harmony 鸿蒙HID DDK Development
HID DDK Development
Overview
The Human Interface Device (HID) Driver Development Kit (DDK) is a toolset that helps you develop HID drivers at the application layer based on the user mode. It provides APIs for accessing HID devices on a host, including creating a HID device, sending events to a device, destroying a device, opening or closing a device, reading and writing a report, and obtaining device information.
The HID DDK can be used to develop drivers for devices that use HID protocol to transfer data over a USB bus, or for devices that use peripheral drivers to create virtual devices to exchange information with non-standard devices.
Basic Concepts
Before developing the HID DDK, you must understand the following basic concepts:
- HID
HID is a type of hardware device that implements interaction between a person and a computer or another electronic device. The primary function of HID is to convert user input (such as a key, a click, or a movement) into a data signal, and send the signal to a host device (such as a computer, tablet, or game console), so that the user can control and operate the device.
- DDK
DDK is a tool package provided by OpenHarmony for developing drivers for non-standard USB serial port devices based on the peripheral framework.
Implementation Principles
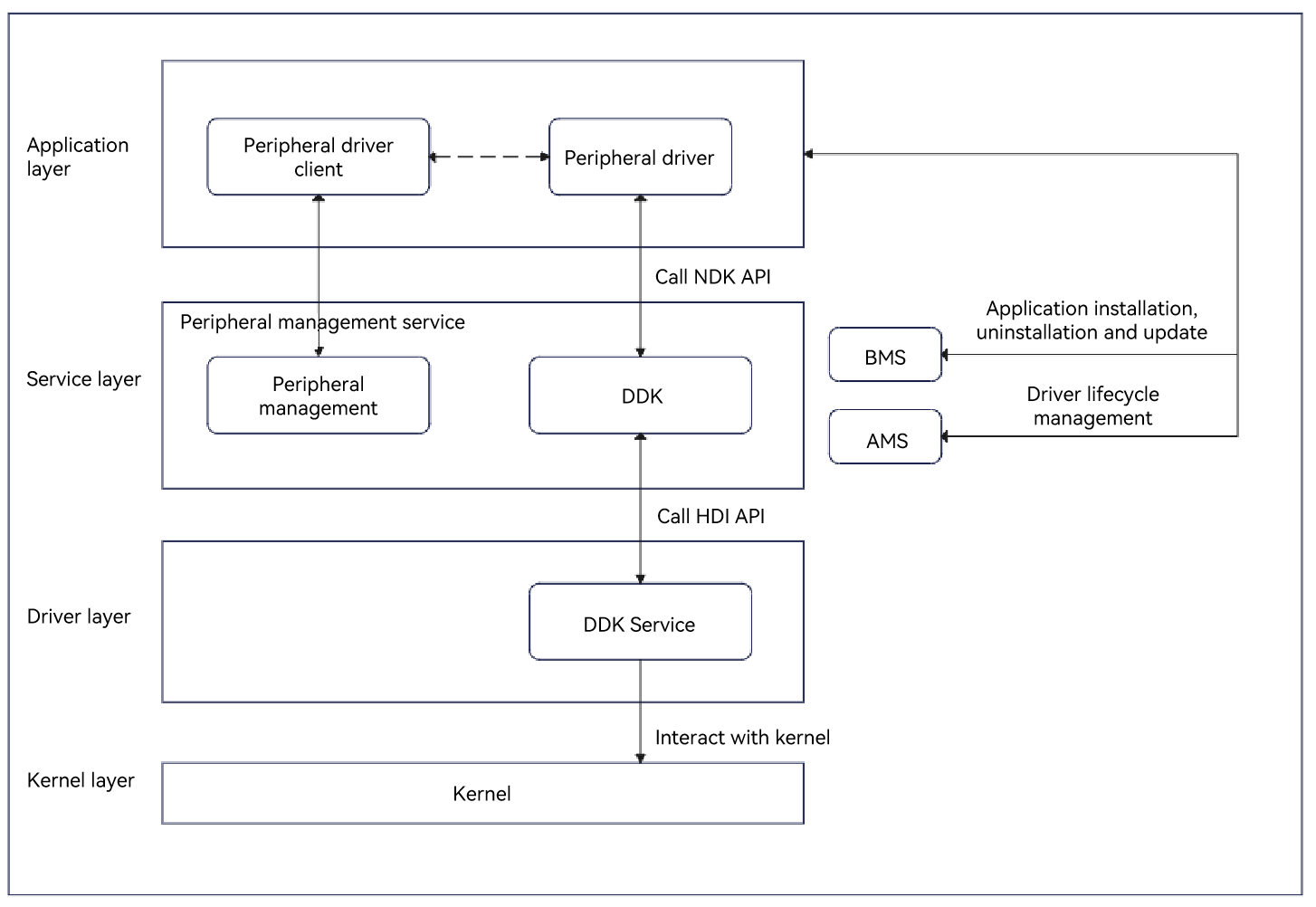
A non-standard peripheral application obtains the HID device ID by using the peripheral management service, and delivers the ID and the action to the HID device driver application through RPC. The driver application calls the HID DDK API to create and destroy a HID device, send events to a HID device, or obtain and parse packets sent from a HID device. The DDK API uses the HDI service to deliver instructions to the kernel driver, and the kernel driver uses instructions to communicate with the device.
Figure 1 Principles of invoking the HID DDK
Constraints
The APIs provided by the HID DDK can be used to develop drivers of non-standard HID devices.
The open APIs of HID DDK can be used only within the lifecycle of DriverExtensionAbility.
Before using the open APIs of the HID DDK, you must declare the matching ACL permissions in module.json5, for example, ohos.permission.ACCESS_DDK_HID.
Available APIs
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| OH_Hid_CreateDevice(Hid_Device *hidDevice, Hid_EventProperties *hidEventProperties) | Creates a HID device. When the device is no longer required, call OH_Hid_DestroyDevice to destroy it. |
| OH_Hid_EmitEvent(int32_t deviceId, const Hid_EmitItem items[], uint16_t length) | Sends an event to a HID device. |
| OH_Hid_DestroyDevice(int32_t deviceId) | Destroys a HID device. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_Init(void) | Initializes the HID DDK. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_Release(void) | Releases the HID DDK. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_Open(uint64_t deviceId, uint8_t interfaceIndex, Hid_DeviceHandle **dev) | Opens the device specified by deviceId and interfaceIndex. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_Close(Hid_DeviceHandle **dev) | Closes a HID device. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_Write(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t length, uint32_t *bytesWritten) | Writes a report to a HID device. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_ReadTimeout(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t buffSize, int timeout, uint32_t *bytesRead) | Reads a report from a HID device within the specified time. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_Read(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t buffSize, uint32_t *bytesRead) | Reads a report from a HID device in the specified mode. The blocking mode (blocking remains active until data can be read) is used by default. You can call OH_Hid_SetNonBlocking to change the mode. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_SetNonBlocking(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, int nonblock) | Sets the device read mode to non-blocking mode. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_GetRawInfo(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, Hid_RawDevInfo *rawDevInfo) | Obtains the raw information of a HID device. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_GetRawName(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, char *data, uint32_t buffSize) | Obtains the raw name of a HID device. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_GetPhysicalAddress(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, char *data, uint32_t buffSize) | Obtains the physical address of a HID device. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_GetRawUniqueId(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, uint8_t *data, uint32_t buffSize) | Obtains the raw unique identifier of a HID device. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_SendReport(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, Hid_ReportType reportType, const uint8_t *data, uint32_t length) | Sends a report to a HID device. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_GetReport(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, Hid_ReportType reportType, uint8_t *data, uint32_t buffSize) | Obtains a report from a HID device. |
| int32_t OH_Hid_GetReportDescriptor(Hid_DeviceHandle *dev, uint8_t *buf, uint32_t buffSize, uint32_t *bytesRead) | Obtains the report descriptor of a HID device. |
For details about the APIs, see HID DDK.
How to Develop
Developing a Basic HID Driver
The following steps you through on how to develop a HID device driver using the HID DDK.
Adding Dynamic Link Libraries
Add the following libraries to CMakeLists.txt.
libhid.z.so
Including Header Files
#include <hid/hid_ddk_api.h>
#include <hid/hid_ddk_types.h>
Create a HID device.
Use OH_Hid_CreateDevice of hid_ddk_api.h to create a HID device. If the operation is successful, a device ID is returned. If the operation fails, an error code is returned.
// Construct HID device properties. std::vector<Hid_DeviceProp> deviceProp = {HID_PROP_DIRECT}; // The vector header file needs to be imported. std::string deviceName = "keyboard"; Hid_Device hidDevice = { .deviceName = deviceName.c_str(), .vendorId = 0x6006, .productId = 0x6006, .version = 1, .bustype = 3, .properties = deviceProp.data(), .propLength = (uint16_t)deviceProp.size() }; // Construct the event properties related to the HID device. std::vector<Hid_EventType> eventType = {HID_EV_ABS, HID_EV_KEY, HID_EV_SYN, HID_EV_MSC}; Hid_EventTypeArray eventTypeArray = {.hidEventType = eventType.data(), .length = (uint16_t)eventType.size()}; std::vector<Hid_KeyCode> keyCode = {HID_BTN_TOOL_PEN, HID_BTN_TOOL_RUBBER, HID_BTN_TOUCH, HID_BTN_STYLUS, HID_BTN_RIGHT}; Hid_KeyCodeArray keyCodeArray = {.hidKeyCode = keyCode.data(), .length = (uint16_t)keyCode.size()}; std::vector<Hid_MscEvent> mscEvent = {HID_MSC_SCAN}; Hid_MscEventArray mscEventArray = {.hidMscEvent = mscEvent.data(), .length = (uint16_t)mscEvent.size()}; std::vector<Hid_AbsAxes> absAxes = {HID_ABS_X, HID_ABS_Y, HID_ABS_PRESSURE}; Hid_AbsAxesArray absAxesArray = {.hidAbsAxes = absAxes.data(), .length = (uint16_t)absAxes.size()}; Hid_EventProperties hidEventProp = { .hidEventTypes = eventTypeArray, .hidKeys = keyCodeArray, .hidAbs = absAxesArray, .hidMiscellaneous = mscEventArray }; // Create a device. The device ID of the device created is returned. int32_t deviceId = OH_Hid_CreateDevice(&hidDevice, &hidEventProp);Send an event to the HID device.
Call OH_Hid_EmitEvent in hid_ddk_api.h to send an event to the device with the specified deviceId.
// Construct the event to be sent. Hid_EmitItem event = {.type = HID_EV_MSC, .code = HID_MSC_SCAN, .value = 0x000d0042}; std::vector<Hid_EmitItem> itemVec; itemVec.push_back(event); // Send the event to a HID device. int32_t ret = OH_Hid_EmitEvent(deviceId, itemVec.data(), (uint16_t)itemVec.size());Release resources.
Call OH_Hid_DestroyDevice in hid_ddk_api.h to destroy the device after all requests are processed and before the application exits.
// Destroy a HID device. int32_t ret = OH_Hid_DestroyDevice(deviceId);
Developing a HID Packet Communication Driver
The following steps you through on how to develop a HID packet communication driver using the HID DDK.
Adding Dynamic Link Libraries
Add the following libraries to CMakeLists.txt.
libhid.z.so
Including Header Files
#include <hid/hid_ddk_api.h>
#include <hid/hid_ddk_types.h>
Initialize the HID DDK.
Call OH_Hid_Init in hid_ddk_api.h to initialize the HID DDK.
// Initialize the HID DDK. OH_Hid_Init();Open the device.
Call OH_Hid_Open in hid_ddk_api.h to open a HID device.
uint64_t deviceId = 0x100000003; uint8_t interfaceIndex1 = 0; uint8_t interfaceIndex2 = 1; Hid_DeviceHandle *dev = NULL; Hid_DeviceHandle *devFeature = NULL; // Open the HID device specified by deviceId and interfaceIndex1. Generally, it is a /dev/hidraw0 file. OH_Hid_Open(deviceId, interfaceIndex1, &dev); // Open the HID device specified by deviceId and interfaceIndex2. Generally, it is a /dev/hidraw1 file. OH_Hid_Open(deviceId, interfaceIndex2, &devFeature);Write/Send a report (a data packet exchanged between a HID device and a host) to the HID device.
If the report type is HID_OUTPUT_REPORT (output report), you can write/send the report in any of the following ways:
Call OH_Hid_Write in hid_ddk_api.h to write an output report to the HID device.
uint8_t data[] = {0x02, 0x02}; uint32_t bytesWritten = 0; // Write a report. int32_t ret = OH_Hid_Write(dev, data, sizeof(data), &bytesWritten);Call OH_Hid_SendReport in hid_ddk_api.h to send an output report to the HID device.
uint8_t data1[2] = {0x00}; // Specify the report ID. data1[0] = 0x02; // Set the report data. data1[1] = 0x02; // Send an output report. int32_t ret = OH_Hid_SendReport(dev, HID_OUTPUT_REPORT, data1, sizeof(data1));
If the report type is HID_FEATURE_REPORT (feature report), call OH_Hid_SendReport in hid_ddk_api.h to send a feature report to the HID device.
uint8_t data2[2] = {0x00}; // Specify the report ID. data2[0] = 0x02; // Set the report data. data2[1] = 0x02; // Send a feature report. int32_t ret = OH_Hid_SendReport(devFeature, HID_FEATURE_REPORT, data2, sizeof(data2));
Read a report from the HID device.
If the report type is HID_INPUT_REPORT (input report), you can read the report in any of the following ways:
Call OH_Hid_Read or OH_Hid_ReadTimeout in hid_ddk_api.h to read an input report from the HID device in blocking mode.
uint8_t data3[9] = {0x00}; uint32_t bytesRead = 0; // Read a report from a HID device. int32_t ret = OH_Hid_Read(dev, data3, sizeof(data3), &bytesRead); uint8_t data4[9] = {0x00}; uint32_t bytesRead = 0; // Read a report from a HID device within the specified time. ret = OH_Hid_ReadTimeout(dev, data4, sizeof(data4), 10000, &bytesRead);Call OH_Hid_SetNonBlocking and OH_Hid_Read in hid_ddk_api.h to read an input report from the HID device in non-blocking mode.
// 1 means to enable non-blocking, and 0 means to disable non-blocking. int32_t ret = OH_Hid_SetNonBlocking(dev, 1); // Wait for user input if no data is input when the code is executed. sleep(1); uint8_t data5[9] = {0}; uint32_t bytesRead = 0; // Read a report from a HID device. ret = OH_Hid_Read(dev, data5, sizeof(data5), &bytesRead);Call OH_Hid_GetReport in hid_ddk_api.h to obtain an input report from the HID device.
uint8_t data6[9] = {0}; // Specify the report ID. data6[0] = 0x00; // Obtain an input report. int32_t ret = OH_Hid_GetReport(dev, HID_INPUT_REPORT, data6, sizeof(data6));
If the report type is HID_FEATURE_REPORT (feature report), call OH_Hid_GetReport in hid_ddk_api.h to obtain a feature report from a HID device.
uint8_t data7[8] = {0}; // Specify the report ID. data7[0] = 0x07; // Obtain a feature report. int32_t ret = OH_Hid_GetReport(devFeature, HID_FEATURE_REPORT, data7, sizeof(data7));
Obtain the raw device information, raw name, physical address, and raw unique identifier of a HID device.
Call OH_Hid_GetRawInfo in hid_ddk_api.h to obtain the raw information about a HID device.
Call OH_Hid_GetRawName to obtain the raw name of a HID device.
Call OH_Hid_GetPhysicalAddress to obtain the physical address of a HID device.
Call OH_Hid_GetRawUniqueId to obtain the raw unique identifier of a HID device. The obtained information can be referenced by applications, for example, displaying device information on the GUI.struct Hid_RawDevInfo rawDevInfo; int32_t ret = OH_Hid_GetRawInfo(dev, &rawDevInfo); char rawName[1024] = {0}; ret = OH_Hid_GetRawName(dev, rawName, sizeof(rawName)); char physicalAddress[1024] = {0}; ret = OH_Hid_GetPhysicalAddress(dev, physicalAddress, sizeof(physicalAddress)); uint8_t uniqueIdData[64] = {0}; ret = OH_Hid_GetRawUniqueId(dev, uniqueIdData, sizeof(uniqueIdData));Obtain the report descriptor.
Call OH_Hid_GetReportDescriptor in hid_ddk_api.h to obtain the HID device report descriptor.
uint8_t desData[1024] = {0}; uint32_t bytesRead = 0; int32_t ret = OH_Hid_GetReportDescriptor(dev, desData, sizeof(desData), &bytesRead);Close the HID device.
Call OH_Hid_Close in hid_ddk_api.h to close the device.
// Close the device. OH_Hid_Close(&dev); OH_Hid_Close(&devFeature);Release the HID DDK.
After the HID device is closed, call OH_Hid_Release in hid_ddk_api.h to release the HID DDK.
// Release the HID DDK. OH_Hid_Release();
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Driver Development Kit
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to Driver Development Kit
harmony 鸿蒙UI-free Driver Development
harmony 鸿蒙Setting Up the Environment
harmony 鸿蒙UI-based Driver Development
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: