harmony 鸿蒙Distributed Extension Development
Distributed Extension Development
Introduction
The distributed service allows a device to extend its capabilities by cooperating with other devices in various complex scenarios.
As it is inconvenient for users to use a single account on different devices, the cross-device collaboration capability is provided, enabling a message synchronization mechanism for collaboration between applications on mobile phones and other devices such as watches.
Available Capabilities
Data interaction: implements cross-device transmission of data, including text messages, byte streams, images, and transport streams. (Only text interaction is supported for third-party applications.)
Typical Use Cases
During cross-device collaboration, when device A is running in the background and device B is running in the foreground, Distributed Management Service (DMS) allows the system to activate DistributedExtension to implement synchronous data transmission across devices. For example, when an application runs in the background on the mobile phone and in the foreground on the watch, DMS starts DistributedExtension to synchronize uplink messages on the watch to the application on the mobile phone.
Basic concepts
Before you get started, familiarize yourself with the following concepts:
- DMS
A framework that provides distributed component management capabilities. * UIAbility
A component that implements tasks specific to application UIs, such as lifecycle management, user interaction, and UI rendering. * Extension
A component that extends application functions or implements cross-device collaboration. It allows applications to run some tasks in the background or migrates some functions to other devices for execution, implementing distributed capabilities. * Byte stream
Data of the ArrayBuffer type, which can be used to store binary data, for example, image or audio data. * Transport stream
Media streams that can be used to transmit images, audios, text information, and bytes.
Implementation Principles
The application on device A integrates DistributedExtension. When DSoftBus on device A receives a message from the application, DistributedExtension starts the application background service on device A to send the application message from device B to the application service.
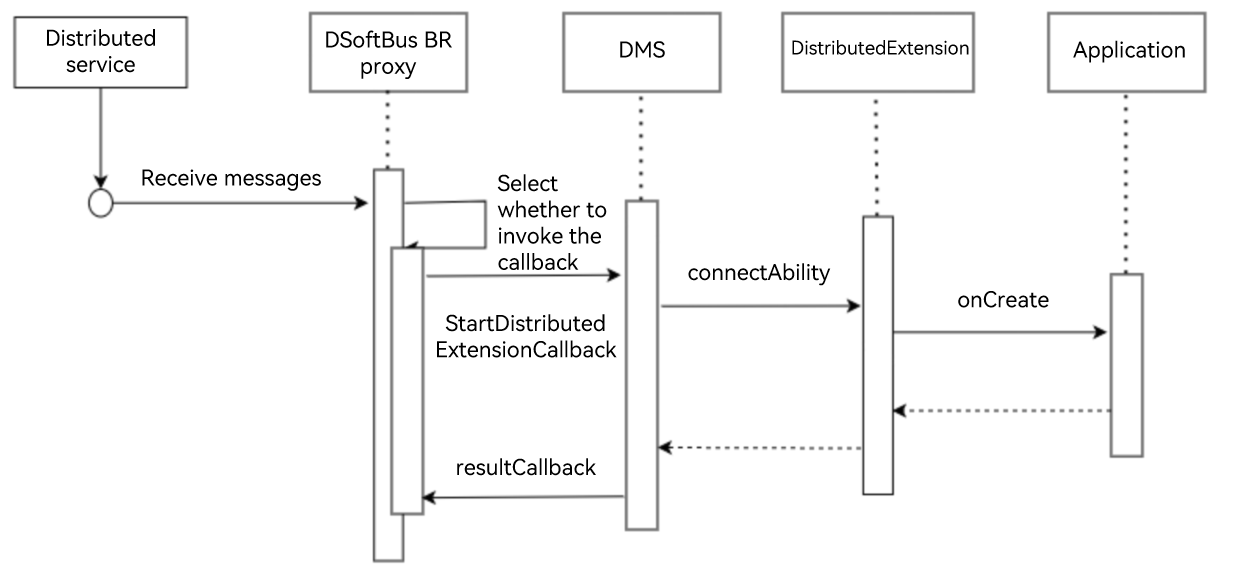
Constraints
- You need to log in with the same HUAWEI ID on different devices.
- Cross-device collaboration is supported only for UIAbility applications with the same bundle name on different devices.
Environment Preparation
Environment requirements
You have logged in to devices A and B with the same HUAWEI ID and the two devices are successfully networked through Bluetooth.
Environment Setup
- Install DevEco Studio 4.1 or later on the PC.
- Update the public-SDK to API version 20 or later. For details, see OpenHarmony SDK Upgrade Assistant.
- Enable Bluetooth on devices A and B to implement networking.
Environment Verification
Connect devices A and B to the PC and run the shell command on the PC:
hdc shell
hidumper -s 4700 -a "buscenter -l remote_device_info"
If the networking is successful, the number of networking devices is displayed, for example, remote device num = 1.
How to Develop
Cross-device connection management enables real-time processing of application background messages through the distributed OS, providing users with more efficient experience.
APIs
For details about how to use the DistributedExtensionAbility APIs, see DistributedExtensionAbility API Reference.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| onCreate(want: Want): void; | Creates a distributed collaboration task. |
| onDestroy(): void; | Destroys a distributed collaboration task. |
| onCollaborate(wantParam: Record): AbilityConstant.CollaborateResult; | Called when distributed collaboration is requested. |
How to Develop
- Register the
Extensioncomponent in the configuration file.
In the application configuration file module.json5, add the "extensionAbilities" field, set "type" to "distributed", and add an entry whose "name" is "ohos.extension.DistributedExtension" to “metadata”.
Example:
"extensionAbilities": [
{
"name": "EntrydistributedAbility",
"srcEntry": "./ets/entrybackupability/EntryDistributedAbility.ets",
"type": "distributed",
"exported": false,
"metadata": [
{
"name": "ohos.extension.DistributedExtension",
}
],
"srcEntry": "./ets/common/MDSExtension.ts",
}
]
- Import the required modules.
import { AbilityConstant, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { abilityConnectionManager, DistributedExtensionAbility } from '@kit.DistributedServiceKit';
- Customize the
MDSExtension.etsfile. Specifically, inherit theDistributedExtensionAbilityclass and rewrite theonCreate,onDestroyandonCollaboratemethods to create and destroy DistributedExtension and implement connection callback.
The following is an empty MDSExtension.ets file. You can observe its lifecycle based on the corresponding Logger.
import { AbilityConstant, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { abilityConnectionManager, DistributedExtensionAbility } from '@kit.DistributedServiceKit';
export default class DistributedExtension extends DistributedExtensionAbility {
onCreate(want: Want) {
console.info(`DistributedExtension Create ok`);
console.info(`DistributedExtension on Create want: ${JSON.stringify(want)}`);
console.info(`DistributedExtension on Create end`);
}
onCollaborate(wantParam: Record<string, Object>) {
console.info(`DistributedExtension onCollabRequest Accept to the result of Ability collaborate`);
let sessionId = -1;
const collaborationValues = wantParam["CollaborationValues"] as abilityConnectionManager.CollaborationValues;
if (collaborationValues == undefined) {
return sessionId;
}
console.info(`onCollab, collaborationValues: ${JSON.stringify(collaborationValues)}`);
return AbilityConstant.CollaborateResult.ACCEPT;
}
onDestroy() {
console.info(`DistributedExtension onDestroy ok`);
}
}
Common Inquiry
What should I do if device B does not receive the response message from device A?
Possible Causes
Devices are not networking. As a result, the connection between device A and device B times out.
Solution
Enable USB debugging on device A and device B, and use a USB cable to connect the devices to the PC. Run the following shell command on the PC:
hdc shell
hidumper -s 4700 -a "buscenter -l remote_device_info"
If remote device num = 0 is displayed in the command output, the networking has failed. Ensure that you log in to devices using the same HUAWEI ID and connect them through Bluetooth. If the networking is successful, the number of networking devices is displayed, for example, remote device num = 1.
What should I do if ongoing collaboration services are interrupted because no operation is performed on the application for a long time?
Possible Causes
During service collaboration, DMS keeps listening for the collaboration lifecycle. After the operation lasts for 10 seconds, the collaboration is ended.
Solution
Resend the message to restart the collaboration.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Distributed Service Kit
harmony 鸿蒙UIAbility Connection Development
harmony 鸿蒙Distributed Camera Development
harmony 鸿蒙Distributed Device Management Development
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: