harmony 鸿蒙Using ArkGuard for Obfuscation
Using ArkGuard for Obfuscation
Enabling Obfuscation
How to Use
The source code obfuscation feature is integrated into the system and can be enabled in DevEco Studio.
Enabling the obfuscation switch
To enable obfuscation, set the enable field to true under arkOptions.obfuscation.ruleOptions in the build-profile.json5 file of your module.
"arkOptions": { "obfuscation": { "ruleOptions": { "enable": true, "files": ["./obfuscation-rules.txt"], } } }Configuring obfuscation rules
Enabling the obfuscation switch activates the default settings, which include obfuscation of local variables and parameters. To enable additional obfuscation features, customize the obfuscation-rules.txt file specified in the files field. Note that the default values in this file may vary across different versions of DevEco Studio.
For example, in DevEco Studio of version 5.0.3.600 and later, the obfuscation configuration file is as follows, which indicates that property name obfuscation, top-level scope name obfuscation, file name obfuscation, and imported/exported name obfuscation are enabled.
-enable-property-obfuscation -enable-toplevel-obfuscation -enable-filename-obfuscation -enable-export-obfuscationYou can also add comments to the obfuscation rule file by prefixing lines with the # symbol. For example:
# options: -enable-property-obfuscation -enable-toplevel-obfuscation -enable-filename-obfuscation # -enable-export-obfuscation -keep-property-name # white list for dynamic property namesFor details about how to configure obfuscation options, see Obfuscation Configuration Guidelines. For details about all configuration files involved in obfuscation, see Obfuscation Configuration Files.
Specifying release compilation
Currently, source code obfuscation is supported only for release builds, not for debug builds. This means that obfuscation will only be applied when a module is compiled in release mode, not in debug mode. You can view and modify the build mode by referring to Specifying a Build Mode.
NOTE
The differences between release and debug builds extend beyond obfuscation. To determine whether application behavior differences are due to obfuscation, you should enable or disable the obfuscation switch rather than simply switching between release and debug builds.
NOTE
- In DevEco Studio versions prior to 5.0.3.600, code obfuscation is enabled by default for new projects, and code developed on the stage model using API version 10 or later is automatically obfuscated.
- In DevEco Studio 5.0.3.600 and later versions, code obfuscation is disabled by default for new projects. If you want to enable obfuscation, set the ruleOptions.enable field in the build-profile.json5 file of the module to true. The obfuscation-rules.txt file has the following options enabled by default: -enable-property-obfuscation, -enable-toplevel-obfuscation, -enable-filename-obfuscation, and -enable-export-obfuscation. You can customize the obfuscation settings as needed.
Obfuscation Configuration Files
obfuscation-rules.txtFor HAP, HAR, and HSP modules, the arkOptions.obfuscation.ruleOptions.files field in the build-profile.json5 file specifies obfuscation rules applied during module compilation. A default obfuscation-rules.txt file is created when a new project is set up.
consumer-rules.txtFor HAR and HSP modules, an additional arkOptions.obfuscation.consumerFiles field is available in the build-profile.json5 file. This field specifies obfuscation rules that should be applied when this package is depended upon in the current compilation process. A default consumer-rules.txt file is created when a new HAR or HSP module is set up. The key difference between consumer-rules.txt and obfuscation-rules.txt is as follows: obfuscation-rules.txt applies to the compilation of the current module, whereas consumer-rules.txt applies to the compilation of other modules that depend on the current module.
"arkOptions": { "obfuscation": { "ruleOptions": { "enable": true, "files": ["./obfuscation-rules.txt"], } "consumerFiles": ["./consumer-rules.txt"] } }obfuscation.txtUnlike the above two files, obfuscation.txt is automatically generated based on consumer-rules.txt and the obfuscation rules of dependent modules during HAR or HSP compilation. It exists as a compilation product within the released HAR or HSP package. When other applications depend on this package, the obfuscation rules are merged and applied to the current compilation process. For details about the generation and merging logic of obfuscation.txt, see Obfuscation Rule Merging Strategies.
NOTE
For third-party libraries, the obfuscation.txt file only takes effect when the module’s oh-package.json5 file depends on the library. If the dependency is specified in the project’s oh-package.json5 file, the obfuscation.txt file in the third-party library will not take effect.
The following table summarizes the differences between these configuration files.
| Configuration File | Configuration Type | Modifiable | Affects Obfuscation of This Module | Affects Obfuscation of Other Modules |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| obfuscation-rules.txt | Customizable | Yes | Yes | No |
| consumer-rules.txt | Customizable | Yes | No | Yes |
| obfuscation.txt | Compilation product | Not applicable (automatically generated during HAR or HSP compilation) | Not applicable | Yes |
Obfuscation Configuration Guidelines
- When -enable-toplevel-obfuscation is configured, access to global variables using globalThis fails. To rectify the fault, use -keep-global-name to retain the global variable name.
- After the preceding adaptation is successful, configure -enable-property-obfuscation, and perform adaptation in the following scenarios:
- If the code statically defines properties but dynamically accesses them (or vice versa), use -keep-property-name to retain the property names. Example:
// Static definition, dynamic access: The property name is static during object definition, but is accessed by dynamically constructing the property name (usually using string concatenation). const obj = { staticName: value // Static definition }; const fieldName = 'static' + 'Name'; // Dynamic construction of the property name console.log(obj[fieldName]); // Use square bracket notation to dynamically access the property.// Dynamic definition, static access: The property name is determined during object definition through a dynamic expression, but is statically accessed using dot notation (assuming that you know the result of the property name). const obj = { [dynamicExpression]: value // Dynamic definition }; console.log(obj.dynamicPropertyName); // Use dot notation to statically access the property. - If the code uses dot notation to access fields not defined in ArkTS/TS/JS code (for example, native so libraries, fixed JSON files, or database fields):
- For API calls to so libraries (for example, import testNapi from ‘library.so’; testNapi.foo();), use -keep-property-name to retain the property name foo.
- For fields in JSON files, use -keep-property-name to retain the JSON field names.
- For database-related fields, use -keep-property-name to retain the database field names.
- When building a HAR module for use by other modules, use -keep-property-name in the consumer-rules.txt file of the HAR module to retain properties that should not be re-obfuscated. The consumer-rules.txt file generates the obfuscation.txt file during HAR compilation. When the HAR module is depended upon by other modules, DevEco Studio parses the obfuscation.txt file to read the trustlist.
- Verify application functionality and identify any missed scenarios. If the application functionality is abnormal, find the code of the error line in the corresponding intermediate products based on the obfuscated error stack, identify the necessary trustlist configurations, and use -keep-property-name to retain them.
- If the code statically defines properties but dynamically accesses them (or vice versa), use -keep-property-name to retain the property names. Example:
- After the preceding adaptations are successful, configure -enable-export-obfuscation, and perform adaptation in the following scenarios:
- For HSP modules that provide interfaces and properties to other modules, use -keep-global-name to retain the interface names and -keep-property-name to retain the property names in exposed classes/interfaces.
- When building HAR modules for use by other modules, use -keep-global-name to retain interface names and -keep-property-name to retain the property names in exposed classes/interfaces in the obfuscation-rules.txt file.
- For API calls to so libraries (for example, import { napiA } from ‘library.so’), use -keep-global-name to retain the so interface name napiA.
- Verify application functionality and interface call functionality when the module is depended upon, and identify any missed scenarios. If the application functionality is abnormal, find the code of the error line in the corresponding intermediate products based on the obfuscated error stack, identify the necessary trustlist configurations, and retain them.
- After the preceding adaptations are successful, configure -enable-filename-obfuscation, and perform adaptation in the following scenarios:
- If the code contains dynamic import statements (for example, const path = ‘./filePath’; import(path)), use -keep-file-name filePath to retain the file path.
- If the application has a routerMap configuration that describes routing information, use -keep-file-name to retain the page source file path, which is specified by pageSourceFile field in the routing information.
- If the code uses ohmUrl for page navigation (for example, router.pushUrl({url: ‘@bundle:com.example.routerPage/Library/Index’})), use -keep-file-name to retain the path.
- Verify application functionality and identify any missed scenarios. If the application function is abnormal and the error stack contains obfuscated paths, you can query the original path in the build/default/[…]/release/obfuscation/nameCache.json file within the module and then locate the source code file. You can also use the hstack plugin to trigger automatic deobfuscation of error stacks. After locating the paths to retain, use -keep-file-name to retain them.
Remarks
- Currently, custom obfuscation plugins are not supported in the hvigor build process.
- If a module that depends on an obfuscated HAR enables obfuscation, the HAR will be obfuscated again.
Viewing Obfuscation Effects
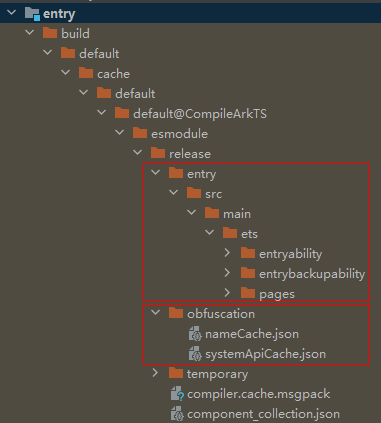
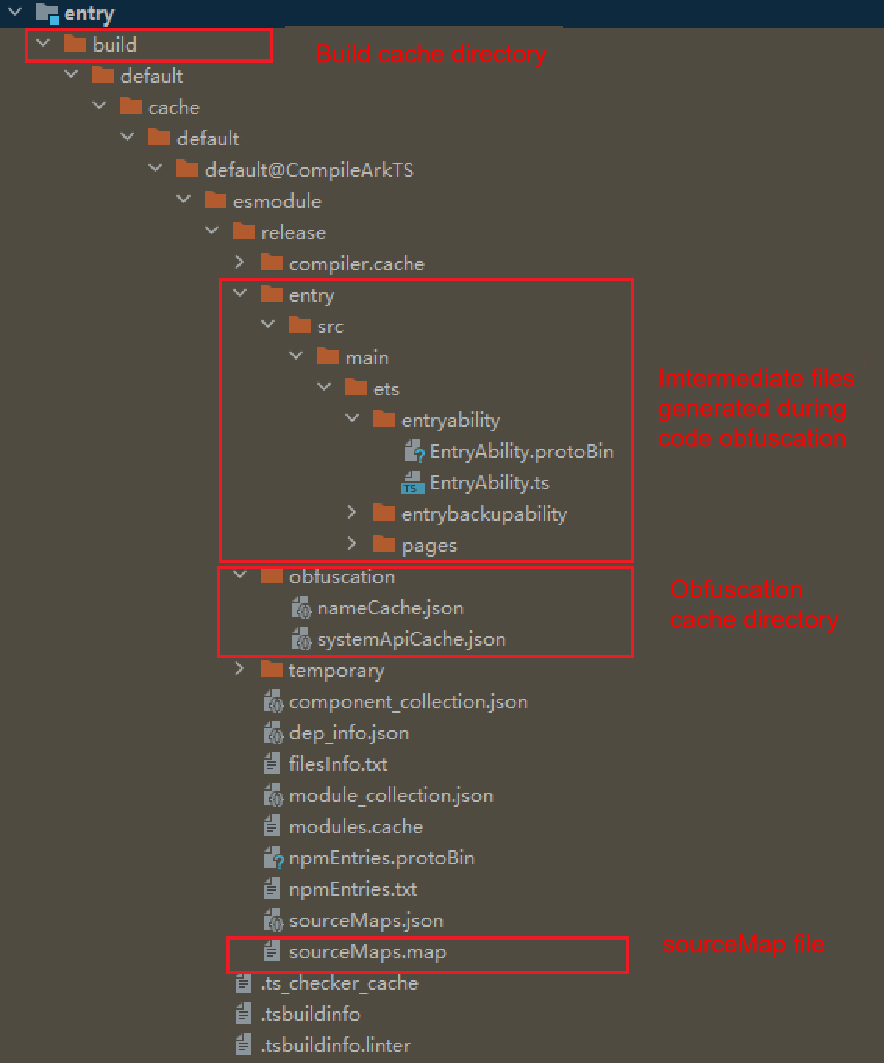
After obfuscation is complete, intermediate products are generated. You can find the obfuscated intermediate products in the build directory of the compilation output, as well as the name mapping file and system API trustlist files.
- Obfuscated file directory: build/default/[…]/release/moduleName
- Directory of the name mapping file and system API trustlist file: build/default/[…]/release/obfuscation
- The name mapping file, named nameCache.json, records the mappings between source code names and names after obfuscation.
- The system API trustlist file, named systemApiCache.json, records the APIs and property names that will not be obfuscated.
Deobfuscating Error Stacks
In applications that have undergone obfuscation, code names are changed, making the error stacks printed during crashes harder to understand because they do not match the source code exactly. You can use the hstack plugin in Command Line Tools of DevEco Studio to deobfuscate the source code stack and analyze issues. The deobfuscation tool requires the sourceMaps.map file and the obfuscation name mapping file nameCache.json generated during compilation. Be sure to back them up locally.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Configuring arkOptions in build-profile.json5
harmony 鸿蒙Ark Bytecode File Format
harmony 鸿蒙Naming Conventions for Ark Bytecode Functions
harmony 鸿蒙Ark Bytecode Fundamentals
harmony 鸿蒙Overview of Ark Bytecode
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: