harmony 鸿蒙Kernel
Kernel
Introduction
OpenHarmony provides LiteOS and Linux for different levels of systems. LiteOS applies to mini and small systems. Linux applies to small and standard systems.
LiteOS
The OpenHarmony LiteOS kernel is a real-time OS kernel developed for IoT devices. It is as lightweight as the real-time operating system (RTOS) and as easy-to-use as Linux.
The OpenHarmony LiteOS kernel provides basic functions, such as process and thread scheduling, memory management, inter-process communication (IPC) mechanism, and timer management.
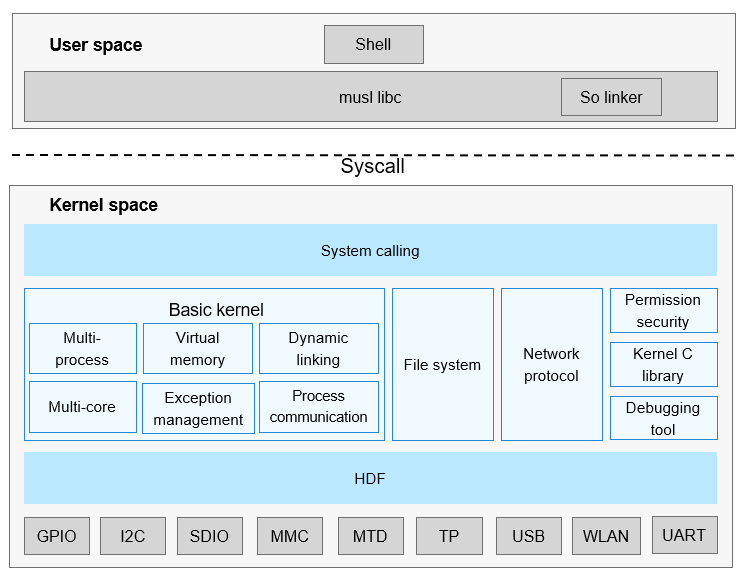
The OpenHarmony LiteOS source code is stored in kernel\_liteos\_a and kernel\_liteos\_m repositories. The kernel\_liteos\_a repository stores kernel code for small and standard systems. The kernel\_liteos\_m repository stores kernel code for mini systems. This document describes the kernel\_liteos\_a repository. The figure below shows the architecture of OpenHarmony LiteOS-A.
Figure 1 OpenHarmony LiteOS-A kernel architecture
Linux
Evolved from the open-source Linux kernel LTS 4.19.y, 5.10.y and 6.6.y, the OpenHarmony Linux kernel has incorporated CVE patches and OpenHarmony features as the OpenHarmony common kernel baseline. Vendors can complete the kernel adaptation by applying the driver patches for boards.
For more information about Linux LTS 4.19.y, visit the official kernel website.
For more information about Linux LTS 5.10.y, visit the official kernel website.
For more information about Linux LTS 6.6.y, visit the official kernel website.
During the build process, you can merge the driver code based on the chip platform and build the kernel image. All patches are licensed under GNU General Public License (GPL) 2.0.
Directory Structure
kernel/
├── linux
│ ├── linux-4.19 # OpenHarmony linux-4.19 common kernel
│ ├── linux-5.10 # OpenHarmony linux-5.10 common kernel
│ ├── linux-6.6 # OpenHarmony linux-6.6 common kernel
│ ├── build
│ │ ├── BUILD.gn # GN file of the build framework
│ │ ├── kernel.mk # Kernel build file
│ │ └── ohos.build # Kernel build component file
│ ├── patches
│ │ ├── linux-4.19 # linux-4.19 patches
│ │ │ ├── common_patch
│ │ │ │ └── hdf.patch # linux-4.19 HDF patches
│ │ │ └── hi3516dv300_patch
│ │ │ └── hi3516dv300.patch # linux-4.19 Hi3516D V300 SOC patches
│ │ ├── linux-5.10
│ │ │ ├── common_patch
│ │ │ │ └── hdf.patch # linux-5.10 HDF patches
│ │ │ └── hi3516dv300_patch
│ │ │ │ └── hi3516dv300.patch # linux-5.10 Hi3516D V300 SOC patches
│ │ │ └── rkrk3568_patch
│ │ │ ├── kernel.patch # linux-5.10 rk3568 SOC patches
│ │ │ └── hdf.patch # linux-5.10 rk3568 customized HDF patches
│ │ └── linux-6.6
│ │ └── rkrk3568_patch
│ │ ├── kernel.patch # linux-6.6 rk3568 SOC patches
│ │ └── hdf.patch # linux-6.6 rk3568 customized HDF patches
│ └── config
│ ├── linux-4.19
│ │ └── arch
│ │ └── arm
│ │ └── configs
│ │ ├── hi3516dv300_small_defconfig # Small-system defconfig of the open-source Hi3516D V300 development board from HiSilicon
│ │ ├── hi3516dv300_standard_defconfig # Standard-system defconfig of the open-source Hi3516D V300 development board from HiSilicon
│ │ ├── small_common_defconfig # Common defconfig of the small-system kernel
│ │ └── standard_common_defconfig # Common defconfig of the standard-system kernel
│ └── linux-5.10 or linux-6.6
│ └── arch
│ └── arm
│ └── configs
│ ├── hi3516dv300_small_defconfig # Small-system defconfig of the open-source Hi3516D V300 development board from HiSilicon
│ ├── hi3516dv300_standard_defconfig # Standard-system defconfig of the open-source Hi3516D V300 development board from HiSilicon
│ ├── small_common_defconfig # Common defconfig of the small-system kernel
│ └── standard_common_defconfig # Common defconfig of the standard-system kernel
└── liteos_a # Baseline code of the LiteOS kernel
├── apps # User-mode init and shell applications
├── arch # Directory of the system architecture, such as arm
│ └── arm # Code for arm
├── bsd # Code of the driver and adaptation layer module related to the FreeBSD, such as the USB module
├── compat # Kernel API compatibility
│ └── posix # POSIX APIs
├── drivers # Kernel drivers
│ └── char # Character device
│ ├── mem # Driver for accessing physical input/output (I/O) devices
│ ├── quickstart # APIs for quick system start
│ ├── random # Driver for random number generators
│ └── video # Framework of the framebuffer driver
├── fs # File system module, which derives from the NuttX open-source project
│ ├── fat # FAT file system
│ ├── jffs2 # JFFS2 file system
│ ├── include # Header files exposed externally
│ ├── nfs # NFS file system
│ ├── proc # proc file system
│ ├── ramfs # Ramfs file system
│ └── vfs # VFS layer
├── kernel # Kernel modules including the process, memory, and IPC modules
│ ├── base # Basic kernel modules, including the scheduling and memory modules
│ ├── common # Common components of the kernel
│ ├── extended # Extended kernel modules, including the dynamic loading, vDSO, and LiteIPC modules
│ ├── include # Header files exposed externally
│ └── user # Init process loading
├── lib # Kernel library
├── net # Network module, which mainly derives from the lwIP open-source project
├── platform # Code for supporting different systems on a chip (SOCs), such as Hi3516D V300
│ ├── hw # Logic code related to clocks and interrupts
│ ├── include # Header files exposed externally
│ └── uart # Logic code related to the serial port
├── platform # Code for supporting different SOCs, such as Hi3516D V300
├── security # Code related to security features, including process permission management and virtual ID mapping management
├── syscall # System calling
└── tools # Building tools as well as related configuration and code
Constraints
LiteOS:
By default, the Hi3518E V300 uses the JFFS2 file system, and Hi3516D V300 uses the FAT file system. Adaptation must be performed if you want to use other file systems.
Usage
LiteOS
For details, see “Usage” in LiteOS-A Kernel README and LiteOS-M Kernel README.
Linux
Apply HDF patches.
Apply the HDF kernel patches matching your kernel version. For details, see the method in kernel.mk in the kernel/linux/build repository.
$(OHOS_BUILD_HOME)/drivers/hdf_core/adapter/khdf/linux/patch_hdf.sh $(OHOS_BUILD_HOME) $(KERNEL_SRC_TMP_PATH) $(KERNEL_PATCH_PATH) $(DEVICE_NAME)Apply the chip driver patches.
The following uses Hi3516D V300 as an example.
Place the patches for the chip component in the corresponding path based on the path and naming rules for the patches of the chip component in kernel.mk in the kernel/linux/build repository.
DEVICE_PATCH_DIR := $(OHOS_BUILD_HOME)/kernel/linux/patches/${KERNEL_VERSION}/$(DEVICE_NAME)_patch DEVICE_PATCH_FILE := $(DEVICE_PATCH_DIR)/$(DEVICE_NAME).patchModify the config file to build.
Place the config file for the chip component in the corresponding path based on the path and naming rules of the chip component in kernel.mk in the kernel/linux/build repository.
KERNEL_CONFIG_PATH := $(OHOS_BUILD_HOME)/kernel/linux/config/${KERNEL_VERSION} DEFCONFIG_FILE := $(DEVICE_NAME)_$(BUILD_TYPE)_defconfigNote:
In the OpenHarmony project build process, patches are installed after kernel/linux/linux-*.* is copied. Before using the version-level build command of OpenHarmony, ensure that the kernel/linux/linux-*.* source code is available.
The kernel built is generated in the kernel directory under the out directory. Modify the config file based on the kernel built, and copy the generated .config file to the corresponding path in the config repository. Then, the configuration takes effect.
Build
The following uses the hispark_taurus development board and Ubuntu x86 server as an example.
Perform a full build for the project to generate the uImage kernel image.
./build.sh --product-name rk3568 # Build the rk3568 image.
--gn-args linux_kernel_version="linux-5.10" # Build the specified kernel version.
Repositories Involved
Kernel
LiteOS:
Linux:
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙DistributedDataManager Subsystem
harmony 鸿蒙System Ability Manager
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: