harmony 鸿蒙C/C++ Library Mechanisms
C/C++ Library Mechanisms
The OpenHarmony NDK provides industry standard libraries libc and libc++. This topic describes the mechanisms of these libraries in OpenHarmony. Understanding these mechanisms helps you avoid pitfalls during NDK development.
C++ Compatibility
In OpenHarmony, both the system library and application native library use C++ standard library (see libc++). However, the C++ standard library used by the system library is updated with the image version, and the C++ standard library used by the app native library is updated with the SDK used for compilation. Since both the C++ standard libraries have multiple major versions, the different update approach may cause ABI compatibility issues. To solve this problem, OpenHarmony differentiates the two C++ standard libraries as follows:
- System library: uses libc++.so, which is released with the system image.
- Application native library: uses libc++_shared.so, which is released with the application.
The two libraries use different C++ namespaces. libc++.so uses __h as the namespace of C++ symbols, and libc++_shared.so uses __n1 as the namespace of C++ symbols.
NOTE
The system and applications must use their own C++ standard library. Currently, native APIs are C interfaces only, which can isolate the C++ running environments of them. When a Harmony Archive (HAR) is used to build an application, if the libc++_shared.so version in the HAR is different from the libc++_shared.so version of the application, only one version will be installed in the application, which may cause compatibility issues. To solve the problem, you can use the same SDK version to update the HAR.
Known C++ Compatibility Issues
If “symbol not found, s=__emutls_get_address” is reported when an application starts or when dlopen() is called, update the SDK of the application or HAR. This symbol is not provided by libc++_shared.so in the SDK of API version 9 or earlier, and is available since API version 11.
musl libc Dynamic Linker
Linker Namespace
Different from the namespace in C++, a linker namespace (also referred to as ns) is a mechanism provided by the dynamic linker to isolate shared libraries within different namespaces. For example, the system native library can load the native library in the system directories, such as /system/lib64 or /vendor/lib64; a common application can load only the common application native library and NDK library, but cannot directly load the system native library.
The dynamic linker must be associated with a specific namespace no matter whether it loads the shared library specified by DT_NEEDED in compilation or calls dlopen to load a shared library.
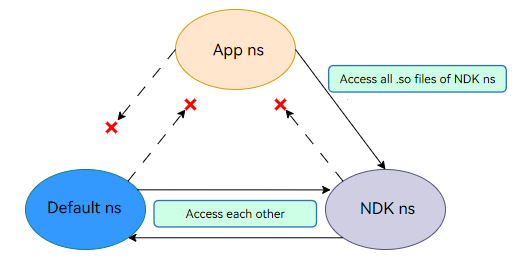
OpenHarmony has the following types of linker namespaces:
Default ns: default namespace created for locating the .so files in /system/lib{abi} and /vendor/lib{abi} when the dynamic linker stats.
NDK ns: default namespace created for exposing the NDK interfaces in .so files in /system/lib{abi}/ndk when the dynamic linker stats.
App ns: namespace created when an application is started. It directs to the application installation path (sandbox path), that is, the .so file used to load the application.
The namespace mechanism restricts the invocation between the application native library and the system native library, as shown in the following figure.
- The default ns and NDK ns can access all .so files of each other, but cannot access the .so files of the app ns.
- The app ns can access all .so files of the NDK ns, but cannot access the .so files of the default ns.
rpath
Run-time path (rpath) is a mechanism for specifying the runtime search path of a shared library. This mechanism allows a runtime search path to be embedded in an executable file or shared library. The dynamic linker uses this path to find required libraries.
The namespace mechanism allows an application to load only the native libraries in its installation directory (for example, libs/arm64 on the ARM64 platform). If an application needs to load multiple native libraries, the native library in the newly created directory cannot be loaded. In this case, you can use the rpath mechanism to specify the search path during compilation.
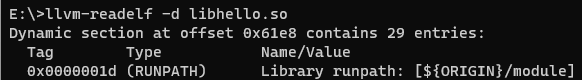
For example, libhello.so in the application installation directory lib/arm64 depends on libworld.so in the newly created directory lib/arm64/module. Set rpath in the CMakeList.txt file of the application and compile the file, and run readelf to view the rpath of libhello.so. As shown in the following figure, $ORIGIN indicates the path of libhello.so. The application can load libworld.so in the module directory during running.
SET(CMAKE_BUILD_WITH_INSTALL_RPATH TRUE)
SET(CMAKE_INSTALL_RPATH "\${ORIGIN}/module")
dlclose
You can use dlclose to uninstall a dynamic library.
symbol-version
symbol-version is a symbol retrieval mechanism provided by libc for symbol relocation in dynamic linking. It supports relocation of the symbols of different versions and helps solve the problem of duplicate symbols. For details, see LD Version Scripts (GNU Gnulib).
Fortified Check of the FD in select()
If the file descriptor (fd) passed in FD_SET or FD_CLR is not within the value range [0, 1024), abort crash will be triggered.
If the fd value passed in FD_ISSET is not within the value range [0, 1024), false will be returned.
Globalization
Since API version 12, locale in newlocale() and setlocale() can be set to any of the following values: C, C.UTF-8, en_US, en_US.UTF-8, zh_CN, and zh_CN.UTF-8. strtod_l, wcstod_l, and localeconv support the locale values zh_CN and zh_CN.UTF-8. Note that strtod_l() and wcstod_l() do not support conversion of hexadecimal numbers and floating-point numbers.
fdsan
File descriptor sanitizer (fdsan) helps detect the user-after-close and double-close issues of FDs.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Building an NDK Project with CMake
harmony 鸿蒙Building an NDK Project with the DevEco Studio Template
harmony 鸿蒙NDK Project Building Overview
harmony 鸿蒙Building an NDK Project with Prebuilt Libraries
harmony 鸿蒙Creating an NDK Project
harmony 鸿蒙C/C++ Memory Error Detection
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: