harmony 鸿蒙\@ObservedV2装饰器和\@Trace装饰器:类属性变化观测
\@ObservedV2装饰器和\@Trace装饰器:类属性变化观测
为了增强状态管理框架对类对象中属性的观测能力,开发者可以使用\@ObservedV2装饰器和\@Trace装饰器装饰类以及类中的属性。
\@ObservedV2和\@Trace提供了对嵌套类对象属性变化直接观测的能力,是状态管理V2中相对核心的能力之一。在阅读本文档前,建议提前阅读:状态管理概述来了解状态管理V2整体的能力架构。
说明:
\@ObservedV2与\@Trace装饰器从API version 12开始支持。
概述
\@ObservedV2装饰器与\@Trace装饰器用于装饰类以及类中的属性,使得被装饰的类和属性具有深度观测的能力:
- \@ObservedV2装饰器与\@Trace装饰器需要配合使用,单独使用\@ObservedV2装饰器或\@Trace装饰器没有任何作用。
- 被\@Trace装饰器装饰的属性property变化时,仅会通知property关联的组件进行刷新。
- 在嵌套类中,嵌套类中的属性property被\@Trace装饰且嵌套类被\@ObservedV2装饰时,才具有触发UI刷新的能力。
- 在继承类中,父类或子类中的属性property被\@Trace装饰且该property所在类被\@ObservedV2装饰时,才具有触发UI刷新的能力。
- 未被\@Trace装饰的属性用在UI中无法感知到变化,也无法触发UI刷新。
- \@ObservedV2的类实例目前不支持使用JSON.stringify进行序列化。
- 使用\@ObservedV2与\@Trace装饰器的类,需通过new操作符实例化后,才具备被观测变化的能力。
状态管理V1版本对嵌套类对象属性变化直接观测的局限性
现有状态管理V1版本无法实现对嵌套类对象属性变化的直接观测。
@Observed
class Father {
son: Son;
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.son = new Son(name, age);
}
}
@Observed
class Son {
name: string;
age: number;
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State father: Father = new Father("John", 8);
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(`name: ${this.father.son.name} age: ${this.father.son.age}`)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
this.father.son.age++;
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
在上述代码中,点击Text组件增加age的值时,不会触发UI刷新。原因在于现有的状态管理框架无法观测到嵌套类中属性age的值变化。V1版本的解决方案是使用\@ObjectLink装饰器与自定义组件来实现观测。
@Observed
class Father {
son: Son;
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.son = new Son(name, age);
}
}
@Observed
class Son {
name: string;
age: number;
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
@Component
struct Child {
@ObjectLink son: Son;
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(`name: ${this.son.name} age: ${this.son.age}`)
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
this.son.age++;
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State father: Father = new Father("John", 8);
build() {
Column() {
Child({son: this.father.son})
}
}
}
通过这种方式虽然能够实现对嵌套类中属性变化的观测,但是当嵌套层级较深时,代码将会变得十分复杂,易用性差。因此推出类装饰器\@ObservedV2与成员变量装饰器\@Trace,增强对嵌套类中属性变化的观测能力。
装饰器说明
| \@ObservedV2类装饰器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 装饰器参数 | 无。 |
| 类装饰器 | 装饰class。需要放在class的定义前,使用new创建类对象。 |
| \@Trace成员变量装饰器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 装饰器参数 | 无。 |
| 可装饰的变量 | class中成员属性。属性的类型可以为number、string、boolean、class、Array、Date、Map、Set等类型。 |
观察变化
使用\@ObservedV2装饰的类中被\@Trace装饰的属性具有被观测变化的能力,当该属性值变化时,会触发该属性绑定的UI组件刷新。
- 在嵌套类中使用\@Trace装饰的属性具有被观测变化的能力。
@ObservedV2
class Son {
@Trace age: number = 100;
}
class Father {
son: Son = new Son();
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {
father: Father = new Father();
build() {
Column() {
// 当点击改变age时,Text组件会刷新
Text(`${this.father.son.age}`)
.onClick(() => {
this.father.son.age++;
})
}
}
}
- 在继承类中使用\@Trace装饰的属性具有被观测变化的能力。
@ObservedV2
class Father {
@Trace name: string = "Tom";
}
class Son extends Father {
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {
son: Son = new Son();
build() {
Column() {
// 当点击改变name时,Text组件会刷新
Text(`${this.son.name}`)
.onClick(() => {
this.son.name = "Jack";
})
}
}
}
- 类中使用\@Trace装饰的静态属性具有被观测变化的能力。
@ObservedV2
class Manager {
@Trace static count: number = 1;
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {
build() {
Column() {
// 当点击改变count时,Text组件会刷新
Text(`${Manager.count}`)
.onClick(() => {
Manager.count++;
})
}
}
}
- \@Trace装饰内置类型时,可以观测各自API导致的变化:
| 类型 | 可观测变化的API |
|---|---|
| Array | push、pop、shift、unshift、splice、copyWithin、fill、reverse、sort |
| Date | setFullYear, setMonth, setDate, setHours, setMinutes, setSeconds, setMilliseconds, setTime, setUTCFullYear, setUTCMonth, setUTCDate, setUTCHours, setUTCMinutes, setUTCSeconds, setUTCMilliseconds |
| Map | set, clear, delete |
| Set | add, clear, delete |
使用限制
\@ObservedV2与\@Trace装饰器存在以下使用限制:
- 非\@Trace装饰的成员属性用在UI上无法触发UI刷新。
@ObservedV2
class Person {
id: number = 0;
@Trace age: number = 8;
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {
person: Person = new Person();
build() {
Column() {
// age被@Trace装饰,用在UI中可以触发UI刷新
Text(`${this.person.age}`)
.onClick(() => {
this.person.age++; // 点击会触发UI刷新
})
// id未被@Trace装饰,用在UI中不会触发UI刷新
Text(`${this.person.id}`) // 当id变化时不会刷新
.onClick(() => {
this.person.id++; // 点击不会触发UI刷新
})
}
}
}
- \@ObservedV2仅能装饰class,无法装饰自定义组件。
@ObservedV2 // 错误用法,编译时报错
struct Index {
build() {
}
}
- \@Trace不能用在没有被\@ObservedV2装饰的class上。
class User {
id: number = 0;
@Trace name: string = "Tom"; // 错误用法,编译时报错
}
- \@Trace是class中属性的装饰器,不能用在struct中。
@ComponentV2
struct Comp {
@Trace message: string = "Hello World"; // 错误用法,编译时报错
build() {
}
}
- \@ObservedV2、\@Trace不能与\@Observed、\@Track混合使用。
@Observed
class User {
@Trace name: string = "Tom"; // 错误用法,编译时报错
}
@ObservedV2
class Person {
@Track name: string = "Jack"; // 错误用法,编译时报错
}
- 使用\@ObservedV2与\@Trace装饰的类不能和\@State等V1的装饰器混合使用,编译时报错。
// 以@State装饰器为例
@ObservedV2
class Job {
@Trace jobName: string = "Teacher";
}
@ObservedV2
class Info {
@Trace name: string = "Tom";
@Trace age: number = 25;
job: Job = new Job();
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State info: Info = new Info(); // 无法混用,编译时报错
build() {
Column() {
Text(`name: ${this.info.name}`)
Text(`age: ${this.info.age}`)
Text(`jobName: ${this.info.job.jobName}`)
Button("change age")
.onClick(() => {
this.info.age++;
})
Button("Change job")
.onClick(() => {
this.info.job.jobName = "Doctor";
})
}
}
}
- 继承自\@ObservedV2的类无法和\@State等V1的装饰器混用,运行时报错。
// 以@State装饰器为例
@ObservedV2
class Job {
@Trace jobName: string = "Teacher";
}
@ObservedV2
class Info {
@Trace name: string = "Tom";
@Trace age: number = 25;
job: Job = new Job();
}
class Message extends Info {
constructor() {
super();
}
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: Message = new Message(); // 无法混用,运行时报错
build() {
Column() {
Text(`name: ${this.message.name}`)
Text(`age: ${this.message.age}`)
Text(`jobName: ${this.message.job.jobName}`)
Button("change age")
.onClick(() => {
this.message.age++;
})
Button("Change job")
.onClick(() => {
this.message.job.jobName = "Doctor";
})
}
}
}
- \@ObservedV2的类实例目前不支持使用JSON.stringify进行序列化。
- 使用\@ObservedV2与\@Trace装饰器的类,需通过new操作符实例化后,才具备被观测变化的能力。
使用场景
嵌套类场景
在下面的嵌套类场景中,Pencil类是Son类中最里层的类,Pencil类被\@ObservedV2装饰且属性length被\@Trace装饰,此时length的变化能够被观测到。
\@Trace装饰器与现有状态管理框架的\@Track与\@State装饰器的能力不同,@Track使class具有属性级更新的能力,但并不具备深度观测的能力;而\@State只能观测到对象本身以及第一层的变化,对于多层嵌套场景只能通过封装自定义组件,搭配\@Observed和\@ObjectLink来实现观测。
- 点击Button(“change length”),length是被\@Trace装饰的属性,它的变化可以触发关联的UI组件,即UINode (1)的刷新,并输出”id: 1 renderTimes: x”的日志,其中x根据点击次数依次增长。
- 自定义组件Page中的son是常规变量,因此点击Button(“assign Son”)并不会观测到变化。
- 当点击Button(“assign Son”)后,再点击Button(“change length”)并不会引起UI刷新。因为此时son的地址改变,其关联的UI组件并没有关联到最新的son。
@ObservedV2
class Pencil {
@Trace length: number = 21; // 当length变化时,会刷新关联的组件
}
class Bag {
width: number = 50;
height: number = 60;
pencil: Pencil = new Pencil();
}
class Son {
age: number = 5;
school: string = "some";
bag: Bag = new Bag();
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Page {
son: Son = new Son();
renderTimes: number = 0;
isRender(id: number): number {
console.info(`id: ${id} renderTimes: ${this.renderTimes}`);
this.renderTimes++;
return 40;
}
build() {
Column() {
Text('pencil length'+ this.son.bag.pencil.length)
.fontSize(this.isRender(1)) // UINode (1)
Button("change length")
.onClick(() => {
// 点击更改length值,UINode(1)会刷新
this.son.bag.pencil.length += 100;
})
Button("assign Son")
.onClick(() => {
// 由于变量son非状态变量,因此无法刷新UINode(1)
this.son = new Son();
})
}
}
}
继承类场景
\@Trace支持在类的继承场景中使用,无论是在基类还是继承类中,只有被\@Trace装饰的属性才具有被观测变化的能力。 以下例子中,声明class GrandFather、Father、Uncle、Son、Cousin,继承关系如下图。
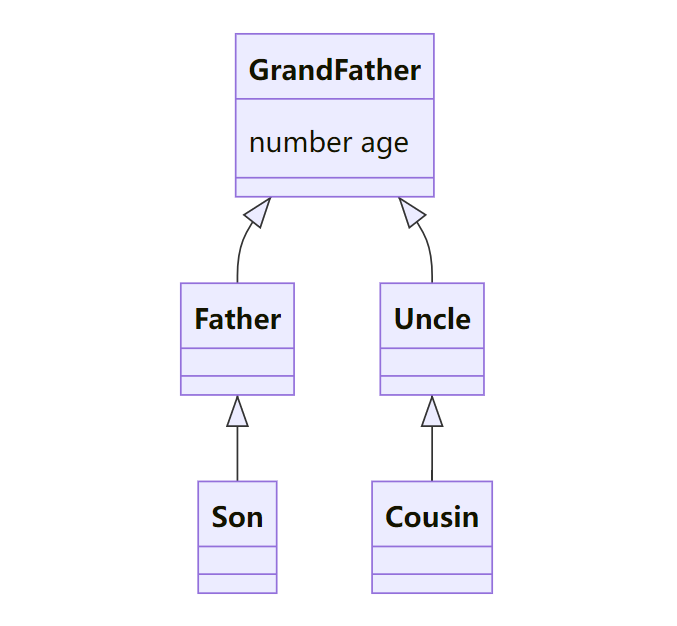
创建类Son和类Cousin的实例,点击Button(‘change Son age’)和Button(‘change Cousin age’)可以触发UI的刷新。
@ObservedV2
class GrandFather {
@Trace age: number = 0;
constructor(age: number) {
this.age = age;
}
}
class Father extends GrandFather{
constructor(father: number) {
super(father);
}
}
class Uncle extends GrandFather {
constructor(uncle: number) {
super(uncle);
}
}
class Son extends Father {
constructor(son: number) {
super(son);
}
}
class Cousin extends Uncle {
constructor(cousin: number) {
super(cousin);
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {
son: Son = new Son(0);
cousin: Cousin = new Cousin(0);
renderTimes: number = 0;
isRender(id: number): number {
console.info(`id: ${id} renderTimes: ${this.renderTimes}`);
this.renderTimes++;
return 40;
}
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(`Son ${this.son.age}`)
.fontSize(this.isRender(1))
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
Text(`Cousin ${this.cousin.age}`)
.fontSize(this.isRender(2))
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
Button('change Son age')
.onClick(() => {
this.son.age++;
})
Button('change Cousin age')
.onClick(() => {
this.cousin.age++;
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
\@Trace装饰基础类型的数组
\@Trace装饰数组时,使用支持的API能够观测到变化。支持的API见观察变化。 在下面的示例中\@ObservedV2装饰的Arr类中的属性numberArr是\@Trace装饰的数组,当使用数组API操作numberArr时,可以观测到对应的变化。注意使用数组长度进行判断以防越界访问。
let nextId: number = 0;
@ObservedV2
class Arr {
id: number = 0;
@Trace numberArr: number[] = [];
constructor() {
this.id = nextId++;
this.numberArr = [0, 1, 2];
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {
arr: Arr = new Arr();
build() {
Column() {
Text(`length: ${this.arr.numberArr.length}`)
.fontSize(40)
Divider()
if (this.arr.numberArr.length >= 3) {
Text(`${this.arr.numberArr[0]}`)
.fontSize(40)
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr[0]++;
})
Text(`${this.arr.numberArr[1]}`)
.fontSize(40)
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr[1]++;
})
Text(`${this.arr.numberArr[2]}`)
.fontSize(40)
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr[2]++;
})
}
Divider()
ForEach(this.arr.numberArr, (item: number, index: number) => {
Text(`${index} ${item}`)
.fontSize(40)
})
Button('push')
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr.push(50);
})
Button('pop')
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr.pop();
})
Button('shift')
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr.shift();
})
Button('splice')
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr.splice(1, 0, 60);
})
Button('unshift')
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr.unshift(100);
})
Button('copywithin')
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr.copyWithin(0, 1, 2);
})
Button('fill')
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr.fill(0, 2, 4);
})
Button('reverse')
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr.reverse();
})
Button('sort')
.onClick(() => {
this.arr.numberArr.sort();
})
}
}
}
\@Trace装饰对象数组
- \@Trace装饰对象数组personList以及Person类中的age属性,因此当personList、age改变时均可以观测到变化。
- 点击Text组件更改age时,Text组件会刷新。
let nextId: number = 0;
@ObservedV2
class Person {
@Trace age: number = 0;
constructor(age: number) {
this.age = age;
}
}
@ObservedV2
class Info {
id: number = 0;
@Trace personList: Person[] = [];
constructor() {
this.id = nextId++;
this.personList = [new Person(0), new Person(1), new Person(2)];
}
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {
info: Info = new Info();
build() {
Column() {
Text(`length: ${this.info.personList.length}`)
.fontSize(40)
Divider()
if (this.info.personList.length >= 3) {
Text(`${this.info.personList[0].age}`)
.fontSize(40)
.onClick(() => {
this.info.personList[0].age++;
})
Text(`${this.info.personList[1].age}`)
.fontSize(40)
.onClick(() => {
this.info.personList[1].age++;
})
Text(`${this.info.personList[2].age}`)
.fontSize(40)
.onClick(() => {
this.info.personList[2].age++;
})
}
Divider()
ForEach(this.info.personList, (item: Person, index: number) => {
Text(`${index} ${item.age}`)
.fontSize(40)
})
}
}
}
\@Trace装饰Map类型
- 被\@Trace装饰的Map类型属性可以观测到调用API带来的变化,包括 set、clear、delete。
- 因为Info类被\@ObservedV2装饰且属性memberMap被\@Trace装饰,点击Button(‘init map’)对memberMap赋值也可以观测到变化。
@ObservedV2
class Info {
@Trace memberMap: Map<number, string> = new Map([[0, "a"], [1, "b"], [3, "c"]]);
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct MapSample {
info: Info = new Info();
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
ForEach(Array.from(this.info.memberMap.entries()), (item: [number, string]) => {
Text(`${item[0]}`)
.fontSize(30)
Text(`${item[1]}`)
.fontSize(30)
Divider()
})
Button('init map')
.onClick(() => {
this.info.memberMap = new Map([[0, "a"], [1, "b"], [3, "c"]]);
})
Button('set new one')
.onClick(() => {
this.info.memberMap.set(4, "d");
})
Button('clear')
.onClick(() => {
this.info.memberMap.clear();
})
Button('set the key: 0')
.onClick(() => {
this.info.memberMap.set(0, "aa");
})
Button('delete the first one')
.onClick(() => {
this.info.memberMap.delete(0);
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
\@Trace装饰Set类型
- 被\@Trace装饰的Set类型属性可以观测到调用API带来的变化,包括 add, clear, delete。
- 因为Info类被\@ObservedV2装饰且属性memberSet被\@Trace装饰,点击Button(‘init set’)对memberSet赋值也可以观察变化。
@ObservedV2
class Info {
@Trace memberSet: Set<number> = new Set([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]);
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct SetSample {
info: Info = new Info();
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
ForEach(Array.from(this.info.memberSet.entries()), (item: [number, number]) => {
Text(`${item[0]}`)
.fontSize(30)
Divider()
})
Button('init set')
.onClick(() => {
this.info.memberSet = new Set([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]);
})
Button('set new one')
.onClick(() => {
this.info.memberSet.add(5);
})
Button('clear')
.onClick(() => {
this.info.memberSet.clear();
})
Button('delete the first one')
.onClick(() => {
this.info.memberSet.delete(0);
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
\@Trace装饰Date类型
- \@Trace装饰的Date类型属性可以观测调用API带来的变化,包括 setFullYear、setMonth、setDate、setHours、setMinutes、setSeconds、setMilliseconds、setTime、setUTCFullYear、setUTCMonth、setUTCDate、setUTCHours、setUTCMinutes、setUTCSeconds、setUTCMilliseconds。
- 因为Info类被\@ObservedV2装饰且属性selectedDate被\@Trace装饰,点击Button(‘set selectedDate to 2023-07-08’)对selectedDate赋值也可以观测到变化。
@ObservedV2
class Info {
@Trace selectedDate: Date = new Date('2021-08-08')
}
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct DateSample {
info: Info = new Info()
build() {
Column() {
Button('set selectedDate to 2023-07-08')
.margin(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.info.selectedDate = new Date('2023-07-08');
})
Button('increase the year by 1')
.margin(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.info.selectedDate.setFullYear(this.info.selectedDate.getFullYear() + 1);
})
Button('increase the month by 1')
.margin(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.info.selectedDate.setMonth(this.info.selectedDate.getMonth() + 1);
})
Button('increase the day by 1')
.margin(10)
.onClick(() => {
this.info.selectedDate.setDate(this.info.selectedDate.getDate() + 1);
})
DatePicker({
start: new Date('1970-1-1'),
end: new Date('2100-1-1'),
selected: this.info.selectedDate
})
}.width('100%')
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙\@AnimatableExtend装饰器:定义可动画属性
harmony 鸿蒙AppStorage:应用全局的UI状态存储
harmony 鸿蒙\@Builder装饰器:自定义构建函数