harmony 鸿蒙Component Transition (transition)
Component Transition (transition)
You can configure the component transition animations through the transition attribute for when a component is inserted or removed.
NOTE
The APIs of this module are supported since API version 7. Updates will be marked with a superscript to indicate their earliest API version.
Attributes
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| transition | TransitionOptions(deprecated) |TransitionEffect10+ | Transition effects for when the component is inserted to show and removed to hide. NOTE For details, see TransitionOptions and TransitionEffect. Atomic service API: This API can be used in atomic services since API version 11. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10. |
| transition12+ | (TransitionEffect, Optional<TransitionFinishCallback>) | Transition effects for when the component is inserted to show and removed to hide, as well as the callback for the end of the transition animation. Atomic service API: This API can be used in atomic services since API version 12. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 12. |
NOTE There are two ways to trigger a component’s transition: 1. When a component is inserted or removed (for example, when there are changes in if conditions, or when components are added or removed in a ForEach loop), the transition effects of all newly inserted/removed components are triggered recursively. 2. When the Visibility attribute of a component changes between visible and invisible, only the transition effect of that component is triggered.
TransitionEdge10+
Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10.
Atomic service API: This API can be used in atomic services since API version 11.
System capability: SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| TOP | Top edge of the window. |
| BOTTOM | Bottom edge of the window. |
| START | Start edge of the window, which is the left edge for left-to-right scripts and the right edge for right-to-left scripts. |
| END | End edge of the window, which is the right edge for left-to-right scripts and the left edge for right-to-left scripts. |
TransitionEffect10+
Defines the transition effect by using the provided APIs, as listed below.
Atomic service API: This API can be used in atomic services since API version 11.
| API | Type | Static Function | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| opacity | number | Yes | Opacity of the component during transition, which is the value of the start point of insertion and the end point of deletion. Value range: [0, 1] NOTE If the value specified is less than 0, the value 0 is used. If the value specified is greater than 1, the value 1 is used. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10. |
| translate | TranslateOptions | Yes | Translation of the component during transition, which is the value of the start point of insertion and the end point of deletion. -x: distance to translate along the x-axis. -y: distance to translate along the y-axis. -z: distance to translate along the z-axis. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10. |
| scale | ScaleOptions | Yes | Scaling of the component during transition, which is the value of the start point of insertion and the end point of deletion. - x: scale factor along the x-axis. - y: scale factor along the y-axis. - z: scale factor along the z-axis (not effective for the current 2D graphics). - centerX and centerY: scale center point. The default values are both “50%”, indicating the center point of the page. - If the center point is (0, 0), it refers to the upper left corner of the component. NOTE If centerX or centerY is set to an invalid string (for example, “illegalString”), the default value “0” is used. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10. |
| rotate | RotateOptions | Yes | Rotation of the component during transition, which is the value of the start point of insertion and the end point of deletion. - x: X-component of the rotation vector. - y: Y-component of the rotation vector. - z: Z-component of the rotation vector. - centerX and centerY: rotation center point. The default values are both “50%”, indicating the center point of the page. - If the center point is (0, 0), it refers to the upper left corner of the component. - centerZ: z-axis anchor point, that is, the z-component of the 3D rotation center point. The default value is 0. - perspective: viewing distance. It is not supported for use in transition animations. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10. |
| move | TransitionEdge | Yes | Slide-in and slide-out of the component from the screen edge during transition. It is essentially a translation effect, which is the value of the start point of insertion and the end point of deletion. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10. |
| asymmetric | appear: TransitionEffect, disappear: TransitionEffect |
Yes | Asymmetric transition effect. The first parameter indicates the transition effect for appearance, and the second parameter indicates the transition effect for disappearance. If the asymmetric function is not used for TransitionEffect, the transition effect takes effect for both appearance and disappearance of the component. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10. |
| combine | TransitionEffect | No | Combination of transition effects. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10. |
| animation | AnimateParam | No | Animation settings. The onFinish callback in AnimateParam does not work here. If combine is used for combining transition effects, the animation settings of a transition effect are applicable to the one following it. Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 10. |
The static functions listed in the preceding table are used to create a TransitionEffect object, while the non-static functions apply to the created TransitionEffect object. TransitionEffect also provides some static member variables for transition effects: |Static Member Variable|Description| |——–|——–| |IDENTITY|Disables the transition effect.| |OPACITY|Applies a transition effect with the opacity changing from 0 to 1 when the component appears and from 1 to 0 when the component disappears. This is equivalent to TransitionEffect.opacity(0).| |SLIDE|Applies a transition effect of sliding in from the start edge when the component appears and sliding out from the end edge when the component disappears. This means sliding in from the left edge and sliding out from the right edge for left-to-right scripts, and sliding in from the right edge and sliding out from the left edge for right-to-left scripts. This is equivalent to TransitionEffect.asymmetric(TransitionEffect.move(TransitionEdge.START), TransitionEffect.move(TransitionEdge.END)).| |SLIDE_SWITCH|Applies a transition effect of sliding in from the right with first scaling down and then scaling up when the component appears and sliding out from the right with first scaling down and then scaling up when the component disappears. This transition effect comes with its own animation parameters, which can also be overridden. The default animation duration is 600 milliseconds, with a specified animation curve of cubicBezierCurve(0.24, 0.0, 0.50, 1.0) and a minimum scale factor of 0.8.|
NOTE
- For transition effects combined through the combine function, animation settings can be configured through the animation parameter on a one-on-one basis. In addition, the animation settings of a transition effect are applicable to the one following it. For example, with TransitionEffect.OPACITY.animation({duration: 1000}).combine(TransitionEffect.translate({x: 100})), the duration settings (1000 ms) apply to both the OPACITY and translate effects.
- The animation settings take effect in the following sequence: animation settings specified in the current TransitionEffect > animation settings specified in the previous TransitionEffect > animation settings specified in animateTo that triggers the component to appear and disappear.
- If animateTo is not used and TransitionEffect does not have the animation parameter specified, the component will appear or disappear without any transition animation.
- If the value of an attribute specified in TransitionEffect is the same as the default value, no transition animation will be applied to the attribute. For example, with TransitionEffect.opacity(1).animation({duration:1000}), because the default value of opacity is also 1, no opacity animation will be applied, and the component appears or disappears without any transition animation.
- For details about the scale and rotate effects, see Transformation.
- If a component’s attach or detach in the component tree or visibility (Visibility) change is triggered within the animation scope (animateTo or animation), and the root component does not have a transition configured, a default opacity transition, namely TransitionEffect.OPACITY, will be applied to the component. The animation parameters will follow the parameters of the surrounding animation environment. If this default behavior is not desired, it can be disabled by configuring TransitionEffect.IDENTITY, which causes the component to appear or disappear instantly without any transition effect.
- To ensure that the complete disappearance transition process is visible when triggering it by deleting an entire subtree, it is necessary to guarantee that the root component of the subtree being deleted has ample time to complete its disappearance transition, as demonstrated in Example 3.
TransitionFinishCallback12+
TransitionFinishCallback = (transitionIn: boolean) => void
Represents the type of callback for the end of a component’s transition animation.
Widget capability: This API can be used in ArkTS widgets since API version 12.
Atomic service API: This API can be used in atomic services since API version 12.
System capability: SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
Parameters
| Name | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| transitionIn | boolean | Yes | Type of callback for the end of the transition animation. The value true indicates that the callback is for the end of an appearance animation, and false indicates that the callback is for the end of a disappearance animation. |
NOTE 1. When a subtree is triggered to attach or detach, which in turn recursively triggers appearance and disappearance transitions, only the root component’s disappearance animation end callback can be guaranteed to be invoked. If a child component’s disappearance animation end callback is scheduled after the root component’s disappearance animation end callback, it will not be invoked because the entire subtree has already been destroyed. 2. The end callback is only invoked after the last of the same type of animation (either appearance or disappearance) for the same component has finished. That is, if appearance and disappearance animations are triggered repeatedly (for example, through changes in Visibility), only the end callback of the final appearance or disappearance will be executed.
TransitionOptions(deprecated)
Defines the transition effect by setting parameters in the struct.
This API is deprecated since API version 10. You are advised to use TransitionEffect instead.
|Name|Type|Mandatory|Description|
|——–|——–|——–|——–|
|type|TransitionType|No|Transition type.
Default value: TransitionType.All
NOTE
If type is not specified, the default value TransitionType.All is used, which means that the transition effect works for both component addition and deletion.|
|opacity|number|No|Opacity of the component during transition, which is the value of the start point of insertion and the end point of deletion.
Value range: [0, 1]
NOTE
If the value specified is less than 0, the value 0 is used. If the value specified is greater than 1, the value 1 is used.|
|translate| TranslateOptions|No|Translation of the component during transition, which is the value of the start point of insertion and the end point of deletion.
-x: distance to translate along the x-axis.
-y: distance to translate along the y-axis.
-z: distance to translate along the z-axis.|
|scale| ScaleOptions|No|Scaling of the component during transition, which is the value of the start point of insertion and the end point of deletion.
- x: scale factor along the x-axis.
- y: scale factor along the y-axis.
- z: scale factor along the z-axis (not effective for the current 2D graphics).
- centerX and centerY: scale center point. The default values are both “50%”, indicating the center point of the page.
- If the center point is (0, 0), it refers to the upper left corner of the component.
NOTE
If centerX or centerY is set to an invalid string (for example, “illegalString”), the default value “0” is used.|
|rotate| RotateOptions|No|Rotation of the component during transition, which is the value of the start point of insertion and the end point of deletion.
- x: X-component of the rotation vector.
- y: Y-component of the rotation vector.
- z: Z-component of the rotation vector.
- centerX and centerY: rotation center point. The default values are both “50%”, indicating the center point of the page.
- If the center point is (0, 0), it refers to the upper left corner of the component.|
NOTE
- When set to a value of the TransitionOptions type, the transition attribute must work with animateTo. The animation duration, curve, and delay follow the settings in animateTo.
- If the value of the TransitionOptions type has only type specified, the transition effect will take on the default opacity. For example, {type: TransitionType.Insert} produces the same effect as {type: TransitionType.Insert, opacity: 0}. If a specific style is specified, the transition effect will not take on the default opacity.
Example
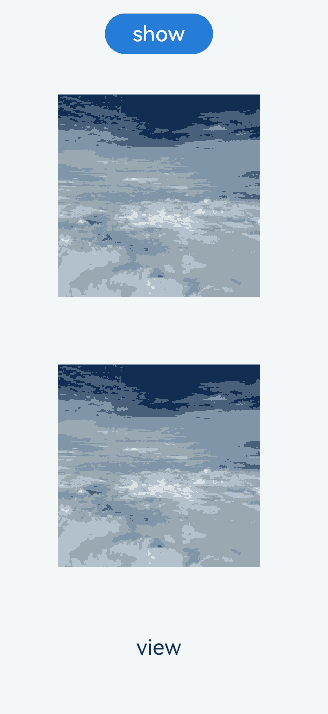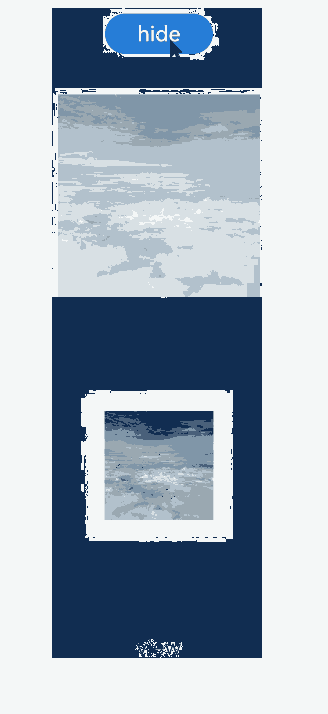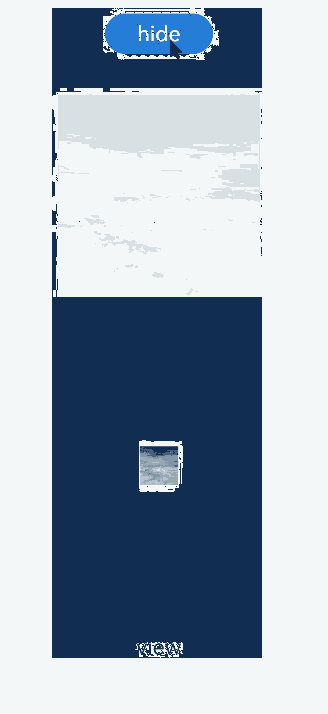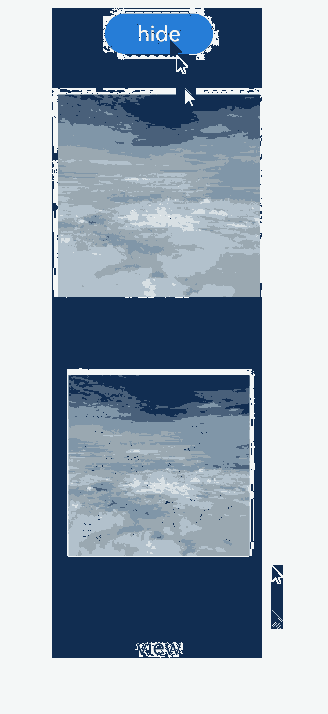
Example 1: Using the Same TransitionEffect Configuration for Image Appearance and Disappearance
This example demonstrates how to use the same TransitionEffect configuration to implement both the appearance and disappearance of an image, where the appearance and disappearance are inverse processes.
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct TransitionEffectExample1 {
@State flag: boolean = true;
@State show: string = 'show';
build() {
Column() {
Button(this.show).width(80).height(30).margin(30)
.onClick(() => {
// Click the button to show or hide the image.
if (this.flag) {
this.show = 'hide';
} else {
this.show = 'show';
}
this.flag = !this.flag;
})
if (this.flag) {
// Apply the same transition effect to the appearance and disappearance of the image.
// When the image appears, it changes from the state where the opacity is 0 and the rotation angle is 180° around the z-axis to the state where the opacity is 1 and the rotation angle is 0°. The durations of the opacity and rotation animations are both 2000 ms.
// When the image disappears, it changes from the state where the opacity is 1 and the rotation angle is 0° to the state where the opacity is 0 and the rotation angle is 180° around the z-axis. The durations of the opacity and rotation animations are both 2000 ms.
Image($r('app.media.testImg')).width(200).height(200)
.transition(TransitionEffect.OPACITY.animation({ duration: 2000, curve: Curve.Ease }).combine(
TransitionEffect.rotate({ z: 1, angle: 180 })
))
}
}.width('100%')
}
}
Below you can see the example in action.

Example 2: Using Different TransitionEffect Configurations for Image Appearance and Disappearance
This example demonstrates how to use different TransitionEffect configurations to implement the appearance and disappearance of an image.
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct TransitionEffectExample2 {
@State flag: boolean = true;
@State show: string = 'show';
build() {
Column() {
Button(this.show).width(80).height(30).margin(30)
.onClick(() => {
// Click the button to show or hide the image.
if (this.flag) {
this.show = 'hide';
} else {
this.show = 'show';
}
animateTo({ duration: 2000 }, () => {
// In the first image, **TransitionEffect** contains **animation**, and therefore the animation settings are those configured in **TransitionEffect**.
// In the second image, **TransitionEffect** does not contain **animation**, and therefore the animation settings are those configured in **animateTo**.
this.flag = !this.flag;
});
})
if (this.flag) {
// Apply different transition effects to the appearance and disappearance of the image.
// When the image appears, its opacity changes 0 to 1 (default value) over the duration of 1000 ms, and after 1000 ms has elapsed, its rotation angle changes from 180° around the z-axis to 0° (default value) over the duration of 1000 ms.
// When the image disappears, after 1000 ms has elapsed, its opacity changes 1 (default value) to 0 over the duration of 1000 ms, and its rotation angle changes from 0° (default value) to 180° around the z-axis over the duration of 1000 ms.
Image($r('app.media.testImg')).width(200).height(200)
.transition(
TransitionEffect.asymmetric(
TransitionEffect.OPACITY.animation({ duration: 1000 }).combine(
TransitionEffect.rotate({ z: 1, angle: 180 }).animation({ delay: 1000, duration: 1000 }))
,
TransitionEffect.OPACITY.animation({ delay: 1000, duration: 1000 }).combine(
TransitionEffect.rotate({ z: 1, angle: 180 }).animation({ duration: 1000 }))
)
)
// When the image appears, the scale along the x- and y- axes is changed from 0 to 1 (default value). The animation duration is 2000 ms specified in **animateTo**.
// When the image disappears, no transition effect is applied.
Image($r('app.media.testImg')).width(200).height(200).margin({ top: 100 })
.transition(
TransitionEffect.asymmetric(
TransitionEffect.scale({ x: 0, y: 0 }),
TransitionEffect.IDENTITY
)
)
}
}.width('100%')
}
}
Below you can see the example in action.

Example 3: Setting transition on Parent and Child Components
This example demonstrates how to configure transition on both parent and child components to implement the appearance and disappearance of images.
// xxx.ets
@Entry
@Component
struct TransitionEffectExample3 {
@State flag: boolean = true;
@State show: string = 'show';
build() {
Column() {
Button(this.show).width(80).height(30).margin(30)
.onClick(() => {
// Click the button to show or hide the image.
if (this.flag) {
this.show = 'hide';
} else {
this.show = 'show';
}
this.flag = !this.flag;
})
if (this.flag) {
// When the flag condition is changed, it will trigger the transition animation for elements with the IDs column1, image1, and image2.
// The component with the ID column1 is the root node of this newly appearing/disappearing subtree.
Column() {
Row() {
Image($r('app.media.testImg')).width(150).height(150).id("image1")
.transition(TransitionEffect.OPACITY.animation({ duration: 1000 }))
}
Image($r('app.media.testImg'))
.width(150)
.height(150)
.margin({ top: 50 })
.id("image2")
.transition(TransitionEffect.scale({ x: 0, y: 0 }).animation({ duration: 1000 }))
Text("view").margin({ top: 50 })
}
.id("column1")
.transition(TransitionEffect.opacity(0.99).animation({ duration: 1000 }),
// The end callback is set on the first layer of disappearing nodes to ensure that there is a callback at the end of the disappearance.
(transitionIn: boolean) => {
console.info("transition finish, transitionIn:" + transitionIn);
}
)
}
}.width('100%')
}
}
Below you can see the example in action.
你可能感兴趣的鸿蒙文章
- 所属分类: 后端技术
- 本文标签: