harmony 鸿蒙Common Issues with ArkGuard
Common Issues with ArkGuard
Troubleshooting Functional Issues
Procedure
- Configure the -disable-obfuscation option in the obfuscation-rules.txt file to disable obfuscation, and check whether the issue is caused by obfuscation.
- If the issue is related to obfuscation, review the documentation for the following options and understand when to configure trustlists to avoid issues:
- -enable-toplevel-obfuscation: obfuscates top-level scope names.
- -enable-property-obfuscation: obfuscates property names. Use -keep-property-name to configure a trustlist for property names used in network calls, JSON field, dynamic accesses, and so library interfaces.
- -enable-export-obfuscation: obfuscates exported names. Generally, it is used together with -enable-toplevel-obfuscation and -enable-property-obfuscation. Use -keep-global-name to configure a trustlist for exported/imported interfaces.
- -enable-filename-obfuscation: obfuscates file names. Use -keep-file-name to configure a trustlist for file paths and names in dynamically import or runtime loading scenarios.
- If your issue matches any cases listed below, apply the suggested solutions.
- If the issue is not covered, use a positive approach to identify the problem (remove specific configuration items if the corresponding functionality is not needed).
- Analyze runtime crashes as follows:
- Open the application runtime logs or the Crash dialog box in DevEco Studio to find the crash stack.
- The line numbers in the crash stack match the compiled product, and method names might be obfuscated. Therefore, you are advised to check the compiled product based on the crash stack, analyze the names that cannot be obfuscated, and add them to the trustlist.
- Analyze functional exceptions (for example, white screens) as follows:
- Opening the application runtime logs: Select HiLog and search for logs directly related to the exceptions.
- Locating the problematic code segment: Identify the specific code block causing the exceptions through log analysis.
- Enhancing log output: Add log records for data fields in the suspected code segment.
- Analyzing and identifying critical fields: Determine if the data exception is caused by obfuscation through the enhanced log output.
- Configuring a trustlist for critical fields: Add fields that directly affect application functionality after obfuscation to the trustlist.
Troubleshooting Unexpected Obfuscation Behavior
If unexpected obfuscation behavior occurs, check whether certain obfuscation options are configured for the dependent local modules or third-party libraries.
Example:
If -compact is not configured for the current module, but the code in the obfuscated intermediate product is compressed into a single line, perform the following steps:
- Check the dependencies field in the oh-package.json5 file of the current module to identify dependencies.
- Search for -compact in the obfuscation configuration file of the dependent modules or third-party libraries.
- Search for -compact in the consumer-rules.txt file in the local libraries.
- Search for -compact in all obfuscation.txt files in the project-level oh_modules directory.
NOTE
You are not advised to configure the following options in the obfuscation.txt file of third-party libraries, as they can cause unexpected behavior or crashes when the main module is obfuscated. Contact the library providers to remove these options and repackage the libraries. -enable-property-obfuscation
-enable-string-property-obfuscation
-enable-toplevel-obfuscation
-remove-log
-compact
Property Obfuscation Issues
Database Field Errors When Property Name Obfuscation is Enabled
Symptom
The error message is “table Account has no column named a23 in ‘INSET INTO Account(a23)’.”
Possible Causes
The SQL statement uses database field names that are obfuscated, whereas the database expects the original names.
Solution
Use the -keep-property-name option to add the database fields to the trustlist.
Properties Obfuscated When Record Is Used as an Object Type
Symptom
When Record
// Before obfuscation:
import { Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
let petalMapWant: Want = {
bundleName: 'com.example.myapplication',
uri: 'maps://',
parameters: {
linkSource: 'com.other.app'
}
}
// After obfuscation:
import type Want from "@ohos:app.ability.Want";
let petalMapWant: Want = {
bundleName: 'com.example.myapplication',
uri: 'maps://',
parameters: {
i: 'com.other.app'
}
};
Possible Causes
In this example, the object’s properties need to be passed to the system to load a specific page, so the property names should not be obfuscated. The type Record
Solution
Add the problematic property names to the property trustlist. The following is an example:
-keep-property-name
linkSource
Property Name Obfuscation Inconsistency Across Files
Symptom
The following obfuscation configuration is used:
-enable-property-obfuscation
-keep
./file1.ts
file2.ts imports an interface from file1.ts, and the interface contains object-type properties. As a result, these properties are retained in file1.ts but obfuscated in file2.ts, leading to function exceptions. Example:
// Before obfuscation:
// file1.ts
export interface MyInfo {
age: number;
address: {
city1: string;
}
}
// file2.ts
import { MyInfo } from './file1';
const person: MyInfo = {
age: 20,
address: {
city1: "shanghai"
}
}
// After obfuscation:
// The code of file1.ts is retained.
// file2.ts
import { MyInfo } from './file1';
const person: MyInfo = {
age: 20,
address: {
i: "shanghai"
}
}
Possible Causes
The -keep option retains the code in the file1.ts file, but properties within exported types (for example, address) are not automatically added to the property trustlist. Therefore, these properties are obfuscated when being used in other files.
Solution
Solution 1: Define the property type using interface and export it. This will automatically add the property to the trustlist. Example:
// file1.ts
export interface AddressType {
city1: string;
}
export interface MyInfo {
age: number;
address: AddressType;
}
Solution 2: Use the -keep-property-name option to add properties within types that are not directly exported to the trustlist. Example:
-keep-property-name
city1
String Literal Property Names Obfuscated When -enable-string-property-obfuscation Is Not Configured
Symptom
// Before obfuscation:
person["age"] = 22;
// After obfuscation:
person["b"] = 22;
Possible Causes
A dependent module may have enabled string property name obfuscation, affecting the main module.
Solution
Solution 1: Check whether any dependent modules have enabled string property name obfuscation. If yes, disable it.
Solution 2: If the problematic module cannot be identified, add the string literal property names to the trustlist directly.
Inconsistent Imported/Exported Names
Dynamic Import of a Class with Mismatched Obfuscation
Symptom
When -enable-property-obfuscation is not configured, dynamically importing a class results in the class being obfuscated during its definition, but not during the call, causing the error.
// Before obfuscation:
// file1.ts
export class Test1 {}
// file2.ts
let mytest = (await import('./file1')).Test1;
// After obfuscation:
// file1.ts
export class w1 {}
// file2.ts
let mytest = (await import('./file1')).Test1;
Possible Causes
The exported class Test1 is a top-level domain name. When being dynamically used, it is a property. Because the -enable-property-obfuscation option is not configured, the class name is confused, but the property name is not.
Solution
Use -keep-global-name to add Test1 to the trustlist.
Exported Method in Namespace with Mismatched Obfuscation
Symptom
When -enable-property-obfuscation is not configured, the definition of the method in the namespace is obfuscated, but not obfuscated during the call, causing the error.
// Before obfuscation:
//file1.ts
export namespace ns1 {
export class person1 {}
}
//file2.ts
import {ns1} from './file1';
let person1 = new ns1.person1();
// After obfuscation:
//file1.ts
export namespace a3 {
export class b2 {}
}
//file2.ts
import {a3} from './file1';
let person1 = new a3.person1();
Possible Causes
person1 in the namespace is an exported element. When being called through ns1.person1, it is a property. Because the -enable-property-obfuscation option is not configured, the property name is not obfuscated during the call.
Solution
Solution 1: Configure the -enable-property-obfuscation option.
Solution 2: Use the -keep-global-name option to add the methods exported from the namespace to the trustlist.
Inter-Module Dependency Issues
Incorrect Obfuscation of HSP Module Exports
Symptom
The exported interfaces of an HSP module are incorrectly obfuscated in the main module.
// Before obfuscation:
import { MyHspClass } from "myhsp";
new MyHspClass().myHspMethod();
// After obfuscation:
import { t } from "@normalized:N&myhsp&&myhsp/Index&";
new t().a1();
Possible Causes
When -enable-export-obfuscation and -enable-toplevel-obfuscation are configured, the following scenarios apply to method name obfuscation when the main module calls methods from other modules:
| Main Module | Dependent Module | Imported/Exported Name Obfuscation |
|---|---|---|
| HAP/HSP | HSP | The HSP and main module are independently compiled, resulting in inconsistent obfuscated names. Both need trustlist configurations. |
| HAP/HSP | Local HAR | The local HAR is compiled together with the main module, resulting in consistent obfuscated names. |
| HAP/HSP | Third-party library | Exported names and their properties in third-party libraries are collected into the trustlist, so they are not obfuscated during import/export. |
Solution
To enable other modules to correctly call the methods of the HSP module, add a trustlist. Since both the main module and the HSP module need consistent trustlist configurations, follow these steps:
- Add the trustlist to the obfuscation configuration file (for example, hsp-white-list.txt) of the HSP module.
- In the obfuscation configuration of other modules that depend on the HSP module, include this configuration file via the files field. This ensures consistent trustlist configurations and avoids redundant maintenance. The configuration method is shown in the figure below.
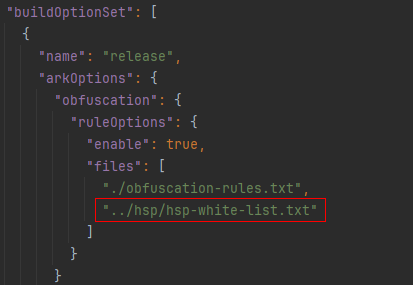
Singleton Function Exceptions and Interface Call Failures in HAP and HSP with a Shared Local Source Code HAR
Symptom
- If file name obfuscation is enabled, the following issue may occur:
- Singleton function exceptions: The reason is that the HAP and HSP modules execute independent build and obfuscation processes. The same file names in the shared local source code HAR may be obfuscated differently in the HAP and HSP packages.
- Interface call failures: The reason is that the HAP and HSP modules execute independent build and obfuscation processes. Different file names in the shared local source code HAR may be obfuscated to the same name in the HAP and HSP packages.
- If -enable-export-obfuscation and -enable-toplevel-obfuscation are configured, the interface loading failures may occur at runtime.
Possible Causes
The HAP and HSP modules execute independent build and obfuscation processes, resulting in different obfuscated names for the interfaces exposed by the shared local source code HAR.
Solution
Solution 1: Change the shared local source code HAR to a bytecode HAR. This prevents the HAR from being re-obfuscated when being depended upon.
Solution 2: Build the shared local source code HAR in release mode. This ensures that file names and exported interfaces are not obfuscated when the HAR is depended upon.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Configuring arkOptions in build-profile.json5
harmony 鸿蒙Ark Bytecode File Format
harmony 鸿蒙Naming Conventions for Ark Bytecode Functions
harmony 鸿蒙Ark Bytecode Fundamentals
harmony 鸿蒙Overview of Ark Bytecode
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: