harmony 鸿蒙UIExtensionAbility
UIExtensionAbility
Overview
UIExtensionAbility is an ExtensionAbility component of the UI type. It is usually used in modular development scenarios where process isolation is required, for example, system dialog boxes, status bars, and capsules. There are two forms: embedded and system pop-ups. - The UIExtensionAbility in embedded mode must be used together with the UIExtensionComponent. Specifically, with the UIExtensionComponent, you can embed the UI provided by the UIExtensionAbility of another application into a UIAbility of your application. The UIExtensionAbility runs in a process independent of the UIAbility for UI layout and rendering. - To start the UIExtensionAbility in system pop-up mode, call requestModalUIExtensionAbility or the specified interface encapsulated in the application.
Constraints
- Currently, the UIExtensionAbility of the sys/commonUI, sysDialog, and sysPicker types can be used only by system applications. For details about the UIExtensionAbility types and corresponding permission control, see the module.json5 file.
- The UIExtensionAbility can be started only by applications that are running in the foreground.
Lifecycle
The UIExtensionAbility class provides the lifecycle callbacks onCreate, onSessionCreate, onSessionDestroy, onForeground, onBackground, and onDestroy. You must override them as required.
- onCreate: called to initialize the service logic when a UIExtensionAbility is created.
- onSessionCreate: called when a UIExtensionContentSession instance is created for the UIExtensionAbility.
- onSessionDestroy: called when a UIExtensionContentSession instance is destroyed for the UIExtensionAbility.
- onForeground: called when the UIExtensionAbility is switched from the background to the foreground.
- onBackground: called when the UIExtensionAbility is switched from the foreground to the background.
- onDestroy: called to clear resources when the UIExtensionAbility is destroyed.
Selecting a Proper Process Model for the UIExtensionAbility
The UIExtensionAbility supports the multiton pattern. Each embedded UI corresponds to a UIExtensionAbility instance. In the multiton scenario, the multi-process model is used by default.
When multiple UIExtensionAbility instances exist in an application, these instances can run in independent processes or share one process. They can also be grouped, and each group share one process. You can select a process model based on the extensionProcessMode field in the module.json5 file. The table below describes the comparison between the process models. |Process Model|extensionProcessMode Field Value|Description| |——–|——–|——–| |One process for all UIExtensionAbility instances in the same bundle|bundle| The UIExtensionAbility instances do not need to communicate with each other across IPCs. Their statuses are dependent and affect each other.| |One process for all UIExtensionAbility instances with the same name|type|The UIExtensionAbility instances of the same type are configured in the same process so that your application can manage them by type.| |One process for each UIExtensionAbility instance|instance|The UIExtensionAbility instances communicate with each other only across IPCs. Their statuses do not affect each other, which is more secure.|
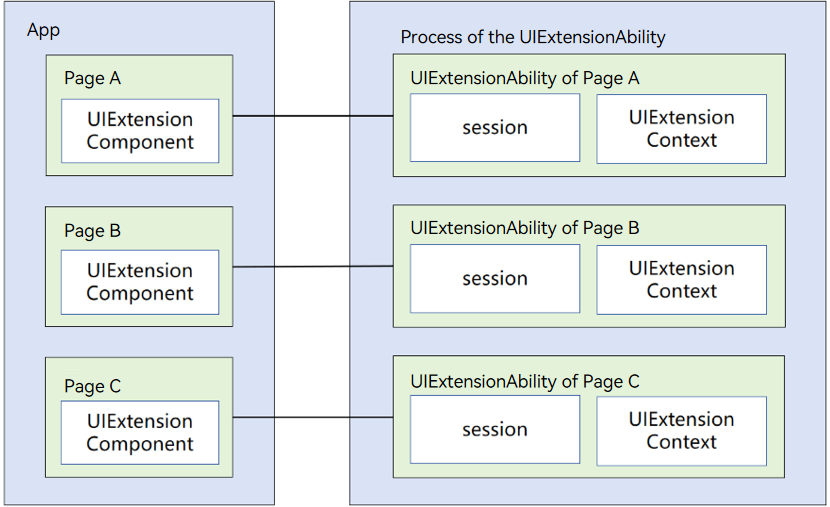
One Process for All UIExtensionAbility Instances in the Bundle
The UIExtensionAbility instances of the same bundle are configured in a process. This makes communication between multiple instances easier. However, the status of these instances affects each other. When an instance in the process exits abnormally, all instances in the process exit.
Figure 1 Bundle-based process model configuration
The sample code of Index.ets is as follows:
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'UIExtension UserA';
private myProxy: UIExtensionProxy|undefined = undefined;
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.fontSize(30)
.size({ width: '100%', height: '50' })
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
UIExtensionComponent(
{
bundleName: 'com.samples.uiextensionability',
abilityName: 'UIExtensionProvider',
moduleName: 'entry',
parameters: {
'ability.want.params.uiExtensionType': 'sys/commonUI',
}
})
.onRemoteReady((proxy) => {
this.myProxy = proxy;
})
.onReceive((data) => {
this.message = JSON.stringify(data);
})
.onTerminated((terminateInfo: TerminationInfo) => {
// This callback is triggered when the started UIExtensionAbility is terminated by calling terminateSelfWithResult or terminateSelf.
// It returns the result of the UIExtensionAbility's normal exit, including the result code and Want data.
this.message = `terminate code: ${terminateInfo.code}, want: ${terminateInfo.want}`;
})
.onError((error: BusinessError) => {
// This callback is invoked when an error occurs during the running of the started UIExtensionAbility.
// It returns the error code and error message when the UIExtensionAbility encounters an exception.
this.message = `error code: ${error.code}, error msg: ${error.message}`;
})
.offset({ x: 0, y: 10 })
.size({ width: 300, height: 300 })
.border({
width: 5,
color: 0x317AF7,
radius: 10,
style: BorderStyle.Dotted
})
UIExtensionComponent(
{
bundleName: 'com.samples.uiextension2',
abilityName: 'UIExtensionProviderB',
moduleName: 'entry',
parameters: {
'ability.want.params.uiExtensionType': 'sys/commonUI',
}
})
.onRemoteReady((proxy) => {
this.myProxy = proxy;
})
.onReceive((data) => {
this.message = JSON.stringify(data);
})
.onTerminated((terminateInfo: TerminationInfo) => {
// This callback is triggered when the started UIExtensionAbility is terminated by calling terminateSelfWithResult or terminateSelf.
// It returns the result of the UIExtensionAbility's normal exit, including the result code and Want data.
this.message = `terminate code: ${terminateInfo.code}, want: ${terminateInfo.want}`;
})
.onError((error: BusinessError) => {
// This callback is invoked when an error occurs during the running of the started UIExtensionAbility.
// It returns the error code and error message when the UIExtensionAbility encounters an exception.
this.message = `error code: ${error.code}, error msg: ${error.message}`;
})
.offset({ x: 0, y: 50 })
.size({ width: 300, height: 300 })
.border({
width: 5,
color: 0x317AF7,
radius: 10,
style: BorderStyle.Dotted
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
Figure 2 Index page generated based on the preceding code
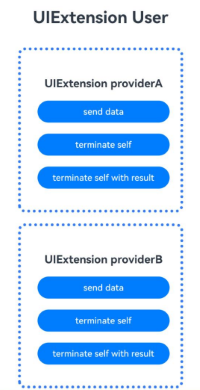
If this process model is used, the process name format is as follows:
process name [{bundleName}:{UIExtensionAbility type}]
Example: process name [com.ohos.intentexecutedemo:xxx]
Figure 3 Bundle-based process model
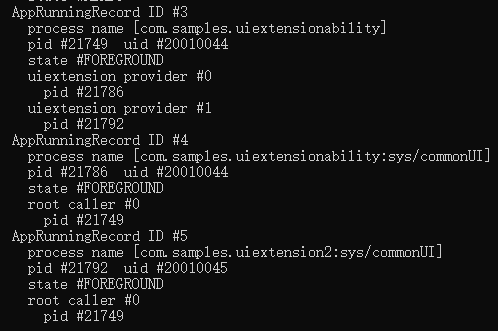
One Process for All UIExtensionAbility Instances of the Same Type
Processes are allocated based on the UIExtensionAbility type. Multiple UIExtensionAbility instances of the same type are configured in the same process so that your application can manage the instances by type.
Figure 4 Type-based process model configuration
The sample code of Index.ets is as follows:
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'UIExtension User';
private myProxy: UIExtensionProxy|undefined = undefined;
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.fontSize(30)
.size({ width: '100%', height: '50' })
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
UIExtensionComponent(
{
bundleName: 'com.samples.uiextensionability',
abilityName: 'UIExtensionProviderA',
moduleName: 'entry',
parameters: {
'ability.want.params.uiExtensionType': 'sys/commonUI',
}
})
.onRemoteReady((proxy) => {
this.myProxy = proxy;
})
.onReceive((data) => {
this.message = JSON.stringify(data);
})
.onTerminated((terminateInfo: TerminationInfo) => {
// This callback is triggered when the started UIExtensionAbility is terminated by calling terminateSelfWithResult or terminateSelf.
// It returns the result of the UIExtensionAbility's normal exit, including the result code and Want data.
this.message = `terminate code: ${terminateInfo.code}, want: ${terminateInfo.want}`;
})
.onError((error: BusinessError) => {
// This callback is invoked when an error occurs during the running of the started UIExtensionAbility.
// It returns the error code and error message when the UIExtensionAbility encounters an exception.
this.message = `error code: ${error.code}, error msg: ${error.message}`;
})
.offset({ x: 0, y: 10 })
.size({ width: 300, height: 300 })
.border({
width: 5,
color: 0x317AF7,
radius: 10,
style: BorderStyle.Dotted
})
UIExtensionComponent(
{
bundleName: 'com.samples.uiextensionability',
abilityName: 'UIExtensionProviderB',
moduleName: 'entry',
parameters: {
'ability.want.params.uiExtensionType': 'sys/commonUI',
}
})
.onRemoteReady((proxy) => {
this.myProxy = proxy;
})
.onReceive((data) => {
this.message = JSON.stringify(data);
})
.onTerminated((terminateInfo: TerminationInfo) => {
// This callback is triggered when the started UIExtensionAbility is terminated by calling terminateSelfWithResult or terminateSelf.
// It returns the result of the UIExtensionAbility's normal exit, including the result code and Want data.
this.message = `terminate code: ${terminateInfo.code}, want: ${terminateInfo.want}`;
})
.onError((error: BusinessError) => {
// This callback is invoked when an error occurs during the running of the started UIExtensionAbility.
// It returns the error code and error message when the UIExtensionAbility encounters an exception.
this.message = `error code: ${error.code}, error msg: ${error.message}`;
})
.offset({ x: 0, y: 50 })
.size({ width: 300, height: 300 })
.border({
width: 5,
color: 0x317AF7,
radius: 10,
style: BorderStyle.Dotted
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
Figure 5 Index page generated based on the preceding code
If this process model is used, the process name format is as follows:
process name [{bundleName}:{UIExtensionAbility name}]
Example: process name [com.ohos.intentexecutedemo:xxx]
Figure 6 Type-based process model
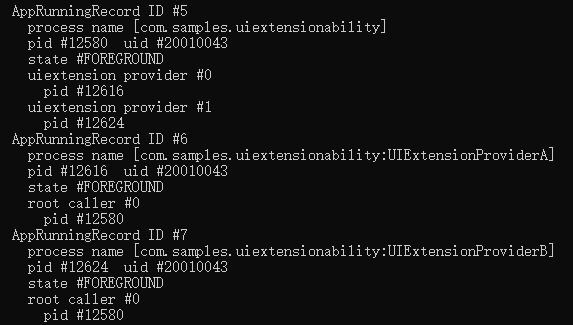
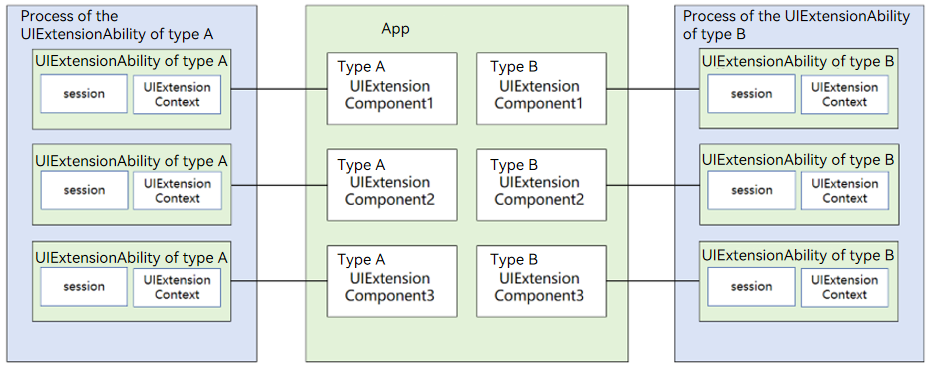
One Process for Each UIExtensionAbility Instance
Processes are allocated based on the UIExtensionAbility instance. That is, each UIExtensionAbility instance has an independent process. In this mode, UIExtensionAbility instances can communicate with each other only through IPCs. However, their statuses do not affect each other, improving security.
Figure 7 Instance-specific process model configuration
The sample code of Index.ets is as follows:
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'UIExtension User'
private myProxy: UIExtensionProxy|undefined = undefined;
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.fontSize(30)
.size({ width: '100%', height: '50' })
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
UIExtensionComponent(
{
bundleName: 'com.samples.uiextensionability',
abilityName: 'UIExtensionProvider',
moduleName: 'entry',
parameters: {
'ability.want.params.uiExtensionType': 'sys/commonUI',
}
})
.onRemoteReady((proxy) => {
this.myProxy = proxy;
})
.onReceive((data) => {
this.message = JSON.stringify(data);
})
.onTerminated((terminateInfo: TerminationInfo) => {
// This callback is triggered when the started UIExtensionAbility is terminated by calling terminateSelfWithResult or terminateSelf.
// It returns the result of the UIExtensionAbility's normal exit, including the result code and Want data.
this.message = `terminate code: ${terminateInfo.code}, want: ${terminateInfo.want}`;
})
.onError((error: BusinessError) => {
// This callback is invoked when an error occurs during the running of the started UIExtensionAbility.
// It returns the error code and error message when the UIExtensionAbility encounters an exception.
this.message = `error code: ${error.code}, error msg: ${error.message}`;
})
.offset({ x: 0, y: 10 })
.size({ width: 300, height: 300 })
.border({
width: 5,
color: 0x317AF7,
radius: 10,
style: BorderStyle.Dotted
})
UIExtensionComponent(
{
bundleName: 'com.samples.uiextensionability',
abilityName: 'UIExtensionProvider',
moduleName: 'entry',
parameters: {
'ability.want.params.uiExtensionType': 'sys/commonUI',
}
})
.onRemoteReady((proxy) => {
this.myProxy = proxy;
})
.onReceive((data) => {
this.message = JSON.stringify(data);
})
.onTerminated((terminateInfo: TerminationInfo) => {
// This callback is triggered when the started UIExtensionAbility is terminated by calling terminateSelfWithResult or terminateSelf.
// It returns the result of the UIExtensionAbility's normal exit, including the result code and Want data.
this.message = `terminate code: ${terminateInfo.code}, want: ${terminateInfo.want}`;
})
.onError((error: BusinessError) => {
// This callback is invoked when an error occurs during the running of the started UIExtensionAbility.
// It returns the error code and error message when the UIExtensionAbility encounters an exception.
this.message = `error code: ${error.code}, error msg: ${error.message}`;
})
.offset({ x: 0, y: 50 })
.size({ width: 300, height: 300 })
.border({
width: 5,
color: 0x317AF7,
radius: 10,
style: BorderStyle.Dotted
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
Figure 8 Index page generated based on the preceding code
If this process model is used, the process name format is as follows:
process name [{bundleName}: {UIExtensionAbility type}: {instance suffix}]
Example: process name [com.ohos.intentexecutedemo:xxx:n]
Figure 9 Instance-specific process model
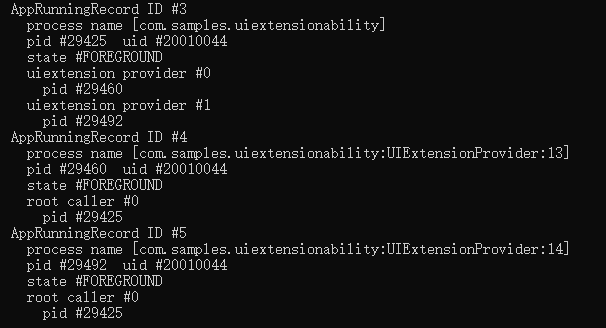
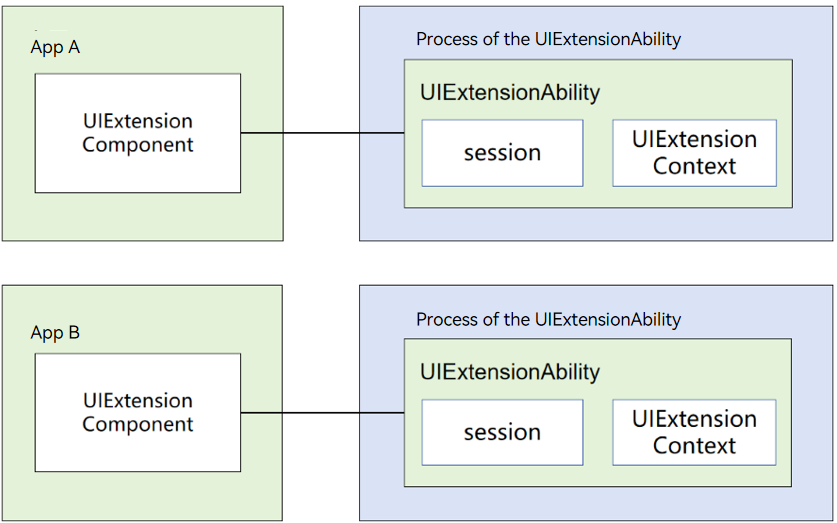
The UIExtensionAbility provides related capabilities through the UIExtensionContext and UIExtensionContentSession. In this document, the started UIExtensionAbility is called the provider, and the UIExtensionComponent that starts the UIExtensionAbility is called the client.
How to Develop
For details about how to develop a system dialog box, see requestModalUIExtension.
Developing the UIExtensionAbility Provider
To implement a provider, create a UIExtensionAbility in DevEco Studio as follows:
In the ets directory of the Module project, right-click and choose New > Directory to create a directory named uiextensionability.
Right-click the uiextensionability directory, and choose New > File to create a file named UIExtensionAbility.ets.
Open the UIExtensionAbility.ets file and import its dependencies. Customize a class that inherits from UIExtensionAbility and implement the lifecycle callbacks onCreate, onSessionCreate, onSessionDestroy, onForeground, onBackground, and onDestroy.
import { Want, UIExtensionAbility, UIExtensionContentSession } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; const TAG: string = '[testTag] UIExtAbility'; export default class UIExtAbility extends UIExtensionAbility { onCreate() { console.log(TAG, `onCreate`); } onForeground() { console.log(TAG, `onForeground`); } onBackground() { console.log(TAG, `onBackground`); } onDestroy() { console.log(TAG, `onDestroy`); } onSessionCreate(want: Want, session: UIExtensionContentSession) { console.log(TAG, `onSessionCreate, want: ${JSON.stringify(want)}}`); let storage: LocalStorage = new LocalStorage(); storage.setOrCreate('session', session); session.loadContent('pages/Extension', storage); } onSessionDestroy(session: UIExtensionContentSession) { console.log(TAG, `onSessionDestroy`); } }Write the entry page file pages/extension.ets, which will be loaded in onSessionCreate of the UIExtensionAbility, and declare “pages/Extension” in the entry\src\main\resources\base\profile\main_pages.json file. The content of extension.ets is as follows:
import { UIExtensionContentSession } from '@kit.AbilityKit'; const TAG: string = `[testTag] ExtensionPage`; @Entry() @Component struct Extension { @State message: string = `UIExtension provider`; localStorage: LocalStorage|undefined = this.getUIContext().getSharedLocalStorage(); private session: UIExtensionContentSession|undefined = this.localStorage?.get<UIExtensionContentSession>('session'); onPageShow() { console.info(TAG, 'show'); } build() { Row() { Column() { Text(this.message) .fontSize(30) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) .textAlign(TextAlign.Center) Button("send data") .width('80%') .type(ButtonType.Capsule) .margin({ top: 20 }) .onClick(() => { this.session?.sendData({ "data": 543321 }); }) Button("terminate self") .width('80%') .type(ButtonType.Capsule) .margin({ top: 20 }) .onClick(() => { this.session?.terminateSelf(); this.localStorage?.clear(); }) Button("terminate self with result") .width('80%') .type(ButtonType.Capsule) .margin({ top: 20 }) .onClick(() => { this.session?.terminateSelfWithResult({ resultCode: 0, want: { bundleName: "com.example.uiextensiondemo", parameters: { "result": 123456 } } }) }) } } .height('100%') } }Register the UIExtensionAbility in the module.json5 file of the module. Set type to that configured for the UIExtensionAbility and srcEntry to the code path of the UIExtensionAbility. The extensionProcessMode field identifies the multiton process model. Here, bundle is used as an example.
{ "module": { "extensionAbilities": [ { "name": "UIExtensionProvider", "srcEntry": "./ets/uiextensionability/UIExtensionAbility.ets", "description": "UIExtensionAbility", "type": "sys/commonUI", "exported": true, "extensionProcessMode": "bundle" }, ] } }Developing the UIExtensionAbility Client
You can load the UIExtensionAbility in the application through the UIExtensionComponent on the UIAbility page. For example, add the following content to the home page file pages/Index.ets:
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'UIExtension User';
private myProxy: UIExtensionProxy|undefined = undefined;
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.fontSize(30)
.size({ width: '100%', height: '50' })
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
UIExtensionComponent(
{
bundleName: 'com.example.uiextensiondemo',
abilityName: 'UIExtensionProvider',
moduleName: 'entry',
parameters: {
'ability.want.params.uiExtensionType': 'sys/commonUI',
}
})
.onRemoteReady((proxy) => {
this.myProxy = proxy;
})
.onReceive((data) => {
this.message = JSON.stringify(data);
})
.onTerminated((terminateInfo: TerminationInfo) => {
// This callback is triggered when the started UIExtensionAbility is terminated by calling terminateSelfWithResult or terminateSelf.
// It returns the result of the UIExtensionAbility's normal exit, including the result code and Want data.
this.message = `terminate code: ${terminateInfo.code}, want: ${terminateInfo.want}`;
})
.onError((error: BusinessError) => {
// This callback is invoked when an error occurs during the running of the started UIExtensionAbility.
// It returns the error code and error message when the UIExtensionAbility encounters an exception.
this.message = `error code: ${error.code}, error msg: ${error.message}`;
})
.offset({ x: 0, y: 30 })
.size({ width: 300, height: 300 })
.border({
width: 5,
color: 0x317AF7,
radius: 10,
style: BorderStyle.Dotted
})
Button("sendData")
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.offset({ x: 0, y: 60 })
.width('80%')
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.margin({
top: 20
})
.onClick(() => {
this.myProxy?.send({
"data": 123456,
"message": "data from component"
})
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Obtaining Reasons for Abnormal Application Exits
harmony 鸿蒙UIAbility Backup and Restore
harmony 鸿蒙Using Explicit Want to Start an Application Component
harmony 鸿蒙Introduction to Ability Kit
harmony 鸿蒙AbilityStage Component Container
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataAbility
harmony 鸿蒙Accessing a DataShareExtensionAbility from the FA Model
harmony 鸿蒙Common action and entities Values (Not Recommended)
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: