harmony 鸿蒙TaskPool简介
TaskPool简介
TaskPool为应用程序提供多线程环境,降低资源消耗、提高系统性能,无需管理线程生命周期。具体接口信息及使用方法详情请见TaskPool。
TaskPool运作机制
TaskPool运作机制示意图
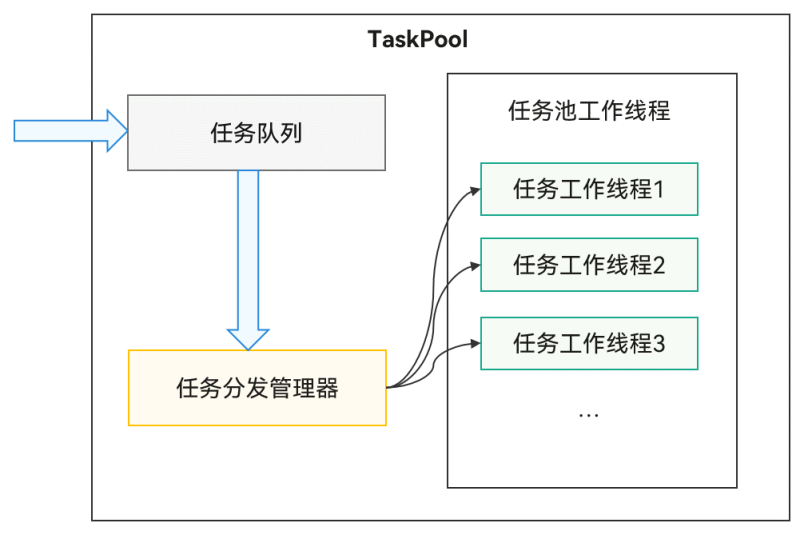
TaskPool支持开发者在宿主线程提交任务到任务队列,系统选择合适的工作线程执行任务,再将结果返回给宿主线程。接口易用,支持任务执行、取消和指定优先级,同时通过系统统一线程管理,结合动态调度及负载均衡算法,可以节约系统资源。系统默认启动一个任务工作线程,任务多时会扩容。工作线程数量上限取决于设备的物理核数,内部管理具体数量,确保调度和执行效率最优。长时间无任务分发时会缩容,减少工作线程数量。具体扩缩容机制详情请见TaskPool扩缩容机制。
TaskPool注意事项
实现任务的函数需要使用@Concurrent装饰器标注,且仅支持在.ets文件中使用。
从API version 11开始,跨并发实例传递带方法的实例对象时,该类必须使用装饰器@Sendable装饰器标注,且仅支持在.ets文件中使用。
任务函数(LongTask除外)在TaskPool工作线程的执行耗时不能超过3分钟(不包含Promise和async/await异步调用的耗时,例如网络下载、文件读写等I/O任务的耗时)。否则,任务将被强制终止。
实现任务的函数入参需满足序列化支持的类型,详情请参见线程间通信对象。目前不支持使用@State装饰器、@Prop装饰器、@Link装饰器等装饰器修饰的复杂类型。
ArrayBuffer参数在TaskPool中默认转移,需要设置转移列表的话可通过接口setTransferList()设置。如果需要多次调用使用ArrayBuffer作为参数的task,则需要通过接口setCloneList()把ArrayBuffer在线程中的传输行为改成拷贝传递,避免对原有对象产生影响。
import { taskpool } from '@kit.ArkTS';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
@Concurrent
function printArrayBuffer(buffer: ArrayBuffer) {
return buffer;
}
function testArrayBuffer() {
const buffer = new ArrayBuffer(1);
const group = new taskpool.TaskGroup();
const task = new taskpool.Task(printArrayBuffer, buffer);
group.addTask(task);
task.setCloneList([buffer]);
for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
taskpool.execute(group).then(() => {
console.info('execute group success');
}).catch((e: BusinessError) => {
console.error(`execute group error: ${e.message}`);
})
}
}
由于不同线程中上下文对象是不同的,因此TaskPool工作线程只能使用线程安全的库,例如UI相关的非线程安全库不能使用。
序列化传输的数据量限制为16MB。
Priority的IDLE优先级是用来标记需要在后台运行的耗时任务(例如数据同步、备份),它的优先级别是最低的。这种优先级的任务只在所有线程都空闲时触发执行,并且同一时间只会有一个IDLE优先级的任务执行。
Promise不支持跨线程传递。TaskPool返回pending或rejected状态的Promise时会失败,返回fulfilled状态的Promise时TaskPool会解析返回的结果,如果结果可以跨线程传递,则返回成功。
不支持在TaskPool工作线程中使用AppStorage。
TaskPool支持开发者在宿主线程封装任务并提交给任务队列,理论上支持的任务数量没有上限。然而,任务的执行效率受限于任务的优先级和系统资源。当工作线程达到最大数量时,任务的执行效率可能会下降。
TaskPool不支持指定任务所运行的线程,任务会被分配到空闲的线程中执行。如果需要指定任务所运行的线程,建议使用Worker。
\@Concurrent装饰器
在使用TaskPool时,执行的并发函数需要使用该装饰器修饰,否则无法通过相关校验。
说明:
从API version 9开始,支持使用\@Concurrent装饰器声明并校验并发函数。
装饰器说明
| \@Concurrent并发装饰器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 装饰器参数 | 无。 |
| 使用场景 | 仅支持在Stage模型的工程中使用。仅支持在.ets文件中使用。 |
| 装饰的函数类型 | 允许标注async函数或普通函数。禁止标注generator、箭头函数、类方法。不支持类成员函数或者匿名函数。 |
| 装饰的函数内的变量类型 | 允许使用local变量、入参和通过import引入的变量。禁止使用闭包变量。 |
| 装饰的函数内的返回值类型 | 支持的类型请查线程间通信对象。 |
说明:
由于\@Concurrent标记的函数不能访问闭包,因此函数内部不能调用当前文件的其他函数,例如:
> function bar() { > } > > @Concurrent > function foo() { > bar(); // 违反闭包原则,报错 > } > ``` ### 装饰器使用示例 #### 并发函数一般使用 并发函数为一个计算两数之和的普通函数,taskpool执行该函数并返回结果。 示例: ```ts import { taskpool } from '@kit.ArkTS'; @Concurrent function add(num1: number, num2: number): number { return num1 + num2; } async function concurrentFunc(): Promise<void> { try { const task: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(add, 1, 2); console.info(`taskpool res is: ${await taskpool.execute(task)}`); // 输出结果:taskpool res is: 3 } catch (e) { console.error(`taskpool execute error is: ${e}}`); } } @Entry @Component struct Index { @State message: string = 'Hello World'; build() { Row() { Column() { Text(this.message) .fontSize(50) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) .onClick(() => { concurrentFunc(); }) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
并发函数返回Promise
并发函数中返回Promise时需要特别关注。如示例所示,testPromise和testPromise1等需处理Promise并返回结果。
示例:
import { taskpool } from '@kit.ArkTS';
@Concurrent
function testPromise(args1: number, args2: number): Promise<number> {
return new Promise<number>((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(args1 + args2);
});
}
@Concurrent
async function testPromise1(args1: number, args2: number): Promise<number> {
return new Promise<number>((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(args1 + args2);
});
}
@Concurrent
async function testPromise2(args1: number, args2: number): Promise<number> {
return await new Promise<number>((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(args1 + args2);
});
}
@Concurrent
function testPromise3() {
return Promise.resolve(1);
}
@Concurrent
async function testPromise4(): Promise<number> {
return 1;
}
@Concurrent
async function testPromise5(): Promise<string> {
return await new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Promise setTimeout after resolve');
}, 1000)
});
}
async function testConcurrentFunc() {
const task1: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise, 1, 2);
const task2: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise1, 1, 2);
const task3: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise2, 1, 2);
const task4: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise3);
const task5: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise4);
const task6: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromise5);
taskpool.execute(task1).then((d: object) => {
console.info(`task1 res is: ${d}`); // 输出结果:task1 res is: 3
}).catch((e: object) => {
console.error(`task1 catch e: ${e}`);
})
taskpool.execute(task2).then((d: object) => {
console.info(`task2 res is: ${d}`);
}).catch((e: object) => {
console.error(`task2 catch e: ${e}`); // 输出结果:task2 catch e: Error: Can't return Promise in pending state
})
taskpool.execute(task3).then((d: object) => {
console.info(`task3 res is: ${d}`); // 输出结果:task3 res is: 3
}).catch((e: object) => {
console.error(`task3 catch e: ${e}`);
})
taskpool.execute(task4).then((d: object) => {
console.info(`task4 res is: ${d}`); // 输出结果:task4 res is: 1
}).catch((e: object) => {
console.error(`task4 catch e: ${e}`);
})
taskpool.execute(task5).then((d: object) => {
console.info(`task5 res is: ${d}`); // 输出结果:task5 res is: 1
}).catch((e: object) => {
console.error(`task5 catch e: ${e}`);
})
taskpool.execute(task6).then((d: object) => {
console.info(`task6 res is: ${d}`); // 输出结果:task6 res is: Promise setTimeout after resolve
}).catch((e: object) => {
console.error(`task6 catch e: ${e}`);
})
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'Hello World';
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Button(this.message)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
testConcurrentFunc();
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
并发函数中使用自定义类或函数
在并发函数中使用自定义类或函数时,需将其定义在不同的文件中,否则会被认为是闭包。如以下示例所示。
示例:
// Index.ets
import { taskpool } from '@kit.ArkTS';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
import { testAdd, MyTestA, MyTestB } from './Test';
function add(arg: number) {
return ++arg;
}
class TestA {
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
name: string = 'ClassA';
}
class TestB {
static nameStr: string = 'ClassB';
}
@Concurrent
function TestFunc() {
// case1:在并发函数中直接调用同文件内定义的类或函数
// 直接调用同文件定义的函数add(),add飘红报错:Only imported variables and local variables can be used in @Concurrent decorated functions. <ArkTSCheck>
// add(1);
// 直接使用同文件定义的TestA构造,TestA飘红报错:Only imported variables and local variables can be used in @Concurrent decorated functions. <ArkTSCheck>
// const a = new TestA('aaa');
// 直接访问同文件定义的TestB的成员nameStr,TestB飘红报错:Only imported variables and local variables can be used in @Concurrent decorated functions. <ArkTSCheck>
// console.info(`TestB name is: ${TestB.nameStr}`);
// case2:在并发函数中调用定义在Test.ets文件并导入当前文件的类或函数
// 输出结果:res1 is: 2
console.info(`res1 is: ${testAdd(1)}`);
const tmpStr = new MyTestA('TEST A');
// 输出结果:res2 is: TEST A
console.info(`res2 is: ${tmpStr.name}`);
// 输出结果:res3 is: MyTestB
console.info(`res3 is: ${MyTestB.nameStr}`);
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'Hello World';
build() {
RelativeContainer() {
Text(this.message)
.id('HelloWorld')
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.alignRules({
center: { anchor: '__container__', align: VerticalAlign.Center },
middle: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.Center }
})
.onClick(() => {
const task = new taskpool.Task(TestFunc);
taskpool.execute(task).then(() => {
console.info('taskpool: execute task success!');
}).catch((e: BusinessError) => {
console.error(`taskpool: execute: Code: ${e.code}, message: ${e.message}`);
})
})
}
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
}
}
// Test.ets
export function testAdd(arg: number) {
return ++arg;
}
@Sendable
export class MyTestA {
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
name: string = 'MyTestA';
}
export class MyTestB {
static nameStr:string = 'MyTestB';
}
并发异步函数中使用Promise
在并发异步函数中使用Promise时,建议搭配await使用。这样TaskPool可以捕获Promise中的异常。推荐使用示例如下。
示例:
import { taskpool } from '@kit.ArkTS';
@Concurrent
async function testPromiseError() {
await new Promise<number>((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(1);
}).then(() => {
throw new Error('testPromise Error');
})
}
@Concurrent
async function testPromiseError1() {
await new Promise<string>((resolve, reject) => {
reject('testPromiseError1 Error msg');
})
}
@Concurrent
function testPromiseError2() {
return new Promise<string>((resolve, reject) => {
reject('testPromiseError2 Error msg');
})
}
async function testConcurrentFunc() {
const task1: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromiseError);
const task2: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromiseError1);
const task3: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(testPromiseError2);
taskpool.execute(task1).then((d: object) => {
console.info(`task1 res is: ${d}`);
}).catch((e: object) => {
console.error(`task1 catch e: ${e}`); // task1 catch e: Error: testPromise Error
})
taskpool.execute(task2).then((d: object) => {
console.info(`task2 res is: ${d}`);
}).catch((e: object) => {
console.error(`task2 catch e: ${e}`); // task2 catch e: testPromiseError1 Error msg
})
taskpool.execute(task3).then((d: object) => {
console.info(`task3 res is: ${d}`);
}).catch((e: object) => {
console.error(`task3 catch e: ${e}`); // task3 catch e: testPromiseError2 Error msg
})
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'Hello World';
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Button(this.message)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
testConcurrentFunc();
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
TaskPool扩缩容机制
扩容机制
一般情况下,开发者向任务队列提交任务时会触发扩容检测。扩容检测首先判断当前空闲的工作线程数是否大于任务数,如果大于,说明线程池中存在空闲工作线程,无需扩容。否则,通过负载计算确定所需工作线程数并创建。
缩容机制
扩容后,TaskPool新建多个工作线程,但当任务数减少后,这些线程就会处于空闲状态,造成资源浪费,因此TaskPool提供缩容机制。TaskPool使用了定时器,定时检测当前负载。定时器30s触发一次,每次尝试释放空闲的工作线程。释放的线程需要满足如下条件:
该线程空闲时长达到30s。
该线程上未执行长时任务(LongTask)。
该线程上没有业务申请且未释放的句柄,例如Timer(定时器)。
该线程处于非调试调优阶段。
该线程中不存在已创建未销毁的子Worker。
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: