harmony 鸿蒙Using the UI Context API for UI Operations (UIContext)
Using the UI Context API for UI Operations (UIContext)
Overview
With the support of the stage model in OpenHarmony, there is a scenario where multiple ArkUI instances run within a single ArkTS engine. In this case, an ArkTS engine may have multiple abilities, each of which may have multiple windows. Each window loads a page through loadContent, generating a UIContent (ArkUI instance).
Figure 1 Multi-instance relationship
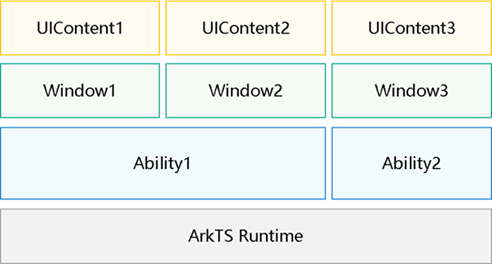
By default, the FA model supports only one ArkUI instance and does not involve multi-instance scenarios. After ArkUI is switched to the stage model, the ArkUI global APIs opened under the FA model cannot clearly determine which instance they are running in when called, leading to ambiguous semantics. In addition, these APIs rely on information related to the ArkUI instance. If the instance is not clear, unexpected behavior at runtime may occur.
To address these issues in multi-instance scenarios, ArkUI has introduced substitute APIs for the stage model. You can use the getUIContext API provided by the Window module or use the component built-in API getUIContext to obtain the UIContext instance where the current component is located, and use the corresponding APIs in UIContext to obtain objects bound to the instance.
Substitute APIs
The table below lists some of the alternative APIs to replace in multi-instance scenarios. The full range of APIs supported is described in UIContext.
| Global API | Substitute API | Description |
|---|---|---|
| @ohos.animator | createAnimator | Custom animation controller. |
| @ohos.arkui.componentSnapshot | getComponentSnapshot | Component snapshot. |
| @ohos.arkui.componentUtils | getComponentUtils | Component utility class. |
| @ohos.arkui.dragController | getDragController | Drag controller. |
| @ohos.arkui.inspector | getUIInspector | Component layout callback. |
| @ohos.arkui.observer | getUIObserver | Observer. |
| @ohos.font | getFont | Custom font registration. |
| @ohos.measure | getMeasureUtil | Text measurement. |
| @ohos.mediaquery | getMediaQuery | Media query. |
| @ohos.promptAction | getPromptAction | Popup. |
| @ohos.router | getRouter | Page routing. |
| AlertDialog | showAlertDialog | Alert dialog box. |
| ActionSheet | showActionSheet | Action sheet. |
| CalendarPickerDialog | Not supported | Calendar picker dialog box. |
| DatePickerDialog | showDatePickerDialog | Date picker dialog box. |
| TimePickerDialog | showTimePickerDialog | Time picker dialog box. |
| TextPickerDialog | showTextPickerDialog | Text picker dialog box. |
| ContextMenu | getContextMenuController | Menu control. |
| vp2px/px2vp/fp2px/px2fp/lpx2px/px2lpx | vp2px/px2vp/fp2px/px2fp/lpx2px/px2lpx | Pixel unit conversion. |
| focusControl | getFocusControl | Focus control. |
| cursorControl | getCursorControl | Cursor control. |
| getContext | getHostContext | Obtains the context of the current ability. |
| LocalStorage.getShared | getSharedLocalStorage | Obtains the storage passed by the current ability. |
| animateTo | animateTo | Explicit animation. |
| animateToImmediately | Not supported | Explicit instant animation. |
How to Switch to Substitute APIs
In the following example, a toast is displayed in a specific window. ArkUI can detect that the API is called on the current page and find the corresponding UI instance. In some complex scenarios, however, the API is not initially called on the current page and has been asynchronously called. In this case, the behavior of the instance may become ambiguous.
import { promptAction } from '@kit.ArkUI'
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
Button()
.onClick(() => {
promptAction.showToast({
message: 'Message Info',
duration: 2000
});
})
}
}
}
In the following example, callNative is a Node-API method. If it is asynchronously triggered by the C side, the current page information cannot be detected at execution, and the UI instance that responds cannot be determined.
import { promptAction } from '@kit.ArkUI'
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
Button()
.onClick(() => {
bridge.callNative("xxxx", ()=> {
promptAction.showToast({
message: 'Message Info',
duration: 2000
});
})
})
}
}
}
To address the above issue, you can use the component built-in API getUIContext to directly obtain the UIContext instance where the current component is located, and then use the getPromptAction API in UIContext to obtain objects bound to the instance. This way, the toast is bound to a specific instance.
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
Button()
.onClick(() => {
let uiContext = this.getUIContext();
let prompt = uiContext.getPromptAction();
bridge.callNative("xxxx", ()=> {
prompt.showToast({
message: 'Message Info',
duration: 2000
});
})
})
}
}
}
If you are using APIs in UIContext that do not have substitutes (such as CalendarPickerDialog and animateToImmediately), or if you are implementing custom service logic that’s tied to specific instances, you can use the runScopedTask API in UIContext to encapsulate these APIs or code snippets.
| API in UIContext | Description |
|---|---|
| runScopedTask | Executes the closure of the bound instance. |
The above example can also be implemented using the following method.
// Execute the closure of the bound instance.
import { promptAction } from '@kit.ArkUI'
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
Button()
.onClick(() => {
let uiContext = this.getUIContext();
uiContext.runScopedTask(() => {
promptAction.showToast({
message: 'Message Info',
duration: 2000
});
})
})
}
}
}
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
harmony 鸿蒙Atomic Service Full Screen Launch Component (FullScreenLaunchComponent)
harmony 鸿蒙Arc Button (ArcButton)
harmony 鸿蒙Frame Animation (ohos.animator)
harmony 鸿蒙Implementing Property Animation
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: