harmony 鸿蒙Asynchronous Task Development Using Node-API
Asynchronous Task Development Using Node-API
When to Use
For time-consuming operations, you can use napi_create_async_work to create an asynchronous work object to prevent the ArkTS thread where env exists from being blocked while ensuring the performance and response of your application. You can use asynchronous work objects in the following scenarios:
File operations: You can use asynchronous work objects in complex file operations or when a large file needs to be read to prevent the ArkTS thread where env exists from being blocked.
Network request: When your application needs to wait for a response to a network request, using an asynchronous worker object can improve its response performance without affecting the main thread.
Database operation: Using asynchronous work objects in complex database query or write operations can improve the concurrency performance of your application without compromising the running of the main thread.
Image processing: When large images need to be processed or complex image algorithms need to be executed, asynchronous work objects can ensure normal running of the main thread and improve the real-time performance of your application.
The napi_queue_async_work API uses the uv_queue_work capability at the bottom layer and manages the lifecycle of napi_value in the callback.
You can use a promise or a callback to implement asynchronous calls. The following are sample codes for the two methods:
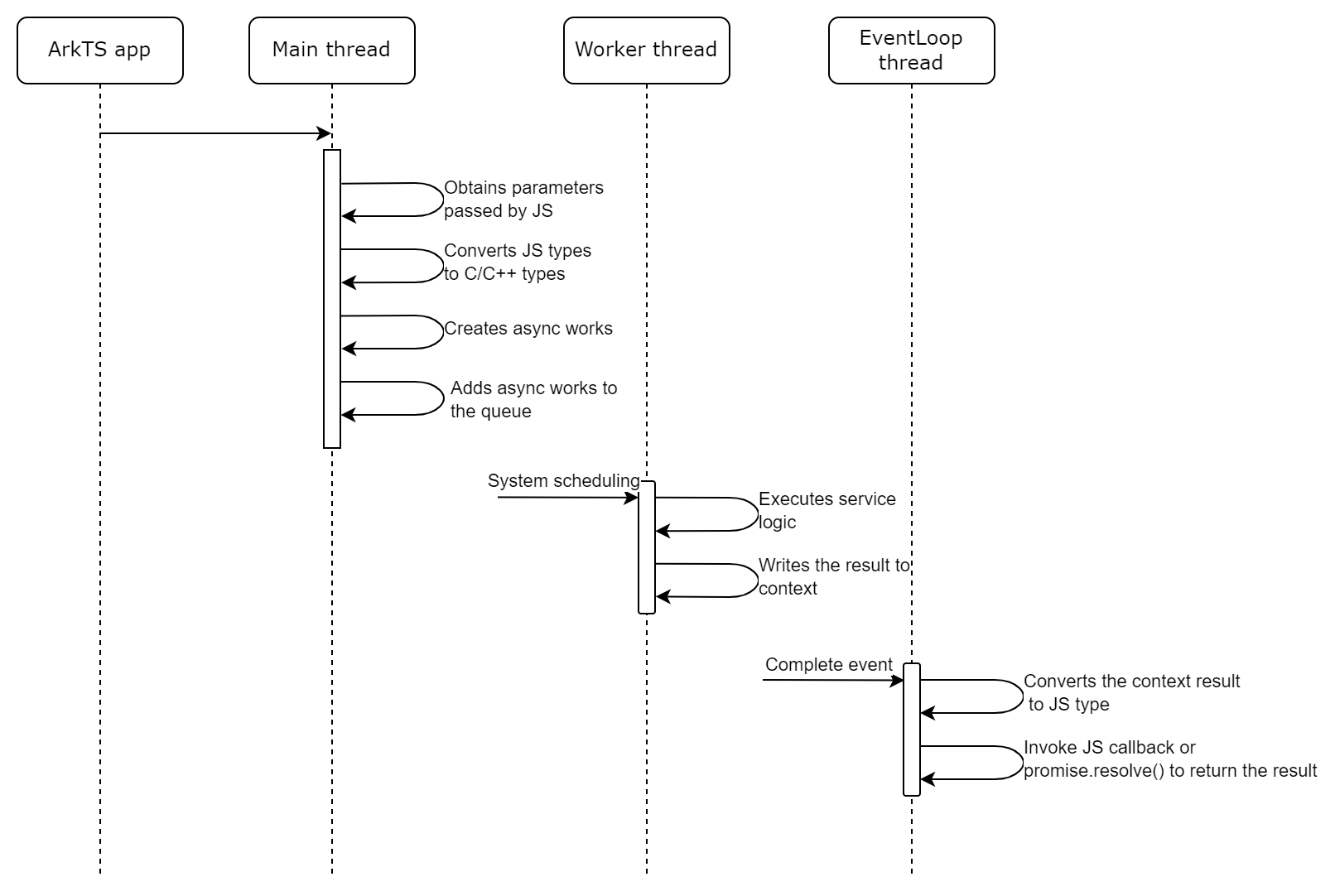
Example (Promise)
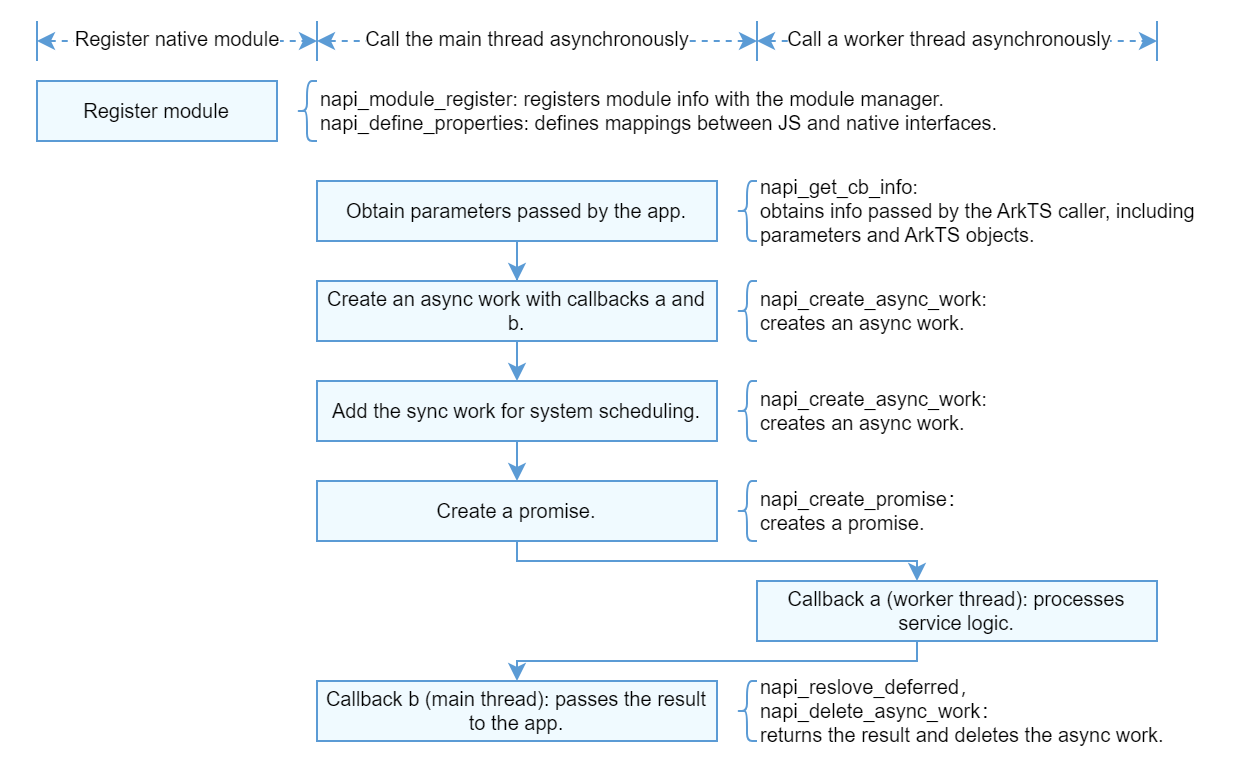
- Call napi_create_async_work to create an asynchronous work object, and call napi_queue_async_work to add the object to a queue.
// Data context provided by the caller. The data is transferred to the execute and complete functions.
struct CallbackData {
napi_async_work asyncWork = nullptr;
napi_deferred deferred = nullptr;
napi_ref callback = nullptr;
double args = 0;
double result = 0;
};
static napi_value AsyncWork(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info)
{
size_t argc = 1;
napi_value args[1];
napi_get_cb_info(env, info, &argc, args, nullptr, nullptr);
napi_value promise = nullptr;
napi_deferred deferred = nullptr;
napi_create_promise(env, &deferred, &promise);
auto callbackData = new CallbackData();
callbackData->deferred = deferred;
napi_get_value_double(env, args[0], &callbackData->args);
napi_value resourceName = nullptr;
napi_create_string_utf8(env, "AsyncCallback", NAPI_AUTO_LENGTH, &resourceName);
// Create an asynchronous work object.
napi_create_async_work(env, nullptr, resourceName, ExecuteCB, CompleteCB, callbackData, &callbackData->asyncWork);
// Add the asynchronous work object to a queue.
napi_queue_async_work(env, callbackData->asyncWork);
return promise;
}
- Define the first callback of the asynchronous work object. This callback is executed in a worker thread to process specific service logic.
static void ExecuteCB(napi_env env, void *data)
{
CallbackData *callbackData = reinterpret_cast<CallbackData *>(data);
callbackData->result = callbackData->args;
}
- Define the second callback of the asynchronous work object. This callback is executed in the main thread to return the result to the ArkTS side.
static void CompleteCB(napi_env env, napi_status status, void *data)
{
CallbackData *callbackData = reinterpret_cast<CallbackData *>(data);
napi_value result = nullptr;
napi_create_double(env, callbackData->result, &result);
if (callbackData->result > 0) {
napi_resolve_deferred(env, callbackData->deferred, result);
} else {
napi_reject_deferred(env, callbackData->deferred, result);
}
napi_delete_async_work(env, callbackData->asyncWork);
delete callbackData;
}
- Initialize the module and call the API of ArkTS.
// Initialize the module.
static napi_value Init(napi_env env, napi_value exports)
{
napi_property_descriptor desc[] = {
{ "asyncWork", nullptr, AsyncWork, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr }
};
napi_define_properties(env, exports, sizeof(desc) / sizeof(desc[0]), desc);
return exports;
}
```
```ts
// Description of the interface in the .d.ts file.
export const asyncWork: (data: number) => Promise<number>;
// Call the API of ArkTS.
nativeModule.asyncWork(1024).then((result) => {
hilog.info(0x0000, 'XXX', 'result is %{public}d', result);
});
Result: result is 1024
Example (Callback)
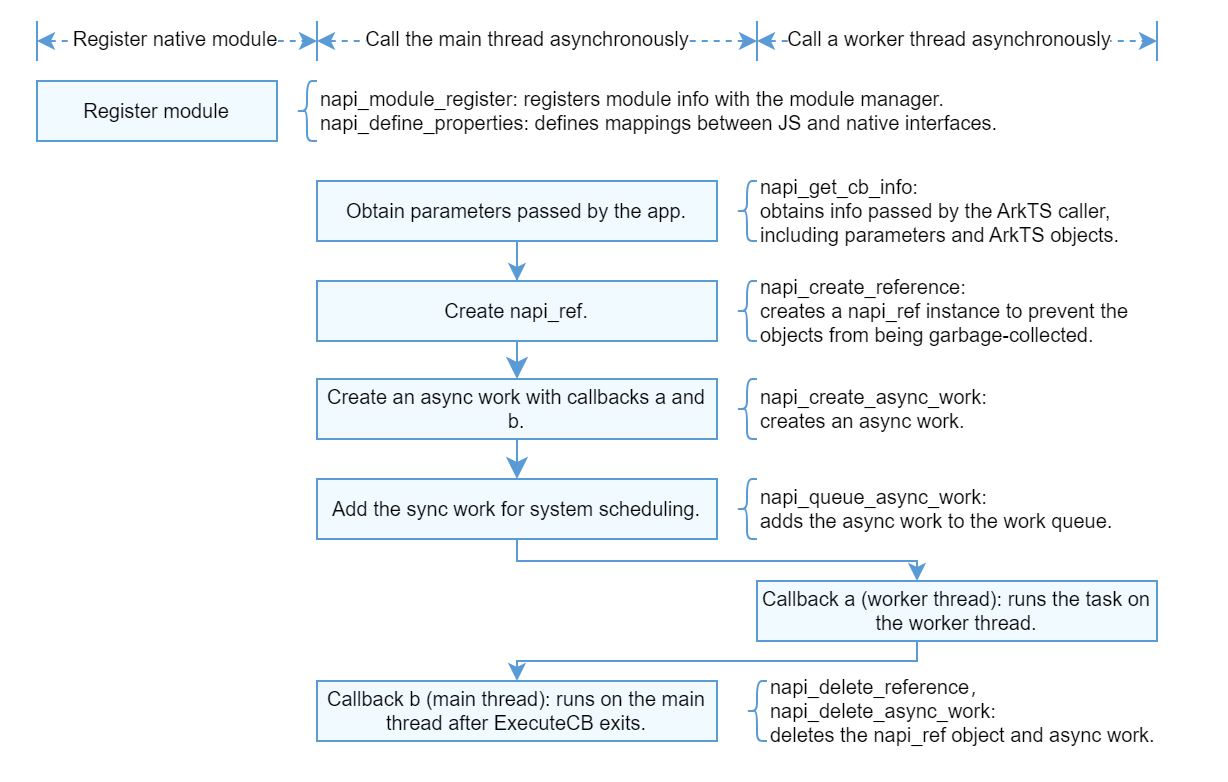
- Call napi_create_async_work to create an asynchronous work object, and call napi_queue_async_work to add the object to a queue.
static constexpr int INT_ARG_2 = 2; // Input parameter index.
// Data context provided by the caller. The data is transferred to the execute and complete functions.
struct CallbackData {
napi_async_work asyncWork = nullptr;
napi_ref callbackRef = nullptr;
double args[2] = {0};
double result = 0;
};
napi_value AsyncWork(napi_env env, napi_callback_info info)
{
size_t argc = 3;
napi_value args[3];
napi_get_cb_info(env, info, &argc, args, nullptr, nullptr);
auto asyncContext = new CallbackData();
// Save the received parameters to callbackData.
napi_get_value_double(env, args[0], &asyncContext->args[0]);
napi_get_value_double(env, args[1], &asyncContext->args[1]);
// Convert the callback to napi_ref to extend its lifecycle to prevent it from being garbage-collected.
napi_create_reference(env, args[INT_ARG_2], 1, &asyncContext->callbackRef);
napi_value resourceName = nullptr;
napi_create_string_utf8(env, "asyncWorkCallback", NAPI_AUTO_LENGTH, &resourceName);
// Create an asynchronous work object.
napi_create_async_work(env, nullptr, resourceName, ExecuteCB, CompleteCB,
asyncContext, &asyncContext->asyncWork);
// Add the asynchronous work object to a queue.
napi_queue_async_work(env, asyncContext->asyncWork);
return nullptr;
}
- Define the first callback of the asynchronous work object. This callback is executed in a worker thread to process specific service logic.
static void ExecuteCB(napi_env env, void *data)
{
CallbackData *callbackData = reinterpret_cast<CallbackData *>(data);
callbackData->result = callbackData->args[0] + callbackData->args[1];
}
- Define the second callback of the asynchronous work object. This callback is executed in the main thread to return the result to the ArkTS side.
static void CompleteCB(napi_env env, napi_status status, void *data)
{
CallbackData *callbackData = reinterpret_cast<CallbackData *>(data);
napi_value callbackArg[1] = {nullptr};
napi_create_double(env, callbackData->result, &callbackArg[0]);
napi_value callback = nullptr;
napi_get_reference_value(env, callbackData->callbackRef, &callback);
// Execute the callback.
napi_value result;
napi_value undefined;
napi_get_undefined(env, &undefined);
napi_call_function(env, undefined, callback, 1, callbackArg, &result);
// Delete the napi_ref object and asynchronous work object.
napi_delete_reference(env, callbackData->callbackRef);
napi_delete_async_work(env, callbackData->asyncWork);
delete callbackData;
}
- Initialize the module and call the API of ArkTS.
// Initialize the module.
static napi_value Init(napi_env env, napi_value exports)
{
napi_property_descriptor desc[] = {
{ "asyncWork", nullptr, AsyncWork, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, napi_default, nullptr }
};
napi_define_properties(env, exports, sizeof(desc) / sizeof(desc[0]), desc);
return exports;
}
// Description of the interface in the .d.ts file.
export const asyncWork: (arg1: number, arg2: number, callback: (result: number) => void) => void;
// Call the API of ArkTS.
let num1: number = 123;
let num2: number = 456;
nativeModule.asyncWork(num1, num2, (result) => {
hilog.info(0x0000, 'XXX', 'result is %{public}d', result);
});
NOTE
- When the napi_cancel_async_work API is called, napi_ok is returned regardless of whether the underlying UV fails. If the task fails to be canceled due to the underlying UV, the corresponding error value is transferred to status in the complete callback. You need to perform the corresponding operation based on the value of status.
- It is recommended that the asynchronous work item of Node-API (napi_async_work) be used only once. After napi_queue_async_work is called, you should release it through napi_delete_async_work during or after the execution of the complete callback. The same napi_async_work can be released only once. Repeated release attempts will cause undefined behavior.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Building an NDK Project with CMake
harmony 鸿蒙Building an NDK Project with the DevEco Studio Template
harmony 鸿蒙NDK Project Building Overview
harmony 鸿蒙Building an NDK Project with Prebuilt Libraries
harmony 鸿蒙C/C++ Library Mechanisms
harmony 鸿蒙Creating an NDK Project
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: