harmony 鸿蒙Overview of ArkTS Inter-Thread Communication
Overview of ArkTS Inter-Thread Communication
Inter-thread communication involves the exchange of data between concurrent threads. Given that ArkTS is compatible with TS/JS, its runtime is implemented using the actor model with memory isolation, similar to other JS engines.
The behavior of inter-thread communication in ArkTS varies depending on the type of data object involved. For instance, regular JS objects, ArrayBuffer objects, and SharedArrayBuffer objects each exhibit different behaviors, including serialization and deserialization, data transfer, and data sharing.
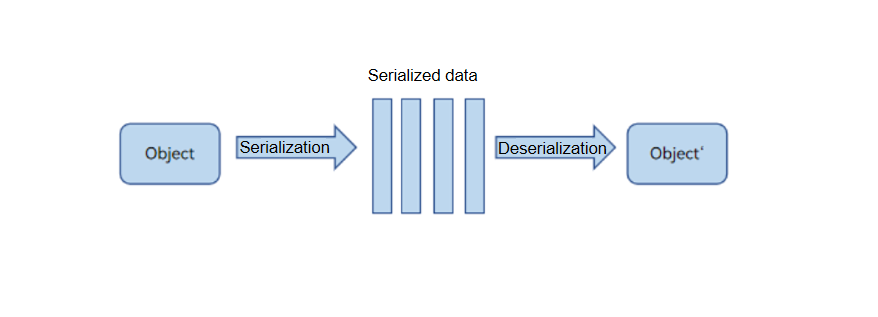
Taking JS objects as an example, inter-thread communication uses the standard Structured Clone algorithm for serialization and deserialization. This process involves converting JS objects into engine-independent data (such as strings or memory blocks) and then restoring them into new objects with the same content in another concurrent instance. This typically requires deep copying, which can be less efficient. In addition to standard JS serialization and deserialization, ArkTS supports the transfer of native JS object and the sharing of Sendable objects.
Currently, ArkTS provides two concurrency capabilities for inter-thread communication: TaskPool and Worker.
Worker is the standard API for cross-thread communication in the actor model. Its usage patterns are similar to those of Web Worker or Node.js Worker.
TaskPool provides a more powerful and user-friendly API for concurrent programming. The behavior of object passing across concurrent instances in TaskPool is consistent with that of Worker, utilizing the standard Structured Clone algorithm. The time required for concurrent communication increases with the size of the objects involved.
Leveraging the TaskPool and Worker concurrency APIs, ArkTS supports a variety of inter-thread communication capabilities to satisfy different development needs in inter-thread communication scenarios. These include scenarios involving independent time-consuming tasks, multiple time-consuming tasks, communication between TaskPool threads and the host thread, asynchronous communication between Worker threads and the host thread, and synchronous calls from Worker threads to the host thread’s interfaces. In addition, ArkTS supports cross-thread calls to ArkTS interfaces from C++ threads, based on the mechanisms provided by Node-API.
Figure 1 Serialization and deserialization principles
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Configuring arkOptions in build-profile.json5
harmony 鸿蒙Ark Bytecode File Format
harmony 鸿蒙Naming Conventions for Ark Bytecode Functions
harmony 鸿蒙Ark Bytecode Fundamentals
harmony 鸿蒙Overview of Ark Bytecode
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: