harmony 鸿蒙Audio Encoding
Audio Encoding
You can call the native APIs provided by the AudioCodec module to encode audio, that is, to compress audio PCM data into a desired format.
PCM data can be from any source. For example, you can use a microphone to record audio data or import edited PCM data. After audio encoding, you can output streams in the desired format and encapsulate the streams into a target file.
For details about the supported encoding capabilities, see AVCodec Supported Formats.
Usage Scenario
- Audio recording
Record incoming PCM data, encode it into the desired stream format, and then wrap it in the target file format. - Audio editing
When exporting edited PCM data as an audio file, the PCM data must be encoded into the appropriate audio format and then wrapped into a file. > NOTE > > AAC encoders adopt the VBR mode by default, which may differ in the configured parameters.
How to Develop
Read AudioCodec for the API reference.
Refer to the code snippet below to complete the entire audio encoding process, including creating an encoder, setting encoding parameters (such as the sampling rate, bit rate, and number of audio channels), and starting, refreshing, resetting, and destroying the encoder.
During application development, you must call the APIs in the defined sequence. Otherwise, an exception or undefined behavior may occur.
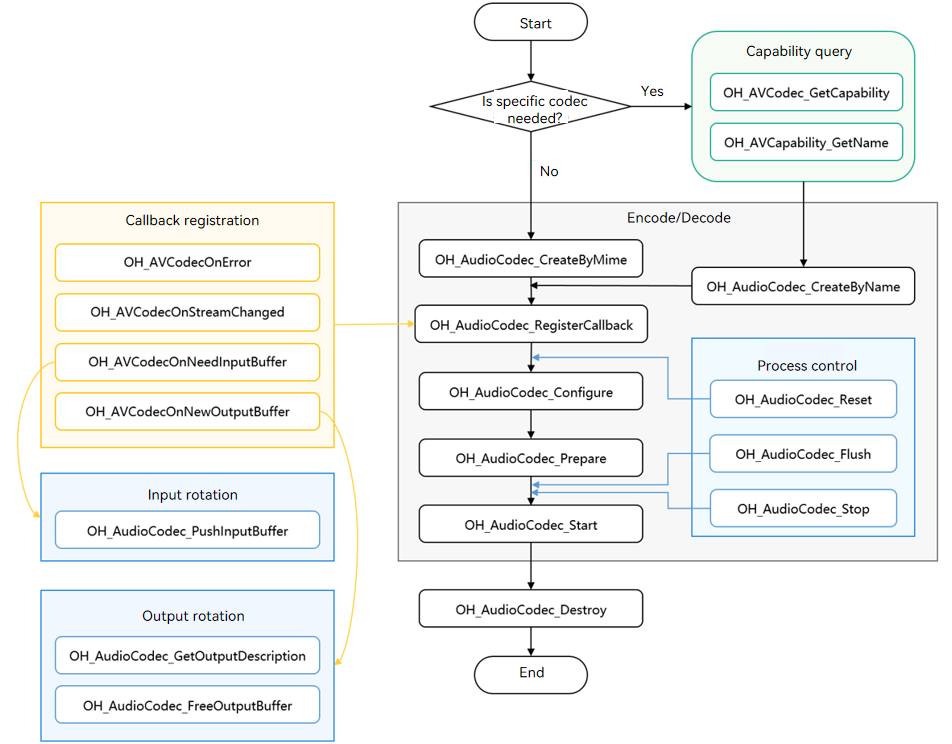
The figure below shows the call relationship of audio encoding.
The dotted line indicates an optional operation.
The solid line indicates a mandatory operation.
Linking the Dynamic Libraries in the CMake Script
target_link_libraries(sample PUBLIC libnative_media_codecbase.so)
target_link_libraries(sample PUBLIC libnative_media_core.so)
target_link_libraries(sample PUBLIC libnative_media_acodec.so)
How to Develop
Add the header files.
#include <multimedia/player_framework/native_avcodec_audiocodec.h> #include <multimedia/native_audio_channel_layout.h> #include <multimedia/player_framework/native_avcapability.h> #include <multimedia/player_framework/native_avcodec_base.h> #include <multimedia/player_framework/native_avformat.h> #include <multimedia/player_framework/native_avbuffer.h>Create an encoder instance. In the code snippet below, **OH_AVCodec *** is the pointer to the encoder instance created.
You can create an encoder by name or MIME type.
```cpp
// Namespace of the C++ standard library.
using namespace std;
// Create an encoder by name.
OH_AVCapability *capability = OH_AVCodec_GetCapability(OH_AVCODEC_MIMETYPE_AUDIO_AAC, true);
const char *name = OH_AVCapability_GetName(capability);
OH_AVCodec *audioEnc_ = OH_AudioCodec_CreateByName(name);
```
```cpp
// Specify whether encoding is used. The value true means encoding.
bool isEncoder = true;
// Create an encoder by MIME type.
OH_AVCodec *audioEnc_ = OH_AudioCodec_CreateByMime(OH_AVCODEC_MIMETYPE_AUDIO_AAC, isEncoder);
```
```cpp
// Initialize the queues.
class AEncBufferSignal {
public:
std::mutex inMutex_;
std::mutex outMutex_;
std::mutex startMutex_;
std::condition_variable inCond_;
std::condition_variable outCond_;
std::condition_variable startCond_;
std::queue<uint32_t> inQueue_;
std::queue<uint32_t> outQueue_;
std::queue<OH_AVBuffer *> inBufferQueue_;
std::queue<OH_AVBuffer *> outBufferQueue_;
};
AEncBufferSignal *signal_;
```
- Call OH_AudioCodec_RegisterCallback() to register callback functions.
Register the OH_AVCodecCallback struct that defines the following callback function pointers:
- OH_AVCodecOnError, a callback used to report a codec operation error
- OH_AVCodecOnStreamChanged, a callback not supported by the audio encoder yet
- OH_AVCodecOnNeedInputBuffer, a callback used to report input data required, which means that the encoder is ready for receiving PCM data
- OH_AVCodecOnNewOutputBuffer, a callback used to report output data generated, which means that encoding is complete
You need to process the callback functions to ensure that the encoder runs properly.
NOTE
You are not advised to perform time-consuming operations in the callback.
```cpp
// Implement the OH_AVCodecOnError callback function.
static void OnError(OH_AVCodec *codec, int32_t errorCode, void *userData)
{
(void)codec;
(void)errorCode;
(void)userData;
}
// Implement the OH_AVCodecOnStreamChanged callback function.
static void OnOutputFormatChanged(OH_AVCodec *codec, OH_AVFormat *format, void *userData)
{
(void)codec;
(void)format;
(void)userData;
}
// Implement the OH_AVCodecOnNeedInputBuffer callback function.
static void OnInputBufferAvailable(OH_AVCodec *codec, uint32_t index, OH_AVBuffer *data, void *userData)
{
(void)codec;
// The input stream is sent to the InputBuffer queue.
AEncBufferSignal *signal = static_cast<AEncBufferSignal *>(userData);
unique_lock<mutex> lock(signal->inMutex_);
signal->inQueue_.push(index);
signal->inBufferQueue_.push(data);
signal->inCond_.notify_all();
}
// Implement the OH_AVCodecOnNewOutputBuffer callback function.
static void OnOutputBufferAvailable(OH_AVCodec *codec, uint32_t index, OH_AVBuffer *data, void *userData)
{
(void)codec;
// The index of the output buffer is sent to OutputQueue_.
// The encoded data is sent to the outBuffer queue.
AEncBufferSignal *signal = static_cast<AEncBufferSignal *>(userData);
unique_lock<mutex> lock(signal->outMutex_);
signal->outQueue_.push(index);
signal->outBufferQueue_.push(data);
}
signal_ = new AEncBufferSignal();
OH_AVCodecCallback cb_ = {&OnError, &OnOutputFormatChanged, &OnInputBufferAvailable, &OnOutputBufferAvailable};
// Set the asynchronous callbacks.
int32_t ret = OH_AudioCodec_RegisterCallback(audioEnc_, cb_, signal_);
if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) {
// Handle exceptions.
}
```
- Call OH_AudioCodec_Configure to configure the encoder.
The following options are mandatory: sampling rate, bit rate, number of audio channels, audio channel type, and bit depth.
The maximum input length is optional.
For FLAC encoding, the compliance level and sampling precision are also mandatory.
The sample below lists the value range of each audio encoding type. |Audio Encoding Type|Sampling Rate (Hz) | Audio Channel Count | |———–|——————————————————————————-|:—————-:| |AAC |8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000, 64000, 88200, 96000|1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8| |FLAC |8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000, 64000, 88200, 96000| 1–8 | |MP3 |8000, 11025, 12000, 16000, 22050, 24000, 32000, 44100, 48000 | 1–2 | |G711mu |8000 | 1 |
The code snippet below shows the API call process, where AAC encoding at the bit rate of 32000 bit/s is carried out on the PCM audio with the 44100 Hz sampling rate, 2-channel stereo, and SAMPLE_S16LE sampling format.
cpp
int32_t ret;
// (Mandatory) Configure the audio sampling rate.
constexpr uint32_t DEFAULT_SAMPLERATE = 44100;
// (Mandatory) Configure the audio bit rate.
constexpr uint64_t DEFAULT_BITRATE = 32000;
// (Mandatory) Configure the number of audio channels.
constexpr uint32_t DEFAULT_CHANNEL_COUNT = 2;
// (Mandatory) Configure the audio channel type.
constexpr OH_AudioChannelLayout CHANNEL_LAYOUT = OH_AudioChannelLayout::CH_LAYOUT_STEREO;
// (Mandatory) Configure the audio bit depth.
constexpr OH_BitsPerSample SAMPLE_FORMAT = OH_BitsPerSample::SAMPLE_S16LE;
// A frame of audio data takes 20 ms.
constexpr float TIME_PER_FRAME = 0.02;
// (Optional) Configure the maximum input length and the size of each audio frame.
constexpr uint32_t DEFAULT_MAX_INPUT_SIZE = DEFAULT_SAMPLERATE * TIME_PER_FRAME * DEFAULT_CHANNEL_COUNT * sizeof(short); // aac
OH_AVFormat *format = OH_AVFormat_Create();
// Set the format.
OH_AVFormat_SetIntValue(format,OH_MD_KEY_AUD_CHANNEL_COUNT, DEFAULT_CHANNEL_COUNT);
OH_AVFormat_SetIntValue(format,OH_MD_KEY_AUD_SAMPLE_RATE, DEFAULT_SAMPLERATE);
OH_AVFormat_SetLongValue(format,OH_MD_KEY_BITRATE, DEFAULT_BITRATE);
OH_AVFormat_SetIntValue(format, OH_MD_KEY_AUDIO_SAMPLE_FORMAT, SAMPLE_FORMAT);
OH_AVFormat_SetLongValue(format,OH_MD_KEY_CHANNEL_LAYOUT, CHANNEL_LAYOUT);
OH_AVFormat_SetIntValue(format,OH_MD_KEY_MAX_INPUT_SIZE, DEFAULT_MAX_INPUT_SIZE);
// Configure the encoder.
ret = OH_AudioCodec_Configure(audioEnc_, format);
if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) {
// Handle exceptions.
}
The following shows the API call process in the case of FLAC encoding.
```cpp
int32_t ret;
// (Mandatory) Configure the audio sampling rate.
constexpr uint32_t DEFAULT_SAMPLERATE = 44100;
// (Mandatory) Configure the audio bit rate.
constexpr uint64_t DEFAULT_BITRATE = 261000;
// (Mandatory) Configure the number of audio channels.
constexpr uint32_t DEFAULT_CHANNEL_COUNT = 2;
// (Mandatory) Configure the audio channel type.
constexpr OH_AudioChannelLayout CHANNEL_LAYOUT = OH_AudioChannelLayout::CH_LAYOUT_STEREO;
// (Mandatory) Configure the audio bit depth. Only SAMPLE_S16LE and SAMPLE_S32LE are available for FLAC encoding.
constexpr OH_BitsPerSample SAMPLE_FORMAT = OH_BitsPerSample::SAMPLE_S32LE;
// Configure the audio compliance level. The default value is 0, and the value ranges from -2 to 2.
constexpr int32_t COMPLIANCE_LEVEL = 0;
// (Mandatory) Configure the audio sampling precision. SAMPLE_S16LE, SAMPLE_S24LE, and SAMPLE_S32LE are available.
constexpr OH_BitsPerSample BITS_PER_CODED_SAMPLE = OH_BitsPerSample::SAMPLE_S24LE;
OH_AVFormat *format = OH_AVFormat_Create();
// Set the format.
OH_AVFormat_SetIntValue(format, OH_MD_KEY_AUD_CHANNEL_COUNT, DEFAULT_CHANNEL_COUNT);
OH_AVFormat_SetIntValue(format, OH_MD_KEY_AUD_SAMPLE_RATE, DEFAULT_SAMPLERATE);
OH_AVFormat_SetLongValue(format, OH_MD_KEY_BITRATE, DEFAULT_BITRATE);
OH_AVFormat_SetIntValue(format, OH_MD_KEY_BITS_PER_CODED_SAMPLE, BITS_PER_CODED_SAMPLE);
OH_AVFormat_SetIntValue(format, OH_MD_KEY_AUDIO_SAMPLE_FORMAT, SAMPLE_FORMAT);
OH_AVFormat_SetLongValue(format, OH_MD_KEY_CHANNEL_LAYOUT, CHANNEL_LAYOUT);
OH_AVFormat_SetLongValue(format, OH_MD_KEY_COMPLIANCE_LEVEL, COMPLIANCE_LEVEL);
// Configure the encoder.
ret = OH_AudioCodec_Configure(audioEnc_, format);
if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) {
// Handle exceptions.
}
```
<!--RP2--><!--RP2End-->
Call OH_AudioCodec_Prepare() to prepare internal resources for the encoder.
ret = OH_AudioCodec_Prepare(audioEnc_); if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) { // Handle exceptions. }Call OH_AudioCodec_Start() to start the encoder.
unique_ptr<ifstream> inputFile_ = make_unique<ifstream>(); unique_ptr<ofstream> outFile_ = make_unique<ofstream>(); // Open the path of the binary file to be encoded. (A PCM file is used as an example.) inputFile_->open(inputFilePath.data(), ios::in|ios::binary); // Configure the path of the output file. (An encoded stream file is used as an example.) outFile_->open(outputFilePath.data(), ios::out|ios::binary); // Start encoding. ret = OH_AudioCodec_Start(audioEnc_); if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) { // Handle exceptions. }Call OH_AudioCodec_PushInputBuffer() to write the data to encode. You should fill in complete input data before calling this API.
Set SAMPLES_PER_FRAME as follows:
For AAC encoding, set SAMPLES_PER_FRAME to the number of PCM samples every 20 ms, that is, sampling rate x 0.02.
For FLAC encoding, set SAMPLES_PER_FRAME based on the table below.
|Sampling Rate|Sample Count| |:—-:|:—-:| | 8000| 576| |16000| 1152| |22050| 2304| |24000| 2304| |32000| 2304| |44100| 4608| |48000| 4608| |88200| 8192| |96000| 8192|
NOTE
It is recommended that SAMPLES_PER_FRAME in AAC encoding be the number of PCM samples every 20 ms, that is, sampling rate x 0.02. In the case of FLAC encoding, if the number of samples is greater than the corresponding value provided in the table, an error code is returned. If the number is less than the corresponding value provided in the table, the encoded file may be damaged.
// Number of samples per frame.
constexpr int32_t SAMPLES_PER_FRAME = DEFAULT_SAMPLERATE * TIME_PER_FRAME;
// Number of audio channels. For AMR encoding, only mono audio input is supported.
constexpr int32_t DEFAULT_CHANNEL_COUNT = 2;
// Length of the input data of each frame, that is, number of audio channels x number of samples per frame x number of bytes per sample (SAMPLE_S16LE used as an example).
// If the last frame of data does not meet the required length,you are advised to discard it or add padding.
constexpr int32_t INPUT_FRAME_BYTES = DEFAULT_CHANNEL_COUNT * SAMPLES_PER_FRAME * sizeof(short);
uint32_t index = signal_->inQueue_.front();
auto buffer = signal_->inBufferQueue_.front();
OH_AVCodecBufferAttr attr = {0};
if (!inputFile_->eof()) {
inputFile_->read((char *)OH_AVBuffer_GetAddr(buffer), INPUT_FRAME_BYTES);
attr.size = INPUT_FRAME_BYTES;
attr.flags = AVCODEC_BUFFER_FLAGS_NONE;
} else {
attr.size = 0;
attr.flags = AVCODEC_BUFFER_FLAGS_EOS;
}
OH_AVBuffer_SetBufferAttr(buffer, &attr);
// Send the data to the input queue for encoding. The index is the subscript of the queue.
ret = OH_AudioCodec_PushInputBuffer(audioEnc_, index);
if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) {
// Handle exceptions.
}
In the preceding example, attr.flags indicates the type of the buffer flag.
To indicate the End of Stream (EOS), pass in the AVCODEC_BUFFER_FLAGS_EOS flag.
|Value|Description| |——–|——–| |AVCODEC_BUFFER_FLAGS_NONE|Common frame.| |AVCODEC_BUFFER_FLAGS_EOS|The buffer is an end-of-stream frame.| |AVCODEC_BUFFER_FLAGS_CODEC_DATA|The buffer contains codec-specific data.|
- Call OH_AudioCodec_FreeOutputBuffer() to release the encoded data.
Once you have retrieved the encoded stream, call OH_AudioCodec_FreeOutputBuffer() to free up the data.
```c++
uint32_t index = signal_->outQueue_.front();
OH_AVBuffer *avBuffer = signal_->outBufferQueue_.front();
// Obtain the buffer attributes.
OH_AVCodecBufferAttr attr = {0};
ret = OH_AVBuffer_GetBufferAttr(avBuffer, &attr);
if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) {
// Handle exceptions.
}
// Write the encoded data (specified by data) to the output file.
outputFile_->write(reinterpret_cast<char *>(OH_AVBuffer_GetAddr(avBuffer)), attr.size);
// Release the output buffer.
ret = OH_AudioCodec_FreeOutputBuffer(audioEnc_, index);
if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) {
// Handle exceptions.
}
if (attr.flags == AVCODEC_BUFFER_FLAGS_EOS) {
// End.
}
```
- (Optional) Call OH_AudioCodec_Flush() to refresh the encoder.
After OH_AudioCodec_Flush() is called, the current encoding queue is cleared.
To continue encoding, you must call OH_AudioCodec_Start() again.
You need to call OH_AudioCodec_Flush() in the following cases:
The EOS of the file is reached.
An error with OH_AudioCodec_IsValid set to true (indicating that the execution can continue) occurs.
// Refresh the encoder. ret = OH_AudioCodec_Flush(audioEnc_); if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) { // Handle exceptions. } // Start encoding again. ret = OH_AudioCodec_Start(audioEnc_); if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) { // Handle exceptions. }(Optional) Call OH_AudioCodec_Reset() to reset the encoder.
After OH_AudioCodec_Reset() is called, the encoder returns to the initialized state. To continue encoding, you must call OH_AudioCodec_Configure() and then OH_AudioCodec_Start().
// Reset the encoder. ret = OH_AudioCodec_Reset(audioEnc_); if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) { // Handle exceptions. } // Reconfigure the encoder. ret = OH_AudioCodec_Configure(audioEnc_, format); if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) { // Handle exceptions. }Call OH_AudioCodec_Stop() to stop the encoder.
After the encoder is stopped, you can call Start to start it again. If you have passed specific data in the previous Start for the encoder, you must pass it again.
// Stop the encoder. ret = OH_AudioCodec_Stop(audioEnc_); if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) { // Handle exceptions. }Call OH_AudioCodec_Destroy() to destroy the encoder instance and release resources.
NOTE
You only need to call the API once.
// Call OH_AudioCodec_Destroy to destroy the encoder. ret = OH_AudioCodec_Destroy(audioEnc_); if (ret != AV_ERR_OK) { // Handle exceptions. } else { audioEnc_ = NULL; // The encoder cannot be destroyed repeatedly. }
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Media Data Demultiplexing
harmony 鸿蒙Media Data Multiplexing
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to AVCodec Kit
harmony 鸿蒙AVCodec Supported Formats
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Supported Codecs
harmony 鸿蒙Concurrently Creating a Video Decoder and Initializing NativeWindow
harmony 鸿蒙Video Encoding Configurations for Typical Scenarios
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: