harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to User Authentication Kit
Introduction to User Authentication Kit
User Authentication Kit provides user authentication based on the lock screen password, facial characteristics, and fingerprints enrolled on a device.
It offers system-level user authentication functionality, including a built-in user authentication widget userAuthIcon that delivers unified user authentication experience across devices with diversified authentication modes (facial, fingerprint, and password authentication).
When a user requests access to personal data or perform sensitive operations, the application or system service invokes the user authentication widget to verify the user identity. The system responds to the user request accordingly only when the authentication is successful.
User Authentication Kit can be used in authentication scenarios, such as in-app login and payment.
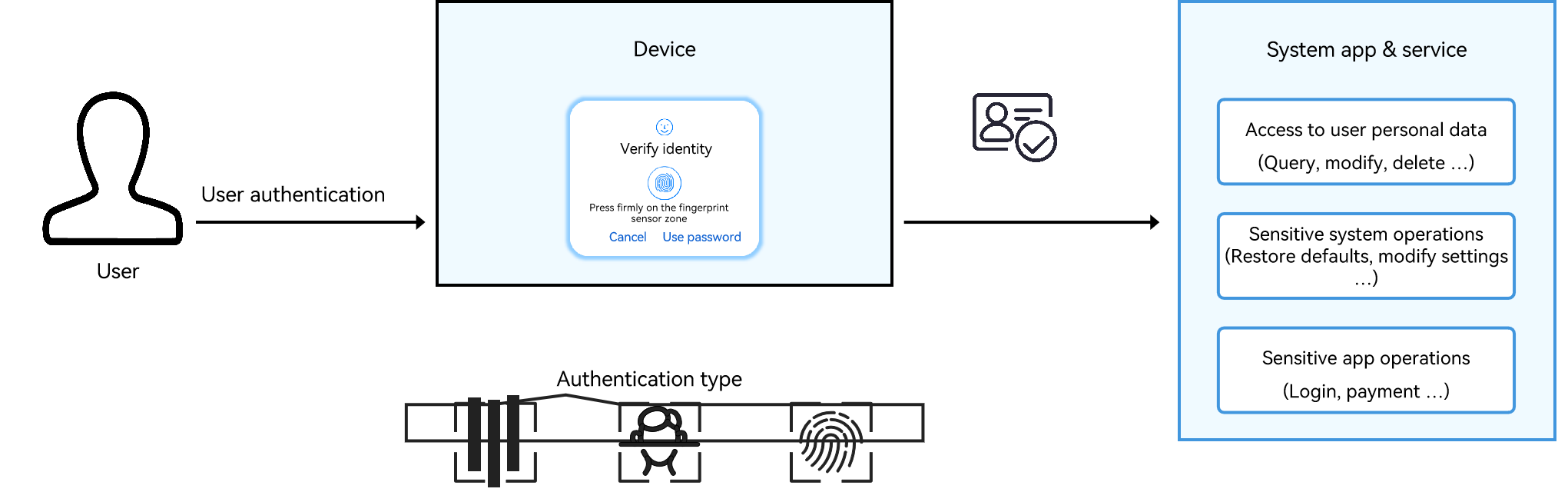
Features
Unified authentication interface
User Authentication Kit provides APIs that shield differences between authentication factors.
With the APIs, you can implement a combined authentication approach using face, fingerprint, and lock screen password.
You can also implement a combined authentication approach using facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and custom authentication.
Trust level awareness in authentication
The caller can specify the expected trust level for authentication. This prevents use of a lower-security authentication capability in security-critical scenarios, such as using 2D facial recognition for payment authentication.
Custom authentication modes
User Authentication Kit provides authentication UI with navigation buttons, allowing users to switch to a custom authentication screen.
Short-term authentication result reuse
The screen lock authentication result or any application’s authentication result can be reused within a caller-specified duration (up to 5 minutes), avoiding redundant authentication requests.
The system supports authentication-agnostic reuse mode. In this mode, the authentication result remains valid regardless of the authentication mode used, as long as it is within the specified duration.
The system also supports authentication-matching reuse mode. In this mode, authentication result is valid only if the same authentication mode is used and the time limit (up to 5 minutes) is not exceeded.
System-level user authentication UX
The caller can customize the title of the authentication page and the text on the navigation button.
The user authentication widget automatically adjusts the window display mode based on the screen status.
Awareness of the change in credential status
When a service is activated, the system can query the credential status or retrieve it from the authentication result and store the credential status. If the caller needs to detect changes in credentials, it can compare the stored credential status with the latest credential status obtained.
Working Mechanism
The following figure shows the architecture of the user authentication framework.
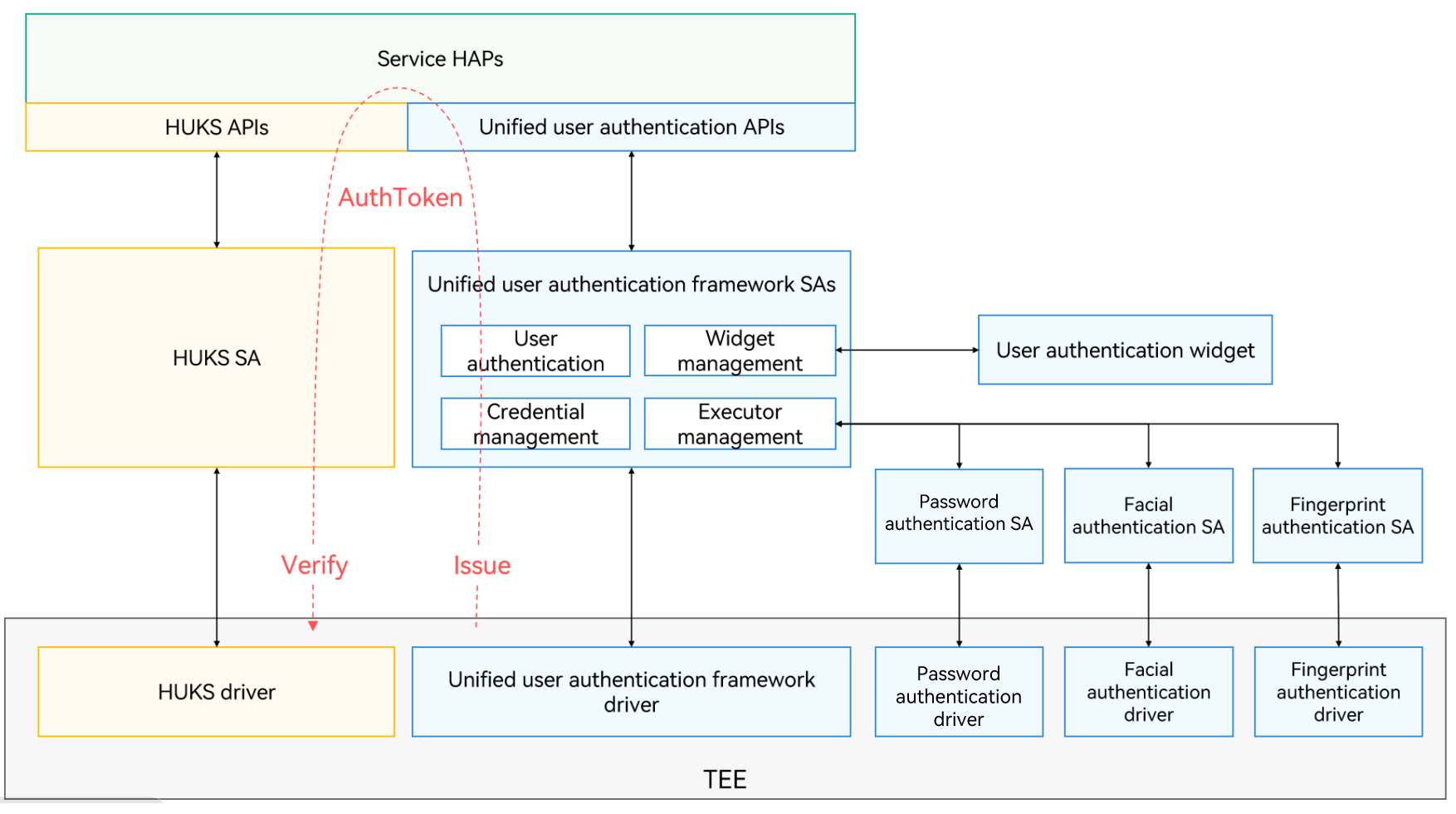
The user authentication framework consists of the following:
Unified user authentication APIs: mask differences between authentication factors, making it easier for implementing authentication capabilities.
Unified user authentication framework: consists of authentication SAs and drivers, responsible for scheduling various authentication capabilities and the user authentication widget to complete user authentication requests initiated by services through the unified user authentication APIs.
User authentication widget: provides interactive authentication interfaces for different authentication modes to ensure consistent user authentication experience.
Authentication capabilities: enable identity verification based on lock screen passwords, facial characteristics, and fingerprints under the scheduling of the unified user authentication framework.
If the user authentication is successful, the unified user authentication framework issues an AuthToken in the trusted execution environment (TEE) of the device.
As shown in the left side of the above figure, user authentication can also be used to control the access to the keys in the universal keystore. For the keys that can be accessed only with user authentication, the application must provide a key invocation request with the obtained AuthToken to the universal keystore service. The AuthToken serves as authentication proof for secondary access control of the key. After verifying the legitimacy and validity of the AuthToken in the TEE, the universal keystore service responds to the service request and performs the related key operation.
AuthToken Struct
Plaintext
| Name | Content | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| version | Token version | uint32_t | The current token version is 2.0. |
| challenge | Random challenge for authentication | uint8_t[32] | One-off random challenge generated by the service that needs to verify the authentication result. |
| time | Authentication timestamp | uint64_t | Timestamp when the authentication is successful. In reuse scenarios, this timestamp is the time when the user is successfully authenticated, rather than the AuthToken issuance time when the authentication result is reused. |
| authTrustLevel | Authentication trust level | uint32_t | Trust level of the authentication result, which relies on the capabilities of the authentication executor on the device. In normal cases, the trust level should be greater than or equal to authTrustLevel provided by the caller. For details, see Principles for Classifying Biometric Authentication Trust Levels. |
| authType | Authentication type | uint32_t | Authentication type, which can be facial authentication, fingerprint authentication, or lock screen password authentication. |
| authMode | Operation type | uint32_t | The operation type can be identification or authentication. |
| securityLevel | Security level of the token issuing environment | uint32_t | Security level of the environment where the token is issued. |
Ciphertext
| Name | Content | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| userId | User ID | int32_t | ID allocated by the system to a user when the user is created. |
| secureUid | Secure user ID | uint64_t | ID randomly allocated to a user who enrolls the system password. The ID is deleted when the user deletes the password and remains unchanged when the password is changed. |
| enrolledId | Credential enrollment ID | uint64_t | ID generated each time a credential of this type is enrolled. The ID remains unchanged if the credential is deleted. |
| credentialId | Credential ID | uint64_t | ID of a credential (such as the face or fingerprint) enrolled by the user. |
Tag
| Name | Content | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| tag | Tag of the ciphertext | uint8_t[16] | Tag generated after the ciphertext is encrypted using AES-GCM. |
| iv | Initialization vector (IV) used to encrypt the ciphertext. | uint8_t[12] | Random IV used for AES-GCM encryption. |
| sign | Signature of the AuthToken | uint8_t[32] | Signature that protects the integrity of the AuthToken. |
Principles for Classifying Biometric Authentication Trust Levels
The authentication trust level evaluates the security of the user identity authentication capability of the system, which depends on the authentication capability level (ACL) and authentication security level (ASL) of the authentication system.
The system uses the following metrics to measure the biometric authentication capability level:
False Rejection Rate (FRR): percentage of the times that a user is incorrectly rejected by a system.
False Acceptance Rate (FAR): percentage of times that an imposter is incorrectly accepted by a system.
Spoof Acceptance Rate (SAR): percentage of times that a non-lived, previously recorded sample is accepted by a system.
The lower the FAR, the higher the FRR, which increases the authentication security but also raises the likelihood of the authorized users being rejected by mistake, reducing convenience. Conversely, the higher FAR, the lower the FRR, which decreases the authentication security but increases convenience.
| Authentication Trust Level | Metrics |
|---|---|
| ATL4 | FAR ≤ 0.001%, SAR ≤ 3% when FRR = 10% |
| ATL3 | FAR ≤ 0.002%, SAR ≤ 7% when FRR = 10% |
| ATL2 | FAR ≤ 0.002%, 7% < SAR ≤ 20% when FRR = 10% |
| ATL1 | FAR ≤ 1%, 7% < SAR ≤ 20% when FRR = 10% |
Generally, the biometric authentication system comprises five execution units: source data collection, biometric feature extraction, biometric feature storage, biometric feature comparison, and authentication result issuance. The following Executor Security Levels (ESLs) are defined for the execution units.
| ESL | Definition |
|---|---|
| ESL3 | Operations are performed in a secure hardware-back trusted environment, such as a secure coprocessor or a secure element (SE). |
| ESL2 | Operations are performed in a trusted execution environment (TEE) based on hardware RoT isolation, such as a TEE and an SGX. |
| ESL1 | Operations are performed in an execution environment with access control, such as Linux. |
| ESL0 | Operations are performed in an execution environment without access control, such as a single-process lightweight system. |
The ASL of the entire authentication system is equal to the lowest ESL among the five execution units of biometric authentication. For example, there is a facial authentication system where the feature storage and comparison are performed in aTEE (ESL=2), but the feature extraction algorithm runs in a common system environment (ESL=1), the ASL of the face authentication system is 1.
The following table lists the mappings between AuthTrustLevels and ACLs & ASLs.
| Authentication Trust Level | Mapping Rule | Description | Application Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATL4 | ACL ≥ 3, ASL ≥ 2 | Capable of accurately identifying individual users with strong liveness detection capabilities, such as specially enhanced secure fingerprint and 3D facial authentication. | Small-amount payment |
| ATL3 | ACL ≥ 3, ASL ≥ 1 ACL ≥ 2, ASL ≥ 2 |
Capable of precisely identifying individual users with moderate liveness detection capabilities, such as specially enhanced secure fingerprint and 2D facial authentication. | Device unlocking, application login, and account login |
| ATL2 | ACL ≥ 2, ASL ≥ 1 ACL ≥ 1, ASL ≥ 2 |
Capable of precisely identifying individual users with regular liveness detection capabilities, such as 2D facial authentication using a common camera to collect images. | Maintaining the unlocked state of a device |
| ATL1 | ACL = 1, ASL = 1 | Capable of identifying individual users with limited liveness detection capabilities, such as voiceprint authentication. | Service risk control, targeted recommendations, and personalized services |
System Identity Authentication Constraints
The built-in user authentication widget must be used when a third-party application needs to use the authentication capability of the system.
Third-party applications are not allowed to initiate user authentication requests in the background.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙User Authentication Kit (User Authentication Service)
harmony 鸿蒙Applying Custom Authentication
harmony 鸿蒙Canceling User Authentication
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Enrolled Credential Status
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Supported Authentication Capabilities
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: