependency between HSP2 and HSP3 cannot be transferred to HAP. - The entire chain of transferred dependencies must consist only of HAR packages. Dependencies cannot be transferred across HSP packages. An incorrect use is as follows: HAP -> HAR1 -> HAR2 -> HSP -> HAR3 -> HAR4.
The dependency of HAR1 on HAR2 can be transferred to a HAP, and the dependency of HAR3 on HAR4 can be transferred to an HSP. However, HAR3 or HAR4 cannot be transferred to the HAP.
Usage Examples
In the following example, HAP dynamically imports HAR package har1, and har1 dynamically imports another HAR package har2 using variables.
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"har1": "file:../har1"
}
// HAP's build-profile.json5
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"packages": [
"har1" // Applicable only when a variable is used to dynamically import a module.
]
}
}
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
let harName = 'har1';
import(harName).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport addHar1 4 + 5 = ' + ns.addHar1(4, 5));
});
// har1's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"har2": "file:../har2"
}
// har1's build-profile.json5
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"packages": [
"har2" // Applicable only when a variable is used to dynamically import a module.
]
}
}
}
// har1's Index.ets
export { addHar1 } from './src/main/ets/utils/Calc'
// har1's src/main/ets/utils/Calc.ets
export function addHar1(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am har1, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
let harName = 'har2';
import(harName).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport addHar2 4 + 5 = ' + ns.addHar2(4, 5));
});
return c;
}
// har2's Index.ets
export { addHar2 } from './src/main/ets/utils/Calc'
// har2's src/main/ets/utils/Calc.ets
export function addHar2(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am har2, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
The dependencies and runtimeOnly configurations of har1 on har2 are transferred to the HAP. In this way, the dependencies and runtimeOnly configuration of har2 do not need to be configured for har1.
// HAP's oh-package.json5
"dependencies": {
"har1": "file:../har1",
"har2": "file:../har2"
}
// HAP's build-profile.json5
"buildOption": {
"arkOptions": {
"runtimeOnly": {
"packages": [
"har1",
"har2"
]
}
}
}
// HAP's src/main/ets/pages/Index.ets
let harName = 'har1';
import(harName).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport addHar1 4 + 5 = ' + ns.addHar1(4, 5));
});
// har1's Index.ets
export { addHar1 } from './src/main/ets/utils/Calc'
// har1's src/main/ets/utils/Calc.ets
export function addHar1(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am har1, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
let harName = 'har2';
import(harName).then((ns:ESObject) => {
console.info('DynamicImport addHar2 4 + 5 = ' + ns.addHar2(4, 5));
});
return c;
}
// har2's Index.ets
export { addHar2 } from './src/main/ets/utils/Calc'
// har2's src/main/ets/utils/Calc.ets
export function addHar2(a:number, b:number):number {
let c = a + b;
console.info('DynamicImport I am har2, %d + %d = %d', a, b, c);
return c;
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Configuring arkOptions in build-profile.json5
harmony 鸿蒙Ark Bytecode File Format
harmony 鸿蒙Naming Conventions for Ark Bytecode Functions
harmony 鸿蒙Ark Bytecode Fundamentals
harmony 鸿蒙Overview of Ark Bytecode
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: